(1)Happy Number

解题思路:使用HashSet,注意HashSet中的元素不能重复,所以不是happy number的数字要无限循环,一定要重复,就会返回false.
代码如下:

1 public class Solution { 2 public boolean isHappy(int n) { 3 Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); 4 int sum, remain; 5 while (set.add(n)) { 6 sum = 0; 7 while (n > 0) { 8 remain = n % 10; 9 sum += remain * remain; 10 n /= 10; 11 } 12 if (sum == 1) { 13 return true; 14 } else { 15 n = sum; 16 } 17 } 18 return false; 19 } 20 }
注意:while(set.add(n))这个判断条件。当不是happy number的数字无限循环时一定会重复,就不能继续加入就返回false.
(2)Find All Anagrams in a String【理解不透】

代码如下:

1 public class Solution { 2 public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) { 3 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 4 if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || p == null || p.length() == 0) return list; 5 int[] hash = new int[256]; //character hash 6 //record each character in p to hash 7 for (char c : p.toCharArray()) { 8 hash[c]++; 9 } 10 //two points, initialize count to p's length 11 int left = 0, right = 0, count = p.length(); 12 while (right < s.length()) { 13 //move right everytime, if the character exists in p's hash, decrease the count 14 //current hash value >= 1 means the character is existing in p 15 if (hash[s.charAt(right)] >= 1) { 16 count--; 17 } 18 hash[s.charAt(right)]--; 19 right++; 20 //when the count is down to 0, means we found the right anagram 21 //then add window's left to result list 22 if (count == 0) { 23 list.add(left); 24 } 25 //if we find the window's size equals to p, then we have to move left (narrow the window) to find the new match window 26 //++ to reset the hash because we kicked out the left 27 //only increase the count if the character is in p 28 //the count >= 0 indicate it was original in the hash, cuz it won't go below 0 29 if (right - left == p.length() ) { 30 if (hash[s.charAt(left)] >= 0) { 31 count++; 32 } 33 hash[s.charAt(left)]++; 34 left++; 35 } 36 } 37 return list; 38 } 39 }
解题思路:
使用滑动窗口,使得时间复杂度为为O(n),这就是算法的力量!
算法介绍:
(1)count= p.length(),用来表示目前窗口中的字符和p的差异度(由于窗口最大时(为p.length())才有可能使count为0,所以count为0时窗口中的字符与p为Anagrams)。count差异度的含义:一开始窗口左右指针都指向第一个,所以差异度最大为p.length();当窗口中进来一个p中有的字符,差异度就减一,出去一个p中有的差异度就增一;至于进来或出去的是p中没有的,则count不变,反正窗口的最大值也不过是p.length()。
(2)窗口的左右两个指针:left和right,分别指向窗口的左端和右端。
滑动窗口具体操作:
先滑动右指针,
1.1 加进来的字符如果该字符在数组hash的计数中大于等于一意味着该字符在p中出现,则count减一,否则不做操作,
1.2无论在不在p中出现,数组hash该字符相应位置计数都减一。
1.3如果count为0,则将此时的left值加入到list中。
判断如果窗口长度到达p.length(),开始滑动左指针:
2.1被踢出窗口的那个字符如果在数组hash的计数中非负意味着原来在p中出现,此时要踢出,则差异度count增一,不在则不做操作。
2.2无论在不在数组hash该字符相应位置计数都加一
3.上面1.1和2.1操作的原理:hash中的记录的数据是代表p中含有的的每个字符的数量去掉当前窗口中存在的p字符串中每个字符的数量,一开始窗口大小为0,啥都不存在,自然hash中记录的就是全部p中含有的的每个字符的数量,如果窗口中有一个,则hash相应的记录中就少一个。如果窗口中多包含一个p中没有的(或者包含的某一个字符的数量比p中有的还多),那么这时候,hash中相应的记录值就会变成负数,代表当前窗口中包含相应字符的“多余”的数量。
所以当进来一个的时候,如果相应记录为非负,那么这个进入是有意义的,则差异度(count)减一;当出去一个的时候,如果相应记录为非负,那么这个出去是有意义的,则差异度(count)加一。
4.hash用到哈希表思想,用来记录p中每一种字符分别有多少个。
(3)Bulls and Cows
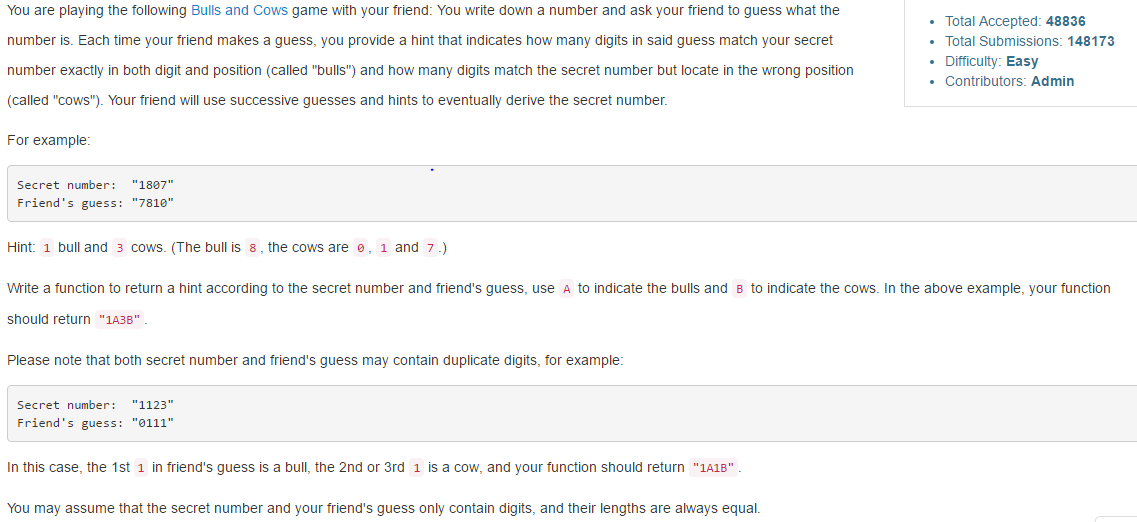
代码如下:

