2B青年欢乐多啊,最近研究spring源码,做点笔记,欢迎继续补充, 持续更新
接上一篇 1. Introduce how to import the Spring Framework sourcecode into an eclipse project
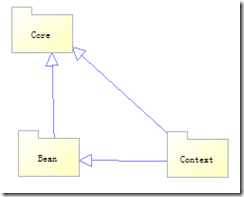
一. 结构
spring中bean管理设计到下面3个包
core 相当于一个工具类,bean包是对IOC的实现包,context是在bean的基础扩展功能
IOC的实现原理简介
简单实现
package org.benson; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; public class Test4DebugSpringIOC { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();//manage bean factory ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource( "applicationContext.xml");//resource XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlReader=new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry)beanFactory); //register public Test4DebugSpringIOC() { // TODO load and registered BeanDefinition xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } public static void main(String[] args) { Test4DebugSpringIOC test4DebugSpring= new Test4DebugSpringIOC(); Test4DebugSpringBean test4DebugSpringBean = (Test4DebugSpringBean) test4DebugSpring.beanFactory .getBean("testAlias"); test4DebugSpringBean.SayHolle(); } }
1,找到bean的定义文件(Resource)
如此处classPathResource,用于找到文件位置
2,把定义文件解析成BeanDefinition对象并进行注册,在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中
int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);//Validation xml file . XmlBeanDefinitionReader doLoadBeanDefinitions Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument( inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());//parse to doc . through documentLoader(DefaultDocumentLoader) return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
一个普通bean的解析step
i 调用DefaultDocumentLoader把XML解析成DOC并进行XSD,DTD等格式验证.
DefaultDocumentLoader调用了SAX的DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(),把XML文件解析成一个org.w3c.dom.Document对象(标准的DOM解析方式),当然也设置XML验证的validationMode,namespace
/** * Load the {@link Document} at the supplied {@link InputSource} using the standard JAXP-configured * XML parser. */ public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver, ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception { DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]"); } DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler); return builder.parse(inputSource); }
ii DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader读取document中的所有Element.
registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)中调用BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions方法获根节点
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
得到XML的根节点,调用doRegisterBeanDefinitions
/** * Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element. * @throws IllegalStateException if {@code <beans profile="..."} attribute is present * and Environment property has not been set * @see #setEnvironment */ protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { ..//profile // any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; this.delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root, parent); preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent; }
然后从获得根结点的所有子节点,进行循环
/** * Parse the elements at the root level in the document: * "import", "alias", "bean". * @param root the DOM root element of the document */ protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);//parse defalut element } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
此处isDefaultNamespace方法是获取namespace为http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans的node,目前对应schema定义的包括"bean" "alis" "beans" "import" ,处理方法为parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate),如果发现是bean标签则调用processBeanDefinition方法
/** * Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition * and registering it with the registry. */ protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); //parse to object of BeanDefinitionHolder if (bdHolder != null) {//if it is not exit. parse it from xml bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder); try { // Register the final decorated instance. BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex); } // Send registration event. getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); } }
iii 调用BeanDefinitionParserDelegate对象完成doc中Element->BeanDefinitionHolder的转换
/** * Parses the supplied <code><bean></code> element. May return <code>null</code> * if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}. */ public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) { String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE); String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); ... ... //vacation AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); .... return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); }
先获得别名,这里叫nameAttr先转成数组,然后通过BeanDefinitionHolder把它和beanName,beandefine绑定在一起
/** * Parse the bean definition itself, without regard to name or aliases. May return * <code>null</code> if problems occurred during the parsing of the bean definition. */ public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement( Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) { this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName)); String className = null; if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) { className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim(); } try { String parent = null; if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) { parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE); } AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent); parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd); bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)); parseMetaElements(ele, bd); parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource()); bd.setSource(extractSource(ele)); return bd; }
