1.面向过程于面向对象
面向过程”(Procedure Oriented)是一种以过程为中心的编程思想
对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming,OOP)是一种计算机编程架构。OOP的一条基本原则是计算机程序由单个能够起到子程序作用的单元或对象组合而成。
面向对象的三个目标:重用性、灵活性和扩展性,OOP=对象+类+继承+多态+消息;
面向对象的三大特性:封装、继承、多态,而封装加抽象则可以对外提供一个低耦合的模块。
无论是面向对象还是面向过程,低耦合,高聚和。这六个字就是亘古不变的真理。高聚和:各模块的相关特性数据和操作函数都封装在结构体(PO)/类(OOP);
低耦合:不仅要做到各独立模块间的数据接口独立,同一个模块内的不同作用的接口也要独立出来。
2.分析rt-thread的对象就可以很好的理解,并写出一个demo
首先是对象,rt-thread内核有基类对象,并由此派生出了 线程对象、内存池对象、ipc通讯对象、定时器对象和设备对象,如下图所示:
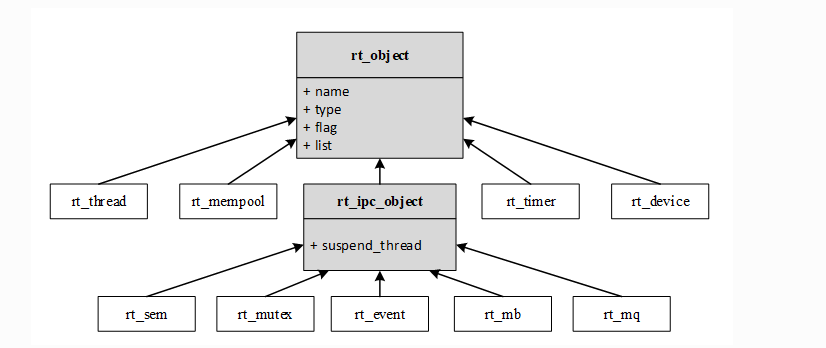
在积累对象rt_object中定义了通用的数据结构用来保存各种对象的共同属性,各类具体对象只需要在加上自己所特有的属性丰富描述自己。而内核对象管理线条将所有的对象链接到各种类型的链表中,以后会详细讲解rt-thread的设备管理方式,并仿照这种方式实现自己freertos上编程。
1 struct rt_object 2 { 3 /* 内核对象名称 */ 4 char name[RT_NAME_MAX]; 5 /* 内核对象类型 */ 6 rt_uint8_t type; 7 /* 内核对象的参数 */ 8 rt_uint8_t flag; 9 /* 内核对象管理链表 */ 10 rt_list_t list; 11 };
1 typedef struct rt_device *rt_device_t; /* 将结构体定义成指针类型,便于动态(malloc)分配,并由调用者删除*/ 2 3 struct rt_device 4 { 5 struct rt_object parent; /**< inherit from rt_object 设备类继承内核对象基类 */ 6 7 enum rt_device_class_type type; /**< device type 区分对象类型 */ 8 rt_uint16_t flag; /**< device flag 设备打开方式IRQ/DMA*/ 9 rt_uint16_t open_flag; /**< device open flag 设备权限,只读/只写/读写*/ 10 11 rt_uint8_t ref_count; /**< reference count 设备调用次数*/ 12 rt_uint8_t device_id; /**< 0 - 255 */ 13 14 /* device call back */ 15 rt_err_t (*rx_indicate)(rt_device_t dev, rt_size_t size); /* 设备接受满回调函数 */ 16 rt_err_t (*tx_complete)(rt_device_t dev, void *buffer); /* 发送完成回调函数 */ 17 18 #ifdef RT_USING_DEVICE_OPS 19 const struct rt_device_ops *ops; 20 #else 21 /* common device interface */ /* 每个设备都有的设备操作函数 */ 22 rt_err_t (*init) (rt_device_t dev); 23 rt_err_t (*open) (rt_device_t dev, rt_uint16_t oflag); 24 rt_err_t (*close) (rt_device_t dev); 25 rt_size_t (*read) (rt_device_t dev, rt_off_t pos, void *buffer, rt_size_t size); 26 rt_size_t (*write) (rt_device_t dev, rt_off_t pos, const void *buffer, rt_size_t size); 27 rt_err_t (*control)(rt_device_t dev, int cmd, void *args); 28 #endif 29 30 #if defined(RT_USING_POSIX) 31 const struct dfs_file_ops *fops; 32 struct rt_wqueue wait_queue; 33 #endif 34 35 void *user_data; /**< device private data */ 36 };
1 rt_device_t rt_device_create(int type, int attach_size) 2 { 3 int size; 4 rt_device_t device; 5 6 size = RT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct rt_device), RT_ALIGN_SIZE); 7 attach_size = RT_ALIGN(attach_size, RT_ALIGN_SIZE); 8 /* use the total size */ 9 size += attach_size; 10 11 device = (rt_device_t)rt_malloc(size); 12 if (device) 13 { 14 rt_memset(device, 0x0, sizeof(struct rt_device)); 15 device->type = (enum rt_device_class_type)type; 16 } 17 18 return device; 19 }
