初始ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是线程安全的无界非阻塞队列,其底层使用单向链表实现,对于入队和出队操作使用 CAS 来实现线程安全。
其类图如下:
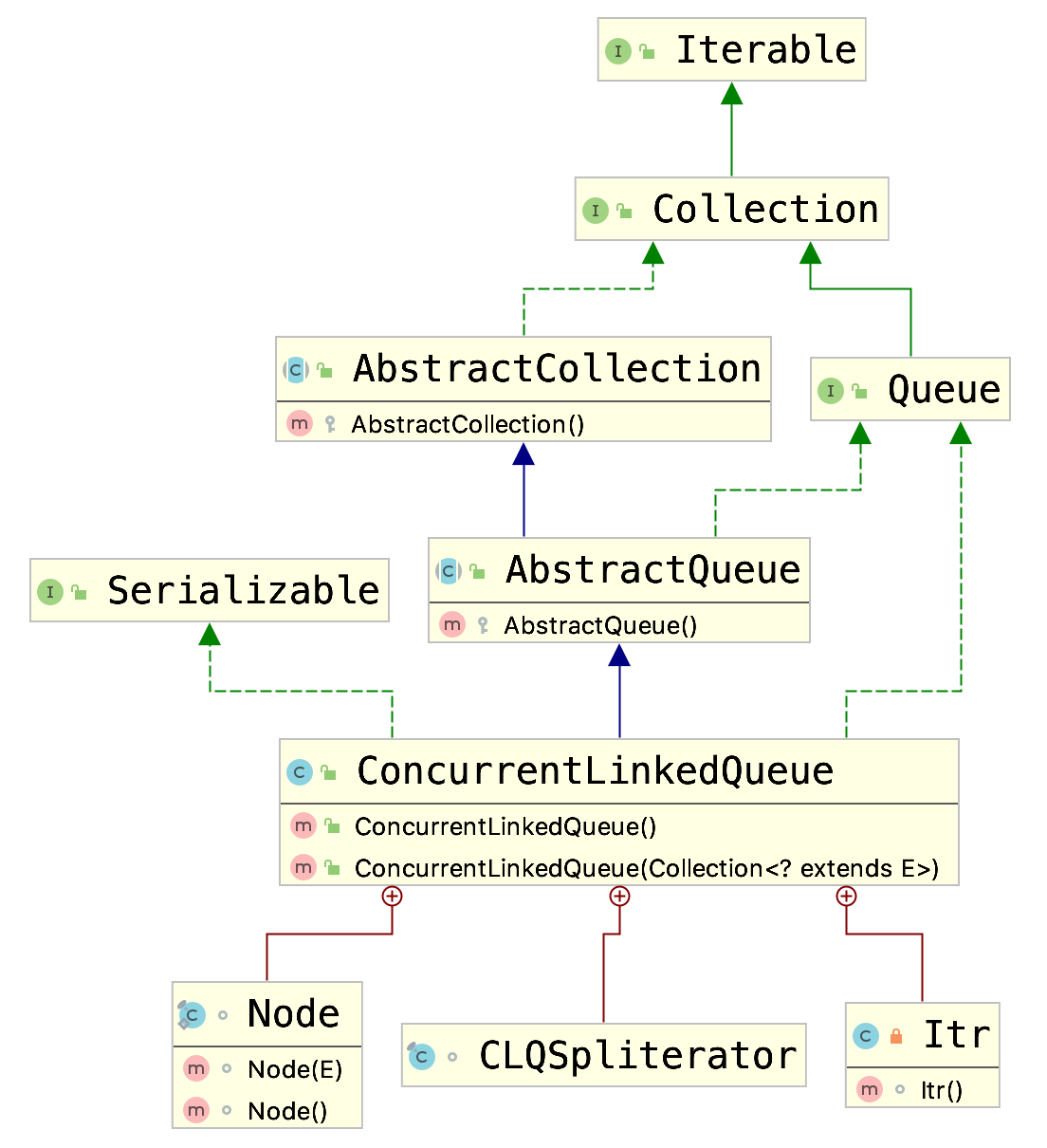
从类图可以发现其与其它阻塞队列的一个明显区别是,ConcurrentLinkedQueue没有实现BlockingQueue接口,所以ConcurrentLinkedQueue没有提供具有阻塞性质的put、take等方法。
其构造函数如下:
/** * Creates a {@code ConcurrentLinkedQueue} that is initially empty. */ public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() { head = tail = new Node<E>(); } /** * Creates a {@code ConcurrentLinkedQueue} * initially containing the elements of the given collection, * added in traversal order of the collection's iterator. * * @param c the collection of elements to initially contain * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any * of its elements are null */ public ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) { Node<E> h = null, t = null; for (E e : c) { Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(Objects.requireNonNull(e)); if (h == null) h = t = newNode; else t.appendRelaxed(t = newNode); } if (h == null) h = t = new Node<E>(); head = h; tail = t; }
解读:
ConcurrentLinkedQueue维护有两个 volatile 类型的 Node 节点分别用来存放队列的首、尾节点。
创建队列时头、尾节点指向一个 item 为 null 的哨兵节点。
Node的定义如下:
static final class Node<E> { volatile E item; volatile Node<E> next; /** * Constructs a node holding item. Uses relaxed write because * item can only be seen after piggy-backing publication via CAS. */ Node(E item) { ITEM.set(this, item); } /** Constructs a dead dummy node. */ Node() {} void appendRelaxed(Node<E> next) { // assert next != null; // assert this.next == null; NEXT.set(this, next); } boolean casItem(E cmp, E val) { // assert item == cmp || item == null; // assert cmp != null; // assert val == null; return ITEM.compareAndSet(this, cmp, val); } }
解读:
在 Node 节点内部维护了一个使用 volatile 修饰的变量 item,用来存放节点的值;
next 用来存放链表的下一个节点,从而链接为一个单向无界链表。
添加元素的方法如下:
/** * Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. * As the queue is unbounded, this method will never return {@code false}. * * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer}) * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null */ public boolean offer(E e) { final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(Objects.requireNonNull(e)); for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) { Node<E> q = p.next; if (q == null) { // p is last node if (NEXT.compareAndSet(p, null, newNode)) { // Successful CAS is the linearization point // for e to become an element of this queue, // and for newNode to become "live". if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a time; failure is OK TAIL.weakCompareAndSet(this, t, newNode); return true; } // Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next } else if (p == q) // We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it // will also be off-list, in which case we need to // jump to head, from which all live nodes are always // reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet. p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head; else // Check for tail updates after two hops. p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q; } }
解读:
offer操作是在队列末尾添加一个元素,如果传递的参数是 null,则抛出 NullPointerException 异常;否则由于 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是无界队列,该方法将一直会返回 true(由于使用 CAS 无阻塞算法,该方法不会阻塞调用线程)。
队列一开始为空时的状态如下图:
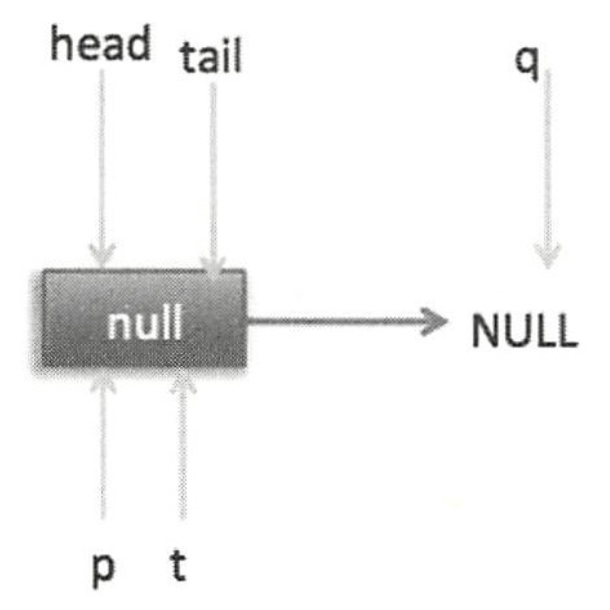
想象一下,当单个或者多个线程操作队列可能发生的情况以理解上述代码中的各个分支。
小结:
offer操作中的关键步骤是通过 CAS 操作来控制某个时间只有一个线程可以追加元素到队列末尾。
CAS 竞争失败的线程会通过循环一次次尝试,直到 CAS 成功才会返回。
这里通过使用无限循环不断进行 CAS 尝试来代替阻塞算法挂起调用线程;相比阻塞算法,这是使用 CPU资源换取阻塞所带来的开销。
移除元素的方法如下:
public E poll() { restartFromHead: for (;;) { for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;; p = q) { final E item; if ((item = p.item) != null && p.casItem(item, null)) { // Successful CAS is the linearization point // for item to be removed from this queue. if (p != h) // hop two nodes at a time updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p); return item; } else if ((q = p.next) == null) { updateHead(h, p); return null; } else if (p == q) continue restartFromHead; } } }
解读:
poll 操作是在队列头部获取并移除一个元素,如果队列为空则返回 null。
Note:
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 需要遍历链表来获取 size,而不是使用原子变量(使用原子变量保存队列元素个数需要保证入队、出队操作是原子性操作)。
由于使用非阻塞 CAS 算法,没有加锁,所以在计算 size 时有可能进行了 offer、poll 或者 remove 操作,导致计算的元素个数不精确,所以在井发情况下 size 函数不是很有用。