1 public class Solution { 2 public String getHint(String secret, String guess) { 3 int[] count = new int[10]; 4 int bulls = 0; 5 int cows = 0; 6 for (int i = 0; i < secret.length(); i++) { 7 int s = secret.charAt(i) - '0'; 8 int g = guess.charAt(i) - '0'; 9 if (s == g) { 10 bulls++; 11 } else { 12 if (count[s] < 0) { 13 cows++; 14 } 15 if (count[g] > 0) { 16 cows++; 17 } 18 count[s]++; 19 count[g]--; 20 } 21 } 22 return bulls + "A" + cows + "B"; 23 } 24 }
解题思路:
使用一个数组记录数字的出现,在secret中出现增加计数,在guess中出现减少计数。使用for循环遍历一次,如果s和g出现完全匹配,bulls计数加一.否则,如果此时s的计数小于零,说明guess中已有该数字,cows加一。如果此时g的计数大于零,说明secret中已有该数字,cows加一。然后s计数加一,g计数减一。
(4)Isomorphic Strings

解题思路一:主要想法是存储两个字符串中当前(第i个)字符的最后出现的位置。如果先前存储的位置不同,则他们同时出现在当前第i个位置是不可能的,故返回false。
代码如下:

1 public class Solution { 2 public boolean isIsomorphic(String s1, String s2) { 3 int[] m = new int[512]; 4 for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) { 5 if (m[s1.charAt(i)] != m[s2.charAt(i) + 256]) { 6 return false; 7 } 8 m[s1.charAt(i)] = m[s2.charAt(i) + 256] = i + 1; 9 } 10 return true; 11 } 12 }
解题思路二:使用一个哈希表map维护两个字符串中字符的映射关系,同时用一个set保存映射的值。(s[i], t[i]),如果s[i]键没有在map中出现过并且t[i]没有在set中出现过,就加入到映射关系中。t[i]值已经出现过,说明是多对一映射,不符合返回false。s[i]键如果已经出现过,设为s[k],对应的映射值为t[k]),即s[i]==s[k],则找出s[k]的对对应值t[k],如果t[i]!=t[k],说明一个同一个字符存在两个不同的映射,两个字符串不是同构的,返回false,继续处理下一个字符,直到结束。
代码如下:

1 public class Solution { 2 public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) { 3 Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<Character, Character>(); 4 Set<Character> set = new HashSet<Character>(); 5 6 for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++) { 7 char c1 = s.charAt(i); 8 char c2 = t.charAt(i); 9 10 if(map.containsKey(c1)) { 11 if(map.get(c1) != c2) return false; 12 } else { 13 if(set.contains(c2)) return false; 14 else { 15 map.put(c1, c2); 16 set.add(c2); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 return true; 21 } 22 }
