1. C语言位及其运算符
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
操作符 作用
────────────────────────────
& 位逻辑与
| 位逻辑或
^ 位逻辑异或
- 位逻辑反
>> 右移
<< 左移
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
※特别注意:逻辑运算符的“!”——逻辑非,不是位运算符!
2. 用途举列
(1)对于以2的指数次方为“*”、“/”或“%”因子的数学运算,转化为移位运算“<<” 、“>>”,通常可以提高算法效率,因为乘除运算指令周期通常比移位运算大。
1 #include "Stdio.h"
#include "Stdio.h"
2 #include "Conio.h"
#include "Conio.h"
3
4 int main(void)
int main(void)
5 {
{
6 unsigned i,j;
unsigned i,j;
7 i = 879 / 16;
i = 879 / 16;
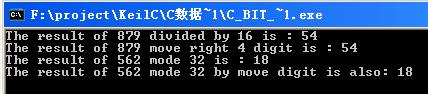
8 printf("The result of 879 divided by 16 is : %d\n",i);
printf("The result of 879 divided by 16 is : %d\n",i);
9 i = 879 >> 4; //等价于879/16
i = 879 >> 4; //等价于879/16
10 printf("The result of 879 move right 4 digit is : %d\n",i);
printf("The result of 879 move right 4 digit is : %d\n",i);
11
12 j = 562 % 32;
j = 562 % 32;
13 printf("The result of 562 mode 32 is : %d\n",j);
printf("The result of 562 mode 32 is : %d\n",j);
14 j = 562 - (562 >> 5 << 5); //等价于562%32
j = 562 - (562 >> 5 << 5); //等价于562%32
15 printf("The result of 562 mode 32 by move digit is also: %d\n",j);
printf("The result of 562 mode 32 by move digit is also: %d\n",j);
16
17 getch();
getch();
18 return 0;
return 0;
19 }
}
 #include "Stdio.h"
#include "Stdio.h"2
 #include "Conio.h"
#include "Conio.h"3

4
 int main(void)
int main(void)5
 {
{6
 unsigned i,j;
unsigned i,j;7
 i = 879 / 16;
i = 879 / 16;8
 printf("The result of 879 divided by 16 is : %d\n",i);
printf("The result of 879 divided by 16 is : %d\n",i);9
 i = 879 >> 4; //等价于879/16
i = 879 >> 4; //等价于879/1610
 printf("The result of 879 move right 4 digit is : %d\n",i);
printf("The result of 879 move right 4 digit is : %d\n",i);11

12
 j = 562 % 32;
j = 562 % 32;13
 printf("The result of 562 mode 32 is : %d\n",j);
printf("The result of 562 mode 32 is : %d\n",j);14
 j = 562 - (562 >> 5 << 5); //等价于562%32
j = 562 - (562 >> 5 << 5); //等价于562%3215
 printf("The result of 562 mode 32 by move digit is also: %d\n",j);
printf("The result of 562 mode 32 by move digit is also: %d\n",j);16

17
 getch();
getch();18
 return 0;
return 0;19
 }
}结果如下:
※特别注意:两个整数相除结果为整数,如879/16的结果值为54!