全部当成属性设置到了AbstractBeanDefinition 的对象中,具体可以看AbstractBeanDefinition 类
最后返回BeanDefinitionHolder;BeanDefinitionHolder是由beanname+aliasArray+beandefinition组成的一个对象
IV 然后回到ii的最后调用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition注册beandefine对象,并调BeanDefinitionRegistry接口进行注册,如DefaultListableBeanFactory
完成转换后,BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition 调用到 BeanDefinitionRegistry接口实现类的registerBeanDefinition方法把对象放入bean的工厂容器中
* Register the given bean definition with the given bean factory. * @param definitionHolder the bean definition including name and aliases * @param registry the bean factory to register with * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException if registration failed */ public static void registerBeanDefinition( BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { // Register bean definition under primary name. String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName(); registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()); // Register aliases for bean name, if any. String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases(); if (aliases != null) { for (String aliase : aliases) { registry.registerAlias(beanName, aliase); } } }
在DefaultListableBeanFactory的实现也很简单了,直接用map添加下就OK了
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { ....//Validation this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);//add it to beanDefinitionMap } resetBeanDefinition(beanName); //reset all exist }
3,查找,通过getbean获得bean,用ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,如DefaultListableBeanFactory
这部分功能主要在abstractbeanfactory中完成,如果是singleton(即spring的default)
i transformedBeanName(name) ,得到SimpleAliasRegistry 的 map 属性 aliasMap,转换为beanname(别名功能)
ii Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); 尝试从DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry的MAP singletonObjects中拿出bean (singleton功能)
iii bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null) 处理factorybean部分,附 Spring FactoryBean源码浅析
iv final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); 从bean注册的信息中找到bean 对应的 BeanDefinition
v return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); 创建新的bean,通过BeanDefinition的描述信息来,并填充到DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry的singletonObjects中
beanfactory的主要代码,加上了些注释
/** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve * @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve * @param args arguments to use if creating a prototype using explicit arguments to a * static factory method. It is invalid to use a non-null args value in any other case. * @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check, * not for actual use * @return an instance of the bean * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected <T> T doGetBean( final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); //get true name from attribute aliasMap of SimpleAliasRegistry Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); //get instance object from the attribute singletonObjects of DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); // it is for that class witch is implement interface factorybean } else { // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: // We're assumably within a circular reference. if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } } if (!typeCheckOnly) { markBeanAsCreated(beanName); } final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);//get BeanDefinition from registered information checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dependsOnBean : dependsOn) { getBean(dependsOnBean); registerDependentBean(dependsOnBean, beanName); } } // Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { //create new instance and put in attribute map singletonObjects of DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry public Object getObject() throws BeansException { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. Object prototypeInstance = null; try { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { public Object getObject() throws BeansException { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; " + "consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) { try { return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type [" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "]", ex); } throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } } return (T) bean; }
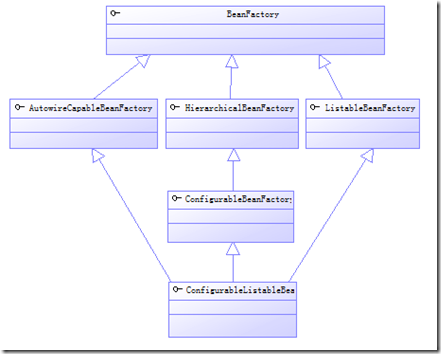
附 bean中的主要结构
主要类,下列类从上往下继承
SimpleAliasRegistry 用于维护一个 aliasMap,维护别名功能
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry map 维护 singletonObjects,维护工厂单例,一个工厂一个单例,非N个工厂一个单例
FactoryBeanRegistrySupport,
AbstractBeanFactory ,factorybean的主要实现类,其doGetBean,getBean是主要获得bean的入口 ,维护一个mergedBeanDefinitions
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,configureableBeanFactory的主要实现类, createBean根据beandefine的信息创建相应的值
DefaultListableBeanFactory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的主要实现类,维护beanDefiniti信息
主要接口关系如下
Parse XML主要用到的几个相关类
* @see DocumentLoader
* @see DefaultDocumentLoader
TODO 对SAX几个工厂属性进行设置,schema等,调用SAX对XML转换成了DOC对象
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
* @see DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
提供registerBeanDefinitions,和setEnvironment方法,用于DOC到beandefine的注册功能,遍历了doc的所有node,调用 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate解析node,并调用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils对解析的beandefine到beandefine注册类的注册
* @BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
主要解析类,各种属性,对beandefine对象属性的设置都是在此类完成
bean中ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口继承了bean中的基本接口,DefaultListableBeanFactory是其唯一实现类,也是预留接口供扩展
接口因为可以多继承,所以用来表示系统的结构最合适不过,而JAVA中类单继承的,一般只是用来实现设计,侧重实现功能,因为类层次肯定是一条线。