可以根据 rt_device_create 看出,创建一个设备就是从堆上分配一个设备大小的内存返回出来,注意函数内的栈空间(数组)不能返回出来,除非是编译器已经分配好的全局变量或静态变量。堆使用后可以由用户随时删除。内存删除后配合特定的内存算法,不至于分配到最后全是碎片。
根据设备类的操作接口函数可以看出,这是很标准的封装方法,相当于c++的类的方法。我们此次就是可以按照此种方式对一个长方形进行描述和设置。
1 #ifndef RECT_H 2 #define RECT_H 3 #include <rtthread.h> 4 5 typedef struct 6 { 7 char *object_name; 8 int lenth; 9 int width; 10 }Rect,*pRect; 11 12 typedef void* rt_handle_rect; 13 14 rt_handle_rect rect_creat(char *object_name); 15 void rect_set(rt_handle_rect rect, int len, int width); 16 int rect_get_area(rt_handle_rect rect); 17 void rect_display(rt_handle_rect rect); 18 void rect_delete(rt_handle_rect rect); 19 20 21 22 23 24 #endif
1 #include "object.h" 2 3 4 5 rt_handle_rect rect_creat(char *object_name) 6 { 7 8 pRect rect = rt_malloc(sizeof(rect)); 9 if (rect == RT_NULL) 10 { 11 rect = RT_NULL; 12 rt_kprintf("rect object mallo err "); 13 return RT_NULL; 14 } 15 16 rect->object_name = rt_malloc(rt_strlen(object_name) + 1); 17 if (rect->object_name == RT_NULL) 18 { 19 rect->object_name = RT_NULL; 20 rt_kprintf("rect object name mallo err "); 21 return RT_NULL; 22 } 23 24 rt_memcpy(rect->object_name, object_name, rt_strlen(object_name) + 1); 25 rect->lenth = 0; 26 rect->width = 0; 27 28 return (rt_handle_rect)rect; 29 30 } 31 32 void rect_set(rt_handle_rect rect, int len, int width) 33 { 34 RT_ASSERT(rect); 35 36 ((pRect)rect)->lenth = len; 37 ((pRect)rect)->width = width; 38 } 39 40 int rect_get_area(rt_handle_rect rect) 41 { 42 RT_ASSERT(rect); 43 44 return (((pRect)rect)->lenth * ((pRect)rect)->width); 45 } 46 47 void rect_display(rt_handle_rect rect) 48 { 49 RT_ASSERT(rect); 50 RT_ASSERT(((pRect)rect)->object_name); 51 52 rt_kprintf("%s len:%d %d area:%d ", ((pRect)rect)->object_name, 53 ((pRect)rect)->lenth, ((pRect)rect)->width,rect_get_area(rect)); 54 55 } 56 57 void rect_delete(rt_handle_rect rect) 58 { 59 RT_ASSERT(rect); 60 RT_ASSERT(((pRect)rect)->object_name); 61 62 rt_free(((pRect)rect)->object_name); 63 rt_free(rect); 64 65 ((pRect)rect)->object_name = RT_NULL; 66 rect = RT_NULL; 67 } 68 69 void rect_sample(void) 70 { 71 rt_handle_rect rect = rect_creat("RECT"); 72 73 if(rect == RT_NULL) 74 { 75 rt_kprintf("rect creat err "); 76 return; 77 } 78 79 rect_set(rect,10,20); 80 rect_display(rect); 81 82 rect_delete(rect); 83 84 } 85 86 MSH_CMD_EXPORT(rect_sample, rect sample);
这是一个很简单的demo,就是使用的面向对象编程的思想,很简单一看就会。这里不再赘述。