定义
将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,适配器模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。可以简单类比我们生活中的变压器,数据线转接口等工具。
结构
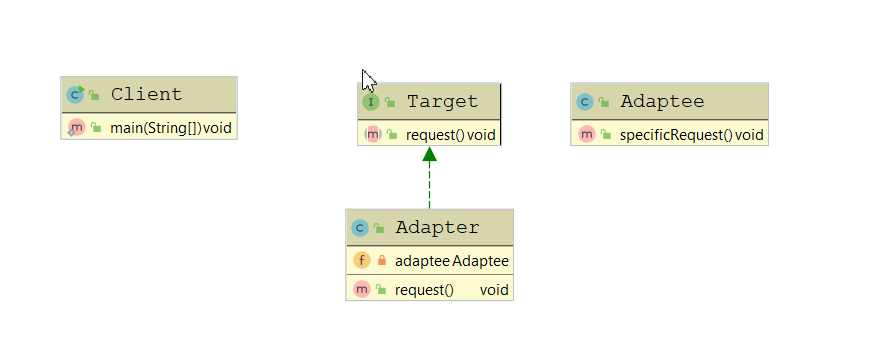
- Target,客户端需要的和特定领域相关的接口。
- Adaptee,已经存在的功能实现,但是接口与客户端要求的特定领域接口不一致,需要被适配。
- Adapter,适配器,将 Adaptee 适配成客户端需要的 Target。
适配器模式可以分为3种:类适配器模式,对象适配器模式,接口适配器模式。
简单实现
对象适配器模式
Target目标接口
public interface Target {
void request();
}
Adaptee,被适配对象
public class Adaptee {
public void specificRequest() {
System.out.println("Adaptee.specificRequest");
}
}
适配器
public class Adapter implements Target {
private Adaptee adaptee;
public Adapter(Adaptee adaptee) {
this.adaptee = adaptee;
}
@Override
public void request() {
adaptee.specificRequest();
}
}
客户端
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Adaptee adaptee = new Adaptee();
Adapter adapter = new Adapter(adaptee);
adapter.request();
}
}
类适配器模式
public class Adapter extends Adaptee implements Target {
@Override
public void request() {
this.specificRequest();
}
}
和对象适配器模式区别在于,适配器对象是通过继承被适配对象,而不是包含被适配对象实例来实现的。
接口适配器模式
存在一个接口,其中定义了很多的方法,但我们现在只使用到其中一到几个方法,如果直接实现接口,就要对所有的方法进行实现,会造成实现类很臃肿,这种情况下我们可以定义一个抽象类即适配器类,实现这个接口并为每个方法提供默认实现(空方法),然后我们继承此抽象类并重写我们需要的方法就可以了。以SpringMVC中的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter为例。
/**
* An implementation of {@link WebMvcConfigurer} with empty methods allowing
* subclasses to override only the methods they're interested in.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 3.1
* @deprecated as of 5.0 {@link WebMvcConfigurer} has default methods (made
* possible by a Java 8 baseline) and can be implemented directly without the
* need for this adapter
*/
@Deprecated
public abstract class WebMvcConfigurerAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>This implementation is empty.
*/
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>This implementation is empty.
*/
@Override
public void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
}
}
在java8及之后的版本,java的接口中可以添加默认方法实现了,就不需要使用抽象类作为适配器的这种方式了。
/**
* Defines callback methods to customize the Java-based configuration for
* Spring MVC enabled via {@code @EnableWebMvc}.
*
* <p>{@code @EnableWebMvc}-annotated configuration classes may implement
* this interface to be called back and given a chance to customize the
* default configuration.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @author Keith Donald
* @author David Syer
* @since 3.1
*/
public interface WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* Helps with configuring HandlerMappings path matching options such as trailing slash match,
* suffix registration, path matcher and path helper.
* Configured path matcher and path helper instances are shared for:
* <ul>
* <li>RequestMappings</li>
* <li>ViewControllerMappings</li>
* <li>ResourcesMappings</li>
* </ul>
* @since 4.0.3
*/
default void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
}
/**
* Configure content negotiation options.
*/
default void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
}
}
适配器模式在jdk中的实现
java中线程池的部分实现
//线程池的一个工具类
public class Executors {
public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result);
}
/**
* A callable that runs given task and returns given result.
*/
private static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> {
private final Runnable task;
private final T result;
RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
this.task = task;
this.result = result;
}
public T call() {
task.run();
return result;
}
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "[Wrapped task = " + task + "]";
}
}
}
将 Runnable 适配成 Callable 接口。
总结
优点
- 更好的复用性,通过增加一个适配器类来复用原有的功能实现。
- 更好的可扩展性。
缺点
- 过多的使用可能增加系统的复杂度。
本质
适配器模式的本质就是转换使用,复用功能。转换使用是手段,复用功能是目的。
使用场景
- 想要复用原有的一些实现,但接口不符合系统的要求,这种情况下可以使用适配器模式来转换接口。
参考
大战设计模式【9】—— 适配器模式
大战设计模式(第二季)【5】———— 从源码看适配器模式
设计模式的征途—7.适配器(Adapter)模式
设计模式(七)——适配器模式(SpringMVC框架分析)
研磨设计模式-书籍