(一)定义
串(string)是由零个或者多个字符组成的有限序列,又名叫字符串。
串是有限序列:所谓序列,说明相邻字符之间具有前驱和后继的关系
零个字符的串称为空串,注意:空串不是空格串,空格串有内容,有长度,空串无内容和长度
子串和主串:串中任意个数的连续字符组成的子序列称为该串的子串。相应的,包含子串的串称为主串
子串在主串中的位置就是子串的第一个字符在主串中的序号
(二)串的比较
通过组成串的字符之间的编码来进行的,而字符的编码是指字符在对应字符集中的序号
与strcmp一样,按顺序比较,只有出现第一个字符不同,比较其大小,就决定了这个串的大小:cmp>cMp比较到第二个字符就结束了
(三)串的抽象数据类型
串的逻辑结构与线性表相似。不同之处在于串中的数据是针对字符集,而线性表可以针对多种。
更大的区别在于:线性表更关注单个元素的操作,如查找一个元素,删除一个元素,插入一个元素,但是串更多是查找子串位置,得到指定位置的子串,替换子串等操作
ADT 串(string)
Data
串中的元素仅由一个字符组成,相邻元素具有前驱和后继更新
Operation
//生成串相关
StrAssign(T,*chars):生成一个其值等于字符串常量的chars的串T
StrCopy(T,S):串S存在,由串S复制得到串T
Concat(T,S1,S2):用T返回由S1和S2连接而成的新串
//基础操作相关
ClearString(S):串S存在,将串清空
StringEmpty(S):若串为空,返回true,否则false
StringLength(S):返回串S的元素个数,长度
//比较串,索引串相关
StrCompare(S,T):若S>T返回>0,=返回0,<返回<0
SubString(Sub,S,pos,len):串S存在,返回S由pos起,长度为len的子串到Sub
Index(S,T,pos):主串S,子串T,返回T在S中位置
//增删改相关
Replace(S,T,V):串S,T和V存在,T非空,用V替换主串S中T串
StrInsert(S,pos,T):在主串S中的pos位置插入串T
StrDelete(S,pos,len):串S存在,从串S中删除第pos个字符串起长度为len的子串
endADT
还有其他扩展:转小写,转大写,左查找子串,右查找子串,去空格...
(四)串的存储结构
串同线性表:分为两种存储结构,顺序存储和链式存储
1.串的顺序存储结构
还是使用数组或者堆分配一个固定长度的存储区。一般使用定长数组来定义,不过,数组存在溢出错误,或者截断现象。
另外注意:我们将串的长度保存在下标为0处位置,方便计算。其他方法来标记也可以:比如在结尾使用0,但是对于我们获取串长度,需要遍历,而且也是需要占用一个空间

2.串的链式存储结构
链式存储结构,一个结点需要消耗一个指针域空间,若是字符串过多,消耗大,所以可以考虑使用一个结点存放多个字符,对于最后的结点未占满,可以使用'#'等其他非串值字符补齐
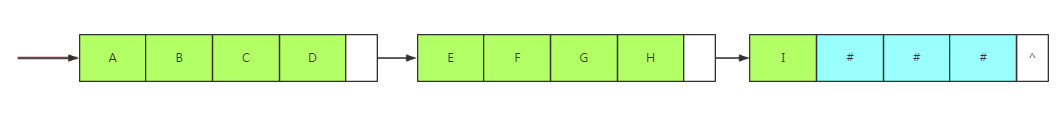
3.比较
链式存储结构除了在连接串与串操作时有一定的方便之外,总的来说不如顺序存储灵活,性能也不如顺序存储结构好。
(五)代码实现(顺序结构)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 40
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
//设置串的存储结构
typedef char String[MAXSIZE+1];
//生成串相关
Status StrAssign(String S,char *chars); //生成一个其值等于字符串常量的chars的串T
Status StrCopy(String T, String S); //串S存在,由串S复制得到串T
Status Concat(String T, String S1, String S2); //用T返回由S1和S2连接而成的新串
//基础操作相关
Status ClearString(String S); //串S存在,将串清空
Status StringEmpty(String S); //若串为空,返回true,否则false
int StringLength(String S); //返回串S的元素个数,长度
//比较串,索引串相关
int StrCompare(String S, String T); //若S > T返回 > 0, = 返回0, < 返回 < 0
Status SubString(String Sub, String S,int pos,int len); //串S存在,返回S由pos起,长度为len的子串到Sub
int Index(String S, String T,int pos); //主串S,子串T,返回T在S中位置
//增删改相关
Status Replace(String S, String T, String V); //串S,T和V存在,T非空,用V替换主串S中T串
Status StrInsert(String S, int pos, String T); //在主串S中的pos位置插入串T
Status StrDelete(String S,int pos,int len); //串S存在,从串S中删除第pos个字符串起长度为len的子串
void PrintStr(String S);
//生成串相关
//生成一个其值等于字符串常量的chars的串T
Status StrAssign(String S, char *chars)
{
int i;
if (strlen(chars) > MAXSIZE)
return ERROR;
else
{
S[0] = strlen(chars);
for (i = 1; i <= S[0];i++)
S[i] = *(chars+i-1);
return OK;
}
}
//串S存在,由串S复制得到串T
