(一)定义
双向链表是在单链表的每个结点中,再设置一个纸箱其前驱结点的指针域
(二)结点结构
typedef struct Node { ElemType data; struct Node* prior; //直接前驱指针 struct Node* next; //直接后继指针 }Node; typedef struct Node* CLinkList;
(三)双向链表结构
双向循环链表
带有头结点的空链表
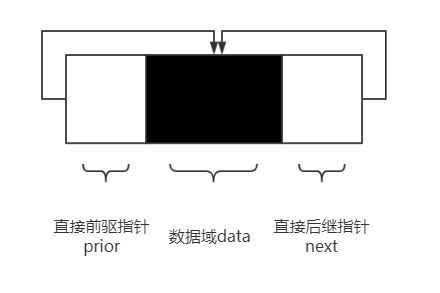
带有头结点的数据链表
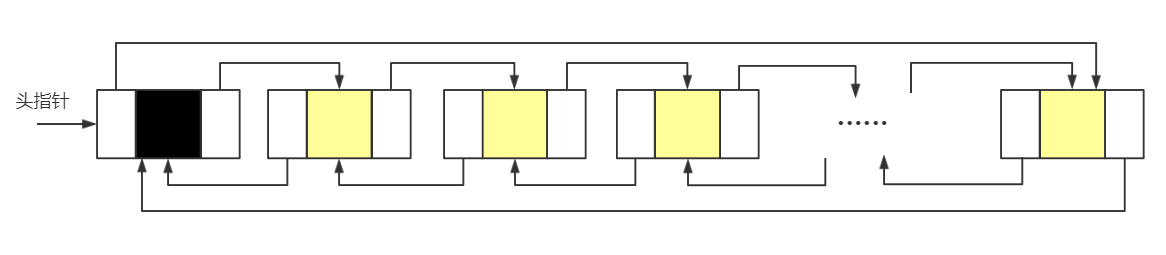
对于非循环的,直接将头结点的直接前驱指针置为空,将尾结点的直接后驱结点置为空即可
(四)实现双向链表
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include <math.h> #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 typedef char ElemType; typedef int Status; typedef struct Node { ElemType data; struct Node* prior; //直接前驱指针 struct Node* next; //直接后继指针 }Node; typedef struct Node* DLinkList; //四个基本操作,初始化,清空,获取长度,是否为空 Status InitList(DLinkList* Dl); Status ClearList(DLinkList* Dl); int GetLength(DLinkList Dl); Status EmptyList(DLinkList Dl); //四个插入,程序,删除操作 Status GetElem(DLinkList Dl, int i, ElemType* e); int LocateElem(DLinkList Dl, ElemType e); Status InsertList(DLinkList* Dl, int i, ElemType e); Status DeleteList(DLinkList* Dl, int i, ElemType* e); //打印链表 void PrintList(DLinkList Dl, int i); int main() { DLinkList dbList; ElemType e='A'; int i = 0; InitList(&dbList);//初始化链表 for (; i < 26;i++) //插入数据 { //InsertList(&dbList, -1, e + i); //尾插法 InsertList(&dbList, GetLength(dbList)+1, e + i); //头插法 } PrintList(dbList, 3); PrintList(dbList, -3); system("pause"); return 0; } //四个基本操作,初始化,清空,获取长度,是否为空 //创建一个带有头结点的双向链表 Status InitList(DLinkList* Dl) { *Dl = (DLinkList)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if (*Dl == NULL) return ERROR; (*Dl)->next = (*Dl)->prior = (*Dl); //都指向头结点,虽然这里数据data为char,也是可以存储链表长度的,但是这里不使用 return OK; } //清空双向链表,头结点也释放掉 Status ClearList(DLinkList* Dl) { DLinkList Dlist = *Dl; DLinkList q; if (Dlist == NULL) return ERROR; //先将尾结点的next指针置为空,一会作为判断循环退出条件 Dlist->prior->next = NULL; while (Dlist) { q = Dlist; Dlist = Dlist->next; free(q); } return OK; } //获取链表长度,不含头结点,使用一条单向指针域即可 int GetLength(DLinkList Dl) { DLinkList cur = Dl->next; int length = 0; while (cur!