数据结构与算法-列表
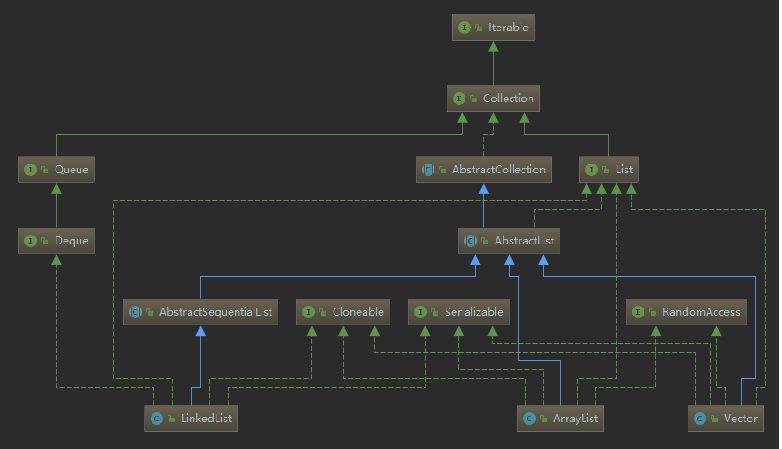
列表的linkedlist
LinkedList 是通过一个双向链表来实现的,它允许插入所有元素,包括 null,同时,它是线程不同步的。双向链表每个结点除了数据域之外,还有一个前指针和后指针,分别指向前驱结点和后继结点(如果有前驱/后继的话)。另外,双向链表还有一个 first 指针,指向头节点,和 last 指针,指向尾节点。
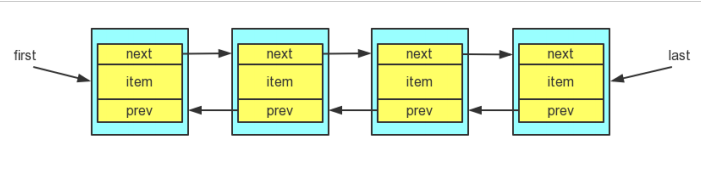
循位置访问
列表:采用动态存储的典型结构。
-
每个元素称为节点( node )。
-
各个节点通过指针或引用彼此联接,在逻辑上构成一个线性序列。相邻节点彼此互称前驱和后继。如果存在前驱和后继,那么必然是唯一的。
-
没有前驱的节点称为首,没有后继的节点称为末。此外,可以认为头存在一个哨兵前驱称为头,末存在一个哨兵后继称为尾。
-
可以认为 头、首、末、尾 节点的秩分别为 -1、0、n-1、n。
-
在访问时尽量不使用循秩访问,而使用循位置访问。即利用节点之间的相互引用,找到特定的节点。
列表中元素(源码解析)
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
*链表的节点个数
*/
transient int size = 0;
/**
* 指向头节点的指针
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* 指向尾节点的指针
*/
transient Node<E> last;
列表构造器
/**
* 空构造器.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* 包含集合中元素的构造器
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;//操作次数
return true;
}
元素的添加
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
/**
* 添加为第一个元素.
*/
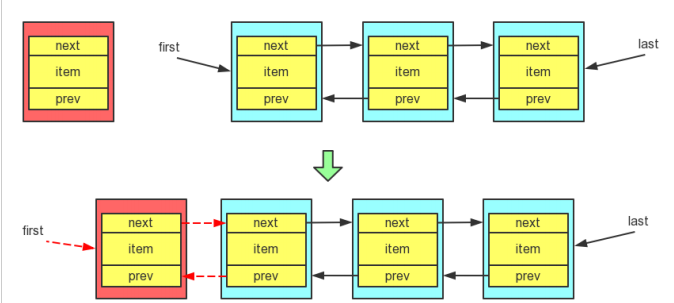
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)//如果第一个为空,则原List为空
last = newNode;//list的first和last都设置为加入元素
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* 添加为尾元素.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)//同上
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
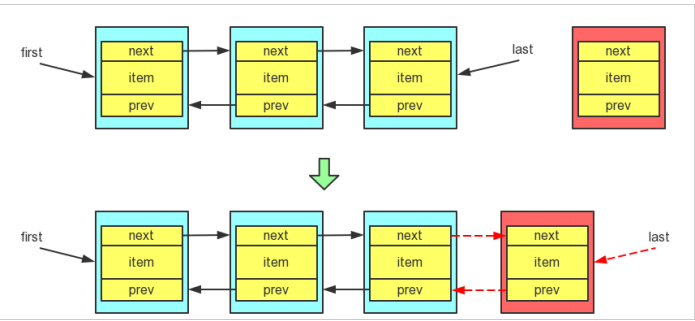
/**
* 添加到指定Node之前.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
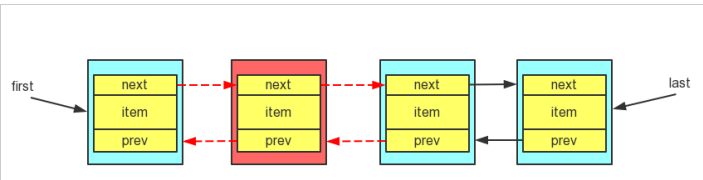
元素的删除
/**
* 去除链接有三种
* 第一种:first链接
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 第二种:last链接
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 第三种:中间链接.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
常用的方法
/**一些常用的方法
* Returns the first element in this list.