Status StrCopy(String T, String S)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i <= S[0];i++)
T[i] = S[i];
return OK;
}
//用T返回由S1和S2连接而成的新串,若是超出,会截断,但是会进行连接,返回FALSE
Status Concat(String T, String S1, String S2)
{
int i,j,interLen; //interLen是截断后S2剩余长度
if (S1[0] + S2[0] > MAXSIZE)
interLen = MAXSIZE - S1[0];
else
interLen = S2[0];
T[0] = S1[0] + S2[0];
for (i = 1; i <= S1[0]; i++)
T[i] = S1[i];
for (j = 1; j <= interLen; j++)
T[i+j-1] = S2[j];
if (interLen != S2[0])
return ERROR;
return OK;
}
//基础操作相关
//串S存在,将串清空
Status ClearString(String S)
{
S[0] = 0;
return OK;
}
//若串为空,返回true,否则false
Status StringEmpty(String S)
{
if (S[0] != 0)
return FALSE;
return TRUE;
}
//返回串S的元素个数,长度
int StringLength(String S)
{
return S[0];
}
//比较串,索引串相关
//若S > T返回 > 0, = 返回0, < 返回 < 0
int StrCompare(String S, String T)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= S[0] && i <= T[0]; i++)
if (S[i] != T[i])
return S[i] - T[i];
return S[0]-T[0]; //若是相同比较长度即可
}
//串S存在,返回S由pos起,长度为len的子串到Sub
Status SubString(String Sub, String S, int pos,int len)
{
int i;
if (pos<1 || len<0 || pos + len - 1 > S[0] || pos>S[0])
return ERROR;
for (i = 0; i < len;i++)
Sub[i + 1] = S[pos + i];
Sub[0] = len;
return OK;
}
//主串S,子串T,返回T在S中位置,pos代表从pos开始匹配
//或者一次截取一段进行比较为0则找到
int Index(String S, String T, int pos)
{
int i, j;
i = pos;
j = 1;
while (i<=S[0]-T[0]+1&&j<=T[0])
{
if (S[i]==T[j])
{
j++;
i++;
}
else
{
i = i - j + 2; //注意这个索引的加2,因为j是从1开始的,导致我们i-j会小一,所以我们要在到下一个位置的基础上i-j+1再加1,补上去
j = 1;
}
}
if (j > T[0])
return i - T[0];
return 0;
}
//增删改相关
//串S,T和V存在,T非空,用V替换主串S中T串
Status Replace(String S, String T, String V)
{
int idx=1;
if (StringEmpty(T))
return ERROR;
while (idx)
{
idx = Index(S, T, idx);
if (idx)
{
StrDelete(S, idx, StringLength(T));
StrInsert(S, idx, V);
idx += StringLength(V);
}
}
return OK;
}
//在主串S中的pos位置插入串T,注意:若是串满,则只插入部分
Status StrInsert(String S, int pos, String T)
{
int i,interLength;
if (S[0] + T[0] > MAXSIZE) //长度溢出
interLength = MAXSIZE - S[0];
else
interLength = T[0];
for (i = S[0]; i >= pos;i--)
S[interLength + i] = S[i]; //将后面的数据后向后移动
//开始插入数据
for (i = 1; i <= interLength; i++)
S[pos + i - 1] = T[i];
S[0] += interLength;
if (interLength != T[0])
return ERROR;
return OK;
}
//串S存在,从串S中删除第pos个字符串起长度为len的子串
Status StrDelete(String S, int pos,int len)
{
int i;
if (pos < 1 || len<1 || pos + len - 1>S[0])
return ERROR;
//将数据前移
for (i = pos+len; i <= S[0];i++)
S[i-len] = S[i];
S[0] -= len;
return OK;
}
void PrintStr(String S)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= StringLength(S);i++)
{
printf("%c", S[i]);
}
printf("
");
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