=Dl) { cur = cur->next; length++; } return length; } //判断是否链表为空,判断头结点一个指针是否指向自己就可以 Status EmptyList(DLinkList Dl) { if (Dl->prior == Dl) return TRUE; return FALSE; } //四个插入,程序,删除操作 //根据索引获取数据,支持双向索引 Status GetElem(DLinkList Dl, int i, ElemType* e) { int j = 0; DLinkList cur = Dl; if (e == NULL||i==0) return ERROR; for (; j < abs(i);j++) { if (i < 0) cur = cur->prior; else cur = cur->next; } *e = cur->data; return OK; } //按照元素进行查找,单向正向查找 int LocateElem(DLinkList Dl, ElemType e) { DLinkList cur = Dl->next; int index=1; while (cur->data != e&&cur != Dl) { cur = cur->next; index++; } if (cur == Dl) return 0; return index; } //支持双向插入 Status InsertList(DLinkList* Dl, int i, ElemType e) { DLinkList cur = *Dl; DLinkList newNode; int j = 0; if (*Dl == NULL || abs(i) > GetLength(*Dl) + 1 || i == 0) return ERROR; for (; j < abs(i);j++) //找到他的后一个节点,一会向前推 { if (i < 0) cur = cur->prior; else cur = cur->next; } //创建一个新的结点 newNode = (DLinkList)malloc(sizeof(Node)); newNode->data = e; if (i<0) { newNode->next = cur->next; newNode->prior = cur; cur->next->prior = newNode; cur->next = newNode; } else { newNode->next = cur; newNode->prior = cur->prior; cur->prior->next = newNode; cur->prior = newNode; } return OK; } //支持双向删除 Status DeleteList(DLinkList* Dl, int i, ElemType* e) { DLinkList cur = *(Dl); DLinkList oldNode; int j = 0; if (*Dl == NULL || abs(i) > GetLength(*Dl) || i == 0 || e == NULL) return ERROR; for (; j < abs(i); j++) //找到要删除的结点 { if (i < 0) cur = cur->prior; else cur = cur->next; } //赋值 *e = cur->data; oldNode = cur; //开始交换指针顺序 oldNode->prior->next = oldNode->next; oldNode->next->prior = oldNode->prior; free(oldNode); return OK; } //打印链表,支持双向打印,其实在main方法中稍微调整传入的结点也可以实现 void PrintList(DLinkList Dl, int i) { DLinkList cur = Dl; DLinkList start; int j = 0; if (i==0) //若是输入0,按照正向找到第一个结点进行输出即可 cur = cur->next; for (; j < abs(i); j++) //找到要开始打印的最开始那个结点 { if (i < 0) cur = cur->prior; else cur = cur->next; } start = cur; //找到最开始打印的那个结点 while (cur->next!=start) //进行判断结点 { if (cur!=Dl) //不打印头结点 printf("%c ", cur->data); cur = cur->next; } if (cur != Dl) printf("%c", cur->data); printf(" "); }
(五)打印预览
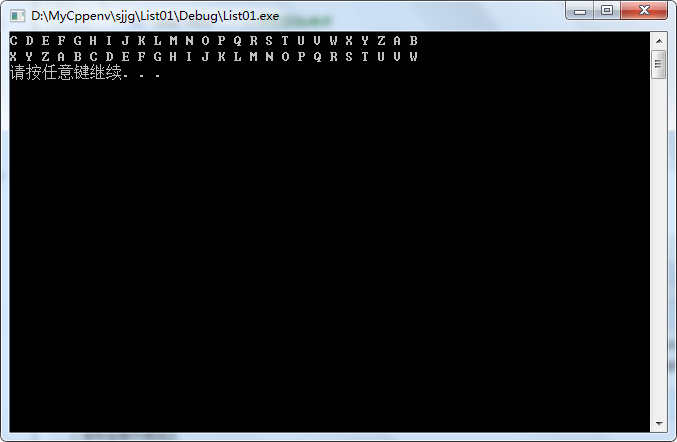
(六)总结
双向链表相对于单链表来说,要复杂些,多了个直接前驱指针,对于初入,删除考虑的指针交换需要格外小心。而且占用空间也增加了。
但是他有良好的对称性,是对于某个结点的前后结点的操作,带来了方便,提高了算法时间性能。也就是使用空间来换取时间。
原来单链表要寻找某个结点的前一个节点的时间复杂度是O(n),使用双向链表去查找前一个节点的时间复杂度是O(1)