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*/
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Removes and returns the last element from this list.
*/
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* 判断是否包含某一元素
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list.
* The list will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
// Positional Access Operations
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.
*/
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
// Search Operations
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
迭代器
/**
* 迭代器有两种:
* ListIterator
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned;
private Node<E> next;
private int nextIndex;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* 第二种:descendingIterator对ListItr的应用
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
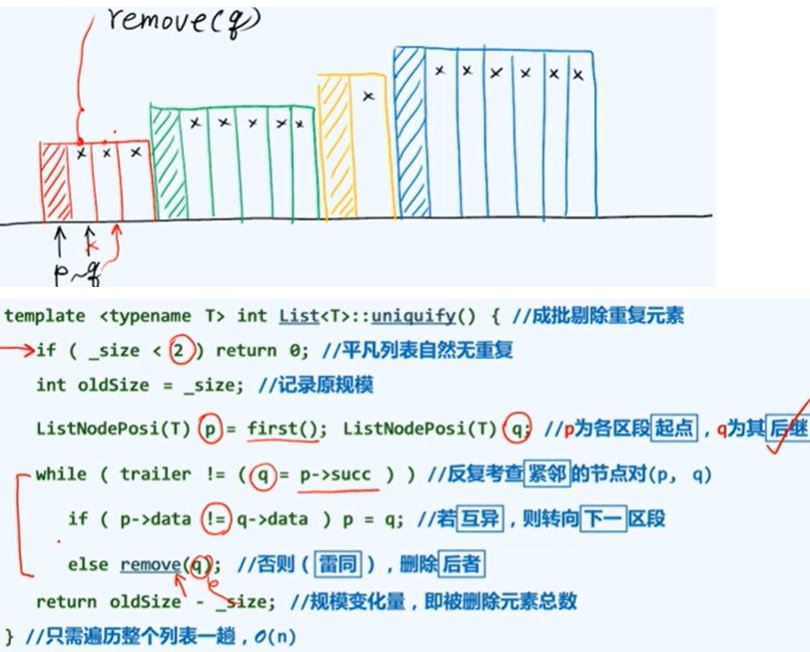
唯一化
无序列表


有序列表
选择排序
原理
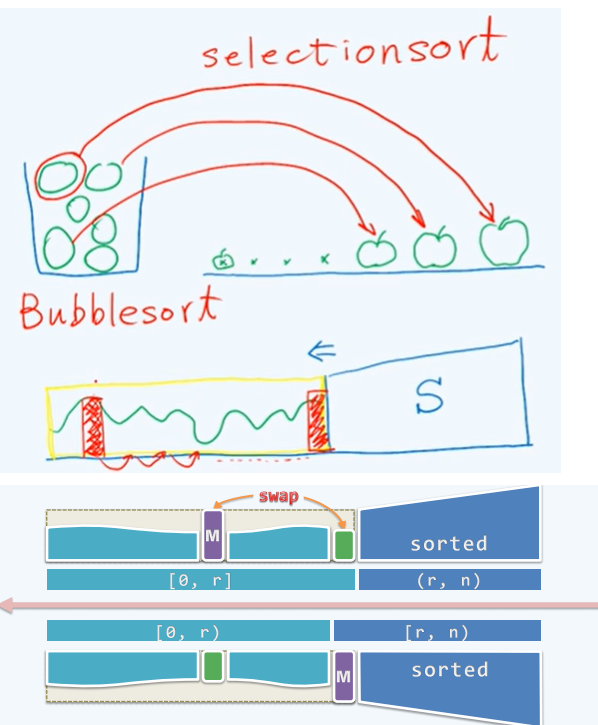
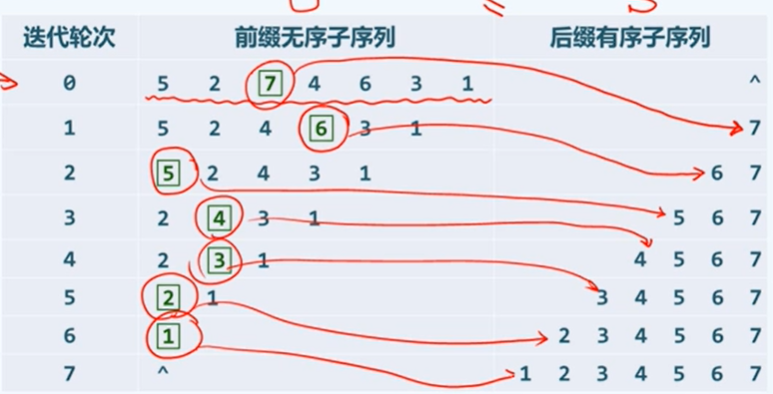
c++方法


性能比较
JAVA方法(不是关于LinkedList的)
public class ChooseSort {
static int[] array = {3,2,4,1,5,0};
public static void chooseSort(int[] a)
{
int max = 0;
int index = 0;
//外层循环,控制选择的次数,数组长度为6,一共需要选择5次
for(int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<a.length-i;j++)
{
if(max < a[j])
{
max = a[j];
index = j;
}
}
//每次选择完成后,max中存放的是该轮选出的最大值
//将max指向位置的元素和数组最后一个元素位置互换
int temp = a[a.length-i-1];
a[a.length-i-1] = max;
a[index] = temp;
//清空max和index,便于下次
max=0;
index =0;
System.out.println("经过第"+(i+1)+"轮选择后,数组为"+Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