String s1,s2,t;
char *str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 40);
memset(str, 0, 40);
printf("enter s1:");
scanf("%s", str);
if (!StrAssign(s1, str))
printf("1.string length is gt %d
", MAXSIZE);
else
printf("1.string StrAssign success
");
printf("enter s2:");
scanf("%s", str);
if (!StrAssign(s2, str))
printf("1.string length is gt %d
", MAXSIZE);
else
printf("1.string StrAssign success
");
i = StrCompare(s1, s2);
printf("print All String:
");
PrintStr(s1);
PrintStr(s2);
printf("2.string StrCompare test
");
if (i < 0)
printf("s1 < s2
");
else if (i > 0)
printf("s1 > s2
");
else
printf("s1 = s2
");
printf("3.string Concat test
");
if (Concat(t,s1,s2))
printf("string Concat success
");
else
printf("string Concat interrupt
");
PrintStr(t);
printf("4.string StrCopy test
");
StrCopy(s1, t);
printf("copy t to s1,print s1:");
PrintStr(s1);
printf("5.string s1 length:%d
",StringLength(s1));
printf("6.substring test
");
SubString(t, s1, 5, 4);
printf("get s1 from 5 to 9-->t:");
PrintStr(t);
printf("7.Index func test
");
i = Index(s1, t, 1);
printf("find t in s1 index:%d", i);
printf("8.replace test
");
printf("please enter string to match:");
scanf("%s", str);
StrAssign(s2, str);
printf("please enter string to replace:");
scanf("%s", str);
StrAssign(t, str);
Replace(s1, s2, t);
PrintStr(s1);
printf("9.please enter string to insert:");
scanf("%s", str);
StrAssign(t, str);
printf("please enter pos to insert:");
scanf("%d", &j);
StrInsert(s1, j, t);
PrintStr(s1);
printf("10.please enter pos to delete:");
scanf("%d", &i);
printf("please enter length to delete:");
scanf("%d", &j);
StrDelete(s1, i, j);
PrintStr(s1);
ClearString(s1);
printf("11.string ClearString s1 test
");
printf("12.s1 has Cleaned,is empty:%d", StringEmpty(s1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}

(六)总结
串的存储结构最好使用顺序存储,而且使用数组是较好,较明了的方法。
对于使用链式存储,若是一个结点存储一个字符,会占用大量的空间去存放指针域。
若是使用一个结点存储多个字符,如同上面图像所描绘,虽然占的空间消耗小了,但是相对于数组,依旧需要太多的额外空间,最不好的是,这种方法会时链表的快速插入删除操作的优点消失,甚至复杂了。
所以使用顺序存储的方法是更加好的。


#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MINSIZE 5
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int Status;
struct StrNode
{
char data[MINSIZE];
struct StrNode* next;
}StrNode;
//设置串的存储结构
typedef struct StrNode* String;
//生成串相关
Status StrAssign(String S, char *chars); //生成一个其值等于字符串常量的chars的串T
Status StrCopy(String* T, String S); //串S存在,由串S复制得到串T
Status Concat(String* T, String S1, String S2); //用T返回由S1和S2连接而成的新串
//基础操作相关
Status ClearString(String S); //串S存在,将串清空
Status StringEmpty(String S); //若串为空,返回true,否则false
int StringLength(String S); //返回串S的元素个数,长度
