树的构成要素:
节点(Node) 边(Edge) 根节点(Root) 路径(Path) 子节点集(Children) 父节点(Parent) 兄弟节点(Sibling)
子树 (Subtree) 叶节点(Leaf Node) 层数(Level) 高度(height)
定义一:树有以下特征:
- 有一个节点是根节点
- 除了根节点外的每一个节点n,都通过一条边与另一个节点p相连,p是n的父节点
- 可以沿着唯一的路径从根节点到达每个节点
- 如果这个树每个节点都至多有两个子节点,我们称它为二叉树
定义二:
每个树或者为空或者包含一个根节点和零个或多个子树,其中每个子树也符合这样的定义
通过嵌套列表来实现树
def BinaryTree(r): return [r,[],[]] #初始化树 def insertLeft(root,newBranch): t = root.pop(1) 将左子节点拿出 if len(t)>1: root.insert(1,[newBranch,t,[]])
插入位置 插入元素 else: root.insert(1,[newBranch,[],[]]) return root def insertRight(root,newBranch): t = root.pop(2) if len(t)>1: root.insert(2,[newBranch,[],t]) else: root.insert(2,[newBranch,[],[]]) return root def getRootVal(root): return root[0] def setRootVal(root,newVal): root[0] = newVal def getLeftChild(root): return root[1] def getRightChild(root): return root[2]
第二种实现树的方式 使用节点和引用 利用对象的方式

class BinaryTree: def __init__(self,rootObj): self.key = rootObj self.leftChild = None self.rightChild = None def insertLeft(self,newNode): if self.leftChild ==None: self.leftChild = BinaryTree(newNode) else: t = BinaryTree(newNode) t.leftChild = self.leftChild self.leftChild=t def insertRight(self,newNode): if self.rightChild == None: self.rightChild = BinaryTree(newNode) else: t = BinaryTree(newNode) t.leftChild = self.leftChild self.leftChild = t def getRightChild(self): return self.rightChild def getLeftChild(self): return self.leftChild def setRootVal(self,obj): self.key = obj def getRootVal(self): return self.key
在插入时我们必须考虑两种情况,第一种情况:当前没有现有左子节点,当没有左子节点时,简单的将新节点添加到树中即可
有左子节点时 我们插入节点时 需要把原有的左子节点进行降级
解析树
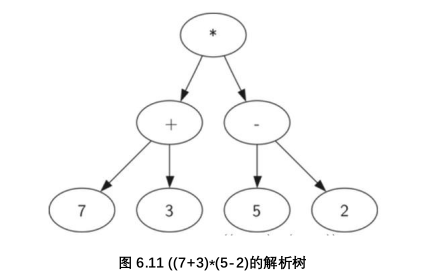
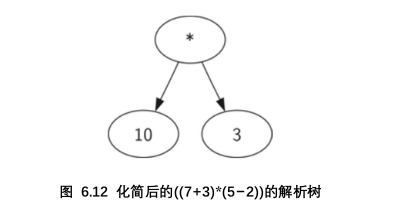
比如(7+3)*(5-2):如果当前读入字符是‘(’添加一个新的节点作为当前节点的子节点,当前节点下降
如果当前读入的字符在列表 ['+','-','/','*'] 中,将当前节点的根值设置为当前读入的字符。添加一个新的节点(node)作为当前节点的右子节点,当前节点下降。
如果当前读入的字符是一个数字,将当前节点的根值设置为该数字,当前节点变为它的父节点
如果当前读入的字符是 ')' ,当前节点变为其父节点(parent)。
写一个解析树
from pythonds.basic.stack import Stack from pythonds.trees.binaryTree import BinaryTree def buildParseTree(parse): fplist = parse.split() 根据空格分割 每个字符串 pstack = Stack() eTree = BinaryTree('') pstack.push(eTree) currentTree = eTree for i in fplist: if i == '(': currentTree.insertLeft('') pstack.push(currentTree) currentTree = currentTree.getLeftChild() elif i not in ['+','-','*','/',')']: currentTree.setRootVal(int(i)) parent = pstack.pop() currentTree = parent elif i in ['+','-','*','/']: currentTree.setRootVal(i) currentTree.insertRight('') pstack.push(currentTree) currentTree = currentTree.getRightChild() elif i == ')': currentTree = pstack.pop() else: raise ValueError return eTree pt = buildParseTree("( ( 1 + 2 ) * 3 )") pt.postorder()
使用堆栈保持对父节点的跟踪,当我们要下降到当前节点的子节点时,我们先将当前节点压入栈中,而当我们想要返回当前节点的父节点时,我们就从堆栈中弹出该父节点
在解析树中,叶节点总是操作数 我们只需检查一个操作符是否是叶节点,递归调用使我们有效的向叶节点移动
import operator
def evaluate(parseTree): opers = {'+':operator.add,'-':operator.sub,'*':operator.mul,'/':operator.truediv} leftc = parseTree.getLeftChild() rightc = parseTree.getRightChild() if leftc and rightc: fn = opers[parseTree.getRootVal()] return fn(evaluate(leftc),evaluate(rightc)) else: return parseTree.getRootVal() print(evaluate(pt))
树的遍历
- 前序遍历 :在前序遍历中,我们先访问根节点,然后递归地前序遍历访问左子树,再递归地前序遍历访问右子树
- 中序遍历:先访问左子树 再根节点 最后右子树
- 后序遍历:先访问左子树和右子树 ,最后访问根节点
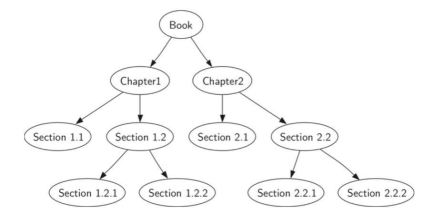
从头到尾阅读这本书 前序遍历正好符合这种规则
前序遍历
def preordder(tree): if tree: print(tree.getRootVal()) preordder(tree.getLeftChild()) preordder(tree.getRightChild()) 后序遍历 def postorder(tree): if tree: postorder(tree.getLeftChild()) postorder(tree.getRightChild()) print(tree.getRootVal()) 中序遍历 def inorder(tree): if tree: inorder(tree.getLeftChild()) print(tree.getRootVal()) inorder(tree.getRightChild())
用遍历来计算解析树
def evaluate(parseTree): opers = {'+': operator.add, '-': operator.sub, '*': operator.mul, '/': operator.truediv} if parseTree: leftc = postorder(parseTree.getLeftChild()) rightc = postorder(parseTree.getRightChild()) if leftc and rightc: return opers[parseTree.getRootVal()](leftc,rightc) else: return parseTree.getRootVal()