chooseSort(array);
}
}
插入排序
原理
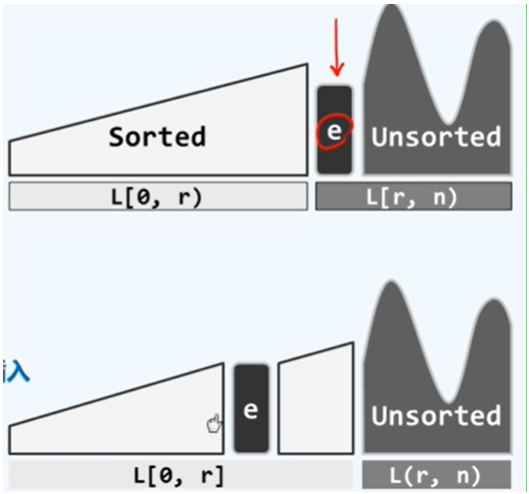
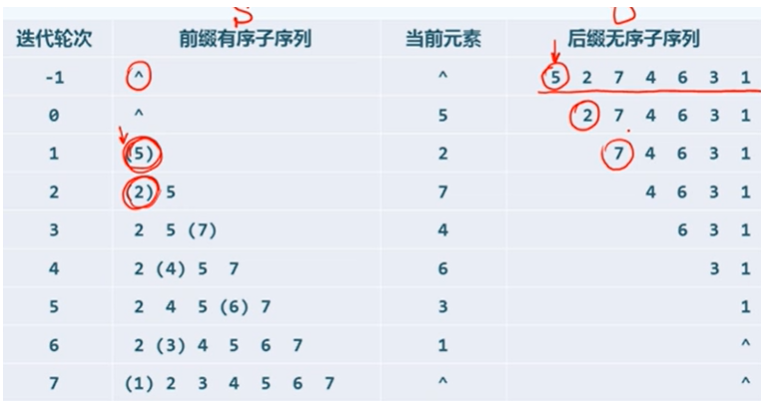
c++方法
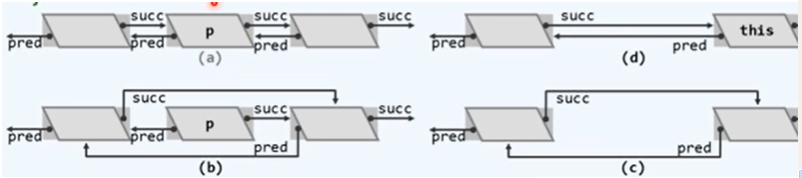
template <typename T> //列表的插入排序算法:对起始于位置p的n个元素排序
void List<T>::insertionSort ( ListNodePosi(T) p, int n ) { //valid(p) && rank(p) + n <= size
for ( int r = 0; r < n; r++ ) { //逐一为各节点
insertA ( search ( p->data, r, p ), p->data ); //查找适当的位置并插入
p = p->succ;
remove ( p->pred ); //转向下一节点
}
}
template <typename T> //在有序列表内节点p(可能是trailer)的n个(真)前驱中,找到不大于e的最后者
ListNodePosi(T) List<T>::search ( T const& e, int n, ListNodePosi(T) p ) const {
// assert: 0 <= n <= rank(p) < _size
do {
p = p->pred; n--; //从右向左
} while ( ( -1 < n ) && ( e < p->data ) ); //逐个比较,直至命中或越界
return p; //返回查找终止的位置
} //失败时,返回区间左边界的前驱(可能是header)——调用者可通过valid()判断成功与否
逆序对

JAVA方法
public class LinkedInsertSort {
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
public static ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return head;
ListNode pre = head;//pre指向已经有序的节点
ListNode cur = head.next;//cur指向待排序的节点
ListNode aux = new ListNode(-1);//辅助节点
aux.next = head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<pre.val){
//先把cur节点从当前链表中删除,然后再把cur节点插入到合适位置
pre.next = cur.next;
//从前往后找到l2.val>cur.val,然后把cur节点插入到l1和l2之间
ListNode l1 = aux;
ListNode l2 = aux.next;
while(cur.val>l2.val){
l1 = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
//把cur节点插入到l1和l2之间
l1.next = cur;
cur.next = l2;//插入合适位置
cur = pre.next;//指向下一个待处理节点
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return aux.next;
}
}