void PrintStr(String S);
//生成串相关
//生成一个其值等于字符串常量的chars的串T,这里是以�结束,通过�来计算长度
Status StrAssign(String* S, char *chars)
{
int i,length;
String rear;
String node;
if (!S||!chars)
return ERROR;
length = strlen(chars);
length = length / MINSIZE + 1;
*S = (String)malloc(sizeof(StrNode));
//(*S)->next = NULL; //这里可以说没用了,因为在下面strcpy拷贝数据时,数据会覆盖掉指针,或者我们使用strncpy保证每次拷贝数据的长度也行
strcpy((*S)->data, chars);
//strncpy((*S)->data, chars, 5);
rear = *S;
i = 1;
while (i<length)
{
node = (String)malloc(sizeof(StrNode));
if (!strlen(chars + i*MINSIZE))
memset(node->data, 0, MINSIZE);
else
strcpy(node->data, chars + i*MINSIZE);
node->next = rear->next;
rear->next = node;
rear = node;
i++;
}
rear->next = NULL; //这里是必须要的
return OK;
}
//基础操作相关
//串S存在,将串清空
Status ClearString(String S)
{
String cur;
if (!S)
return OK;
while (S)
{
cur = S;
S = S->next;
free(cur);
}
return OK;
}
//若串为空,返回true,否则false
Status StringEmpty(String S)
{
if (!S)
return FALSE;
return TRUE;
}
//返回串S的元素个数,长度
int StringLength(String S)
{
String q,p;
int length=0;
int i=0;
q = S;
while (q->next)
{
length += MINSIZE;
q = q->next;
}
while (i<5&&q->data[i])
i++;
length += i;
return length;
}
//串S存在,由串S复制得到串T
Status StrCopy(String* T, String S)
{
int i;
String q, p,rear;
if (!S)
return ERROR;
if (StringEmpty(*T))
ClearString(*T);
p = S;
*T = (String)malloc(sizeof(StrNode));
memcpy(*T, p, sizeof(StrNode));
p = p->next;
rear = *T;
while (p)
{
q = (String)malloc(sizeof(StrNode));
memcpy(q, p, sizeof(StrNode));
q->next = rear->next;
rear->next = q->next;
rear = q;
p = p->next;
}
return OK;
}
void PrintStr(String S)
{
int i;
String q=S;
while (q)
{
for (i = 0; i < MINSIZE;i++)
{
if (!q->data[i])
break;
printf("%c", q->data[i]);
}
q = q->next;
}
printf("
");
}
//用T返回由S1和S2连接而成的新串,若是超出,会截断,但是会进行连接,返回FALSE
Status Concat(String* T, String S1, String S2)
{
String cS1, cS2;
cS1 = cS2 = NULL;
if (!StrCopy(&cS1, S1)||!StrCopy(&cS2, S2))
{
if (StringEmpty(cS1))
ClearString(cS1);
if (StringEmpty(cS2))
ClearString(cS2);
}
//需要考虑一个结点中的多个字符是否填满,没有填满,后面数据全部需要前移,逻辑复杂且时间复杂度增加了
return OK;
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
String s1;
String s2=NULL;
String t = NULL;
char *str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 40);
memset(str, 0, 40);
printf("enter s1:");
scanf("%s", str);
StrAssign(&s1, str);
printf("1.string StrAssign s1 success
");
printf("2.string s1 length:%d
", StringLength(s1));
printf("3.string s2 copy from s1
");
StrCopy(&s2, s1);
PrintStr(s2);
printf("4.string Concat test
");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
完成了部分链式存储的方法:生成串,获取串长度,拷贝串,清空串,判断是否为空




