实验二 进程/线程基本编程练习
【要求】所有练习题保留题目要求,在题目要求后面作答:
代码要求有注释,代码中适当标注关键代码为红色。
要有运行结果的截图。
每题最后应该有对程序的适当分析和总结!
注意格式排版,内容分析注意列条目,展开清楚地阐述。
进程/线程这一块需要重点注意的一个函数为fork()函数,首先来看一下fork()函数的解释(摘自百度百科fork):
复刻(英语:fork,又译作派生、分支)是UNIX或类UNIX中的分叉函数,fork函数将运行着的程序分成2个(几乎)完全一样的进程,每个进程都启动一个从代码的同一位置开始执行的线程。这两个进程中的线程继续执行,就像是两个用户同时启动了该应用程序的两个副本。
fork调用的一个奇妙之处就是它仅仅被调用一次,却能够返回两次,它可能有三种不同的返回值:
(1)在父进程中,fork返回新创建子进程的进程ID;
(2)在子进程中,fork返回0;
(3)如果出现错误,fork返回一个负值。

下面来进行实验:
1、分析理解多个进程的创建
1)若一个程序中有这样的代码,则有几个进程,父子关系如何?
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
pid_t pid,pid2;
char *message;
int x;
pid = fork();
pid2 = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{ perror("fork failed");
exit(1); }
补充完整后面的代码,使多个进程输出各自身份,并符合正确的亲缘关系
if ( )
{ message = "This is the child ";
x = 0; }
……
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d ",message,x,getpid(),getppid());
return 0;
}//main
给出代码及执行效果抓图,并要有说明分析!!!!谁先谁后,为什么。
实现:
具体代码:
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid,pid2;
char *message;
int x;
pid = fork();
pid2 = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
}
//补充完整后面的代码,使多个进程输出各自身份,并符合正确的亲缘关系
if (pid==0&&pid2==0) //都返回0表示子进程的子进程,即第一个child的child
{
message = "This is the first child of child ";
x = 4;
}else if(pid==0&&pid2>0){ //pid返回0表示为子进程(pid角度上),但pid2>0又表示父进程(pid2角度上),即子进程1
message = "This is the first child ";
sleep(1);
x = 3;
}else if(pid>0&&pid2==0){ //pid>0表示该进程为父进程(pid角度上),但pid2=0表示该进程又为子进程(pid2角度上),即子进程2
message = "This is the second child ";
x = 2;
}else{ //pid>0&&pid2>0表示本进程
message = "This is the father ";
x = 1;
sleep(2);
}
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d ",
message,getpid(),x,getppid());
return 0;
}
执行过程分析:


当不限制休眠时间sleep时,可能会出现四个进程共同运行的情况,pid顺序:9688(该进程的父进程);9694(该进程),9695,(child1),9696(child2),9697(child1的child)
也可能会出现其他不可预料的情况(子进程没有运行完毕但因父进程执行完毕被回收导致子进程也无法执行):
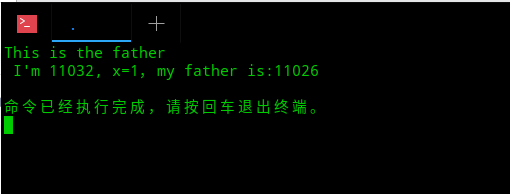

这时为了保证子进程都能运行完毕,可以使相应的父进程(该父进程及子进程1作父进程)进行sleep等待子进程执行完毕后回收:
此时虽然会因调度问题有一些执行顺序上的不统一,但是基本上可以保证所有进程都可以执行完毕:
例:

2)若有如下的代码
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
pid = fork();
……
请分析将产生多少个进程?要有说明分析!!!!
32个
实现:
具体代码(模拟上述for循环):
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
pid=fork();
pid=fork();
pid=fork();
pid=fork();
pid=fork();
printf("%d ",getpid());
return 0;
}
执行过程分析:
12318
12317
12344
12340
12342
12343
12325
12336
12321
12322
12346
12330
12320
12341
12337
12326
12331
12329
12338
12323
12339
12316
12347
12319
12332
12345
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ 12328
12334
12335
12327
12324
12333
上述为执行结果,首先我们可以从第一个fork()函数分析,父进程返回两个进程ID,此时有两个进程继续执行下一条fork()函数,两个进程返回四个进程ID,以此类推,规律表明进程数量=2^n(n表示执行n次fork())
(当然也可以对每一个进程进行分析,分析其产生的子进程数,但是由于子进程的循环产生的数量呈指数型增长,极易分析错误。)
2、解释执行效果
若有下面的功能代码,执行会有怎样的输出?不只有抓图,要有说明分析!!!!谁先谁后,哪里停顿过。
int main(void){
pid_t a;
a = fork();
if (a == 0) {
sleep(2);
execlp ("ps" ,"ps",NULL);
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d ",message,getpid(),getppid());
}
else
printf("%s I'm %d, x=%d,my father is:%d ",message,getpid(),getppid());
return 0;
}
实现:
具体代码:
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int main(void)
{
pid_t a;
a = fork();
if (a == 0)
{
printf("I'm %d,my father is:%d ",getpid(),getppid());
sleep(2);
execlp ("ps","ps",NULL);
printf("I'm %d,my father is:%d ",getpid(),getppid());
}
else
printf("I'm %d,my father is:%d ",getpid(),getppid());
return 0;
}
执行过程分析:
执行结果:
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ gcc test2.2.c -o test2.2.out
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ ./test2.2.out
I'm 14136,my father is:9242
I'm 14137,my father is:14136
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ PID TTY TIME CMD
9242 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
14137 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
上述代码执行父进程时,直接执行相应的语句,执行子进程时,先执行语句后再休眠2秒,然后执行execlp进程载入ps程序,替换当前内存空间,运行ps程序。
3. 体验进程/线程的顺序控制。(基于对例5-9,5-11的理解,注意不是用sleep控制)
1)编写一个可产生父子进程的程序,使执行时子进程先printf输出内容,然后父进程再printf输出。
实现:
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int main(void)
{
pid_t a,pw1;
a = fork();
if(a<0){
printf("生成失败");
exit(1);
}
if(a>0){//父进程
pw1=wait(NULL);//等待其有亲缘的进程死亡
printf("catch a dead child process with pid:%d ",pw1);
printf("I'm %d,The main process leave(father process) ",getpid());
}else{
printf("I'm %d,the child process,my father process is%d ",getpid(),getppid());
}
return 0;
}
执行结果:
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ gcc test3.1.c -o test3.1.out
test3.1.c: In function ‘main’:
test3.1.c:14:13: warning: implicit declaration of function ‘wait’; did you mean ‘main’? [-Wimplicit-function-declaration]
pw1=wait(NULL);//等待其有亲缘的进程死亡
^~~~
main
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ ./test3.1.out
I'm 14968,the child process,my father process is14967
catch a dead child process with pid:14968
I'm 14967,The main process leave(father process)
- 编写一个可产生两个线程(一个输出AAAAAA,一个输出BBBBBB)的程序,代码中要求控制线程的输出为AAAAAABBBBBB的顺序。然后修改控制代码,重新编译执行,得到另一种输出顺序,得到BBBBBBAAAAAA的输出。
实现1:
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "pthread.h"
char message[50]="hello";
void *thread_function1(void *arg){
printf("AAAAAA ");
pthread_exit("子进程结束");
}
int main(void)
{
int res;
pthread_t threadC ;
void *thread_result;
res=pthread_create(&threadC,NULL,thread_function1,(void*)message);
if(res!=0){
perror("thread creation failed!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
res=pthread_join(threadC,&thread_result);
printf("BBBBBB ");
}
执行过程1:
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ gcc test.c -l pthread
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ ./a.out
AAAAAA
BBBBBB
实现2:
#include "sys/types.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "pthread.h"
char message[50]="hello";
void *thread_function1(void *arg){
printf("AAAAAA ");
pthread_exit("子进程结束");
}
int main(void)
{
printf("BBBBBB ");
int res;
pthread_t threadC ;
void *thread_result;
res=pthread_create(&threadC,NULL,thread_function1,(void*)message);
if(res!=0){
perror("thread creation failed!");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
res=pthread_join(threadC,&thread_result);
}
执行过程2:
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ gcc test.c -l pthread
deepin@deepin-MJG:~/Desktop/MJG$ ./a.out
BBBBBB
AAAAAA