1、什么是JMS
JMS即Java消息服务(Java Message Service)应用程序接口,是一个Java平台中关于面向消息中间件(MOM)的API,用于在两个应用程序之间,或分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。Java消息服务是一个与具体平台无关的API,绝大多数MOM提供商都对JMS提供支持(百度百科给出的概述)。我们可以简单的理解:两个应用程序之间需要进行通信,我们使用一个JMS服务,进行中间的转发,通过JMS 的使用,我们可以解除两个程序之间的耦合。
2、JMS的优势
-
Asynchronous(异步)
JMS is asynchronous by default. So to receive a message, the client is not required to send the request. The message will arrive automatically to the client as they become available.(JMS 原本就是一个异步的消息服务,客户端获取消息的时候,不需要主动发送请求,消息会自动发送给可用的客户端)
-
Reliable(可靠)
JMS provides the facility of assurance that the message will delivered once and only once. You know that duplicate messages create problems. JMS helps you avoiding such problems.(JMS保证消息只会递送一次。大家都遇到过重复创建消息问题,而JMS能帮你避免该问题。)
3、JMS的消息模型
JMS具有两种通信模式:
1、Point-to-Point Messaging Domain (点对点)
2、Publish/Subscribe Messaging Domain (发布/订阅模式)
在JMS API出现之前,大部分产品使用“点对点”和“发布/订阅”中的任一方式来进行消息通讯。JMS定义了这两种消息发送模型的规范,它们相互独立。任何JMS的提供者可以实现其中的一种或两种模型,这是它们自己的选择。JMS规范提供了通用接口保证我们基于JMS API编写的程序适用于任何一种模型。
(1)、Point-to-Point Messaging Domain(点对点通信模型)
a、模式图:
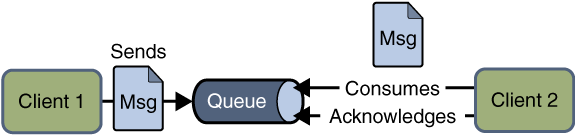
b、涉及到的概念:
在点对点通信模式中,应用程序由消息队列,发送方,接收方组成。每个消息都被发送到一个特定的队列,接收者从队列中获取消息。队列保留着消息,直到他们被消费或超时。
c、特点:
-
-
- 每个消息只要一个消费者
- 发送者和接收者在时间上是没有时间的约束,也就是说发送者在发送完消息之后,不管接收者有没有接受消息,都不会影响发送方发送消息到消息队列中。
- 发送方不管是否在发送消息,接收方都可以从消息队列中去到消息(The receiver can fetch message whether it is running or not when the sender sends the message)
- 接收方在接收完消息之后,需要向消息队列应答成功
-
(2)、Publish/Subscribe Messaging Domain(发布/订阅通信模型)
a、模式图:
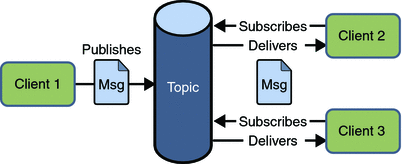
b、涉及到的概念:
在发布/订阅消息模型中,发布者发布一个消息,该消息通过topic传递给所有的客户端。该模式下,发布者与订阅者都是匿名的,即发布者与订阅者都不知道对方是谁。并且可以动态的发布与订阅Topic。Topic主要用于保存和传递消息,且会一直保存消息直到消息被传递给客户端。
c、特点:
-
-
- 一个消息可以传递个多个订阅者(即:一个消息可以有多个接受方)
- 发布者与订阅者具有时间约束,针对某个主题(Topic)的订阅者,它必须创建一个订阅者之后,才能消费发布者的消息,而且为了消费消息,订阅者必须保持运行的状态。
- 为了缓和这样严格的时间相关性,JMS允许订阅者创建一个可持久化的订阅。这样,即使订阅者没有被激活(运行),它也能接收到发布者的消息。
-
4、JMS接收消息
在JMS中,消息的产生和消息是异步的。对于消费来说,JMS的消息者可以通过两种方式来消费消息。
(1)、同步(Synchronous)
在同步消费信息模式模式中,订阅者/接收方通过调用 receive()方法来接收消息。在receive()方法中,线程会阻塞直到消息到达或者到指定时间后消息仍未到达。
(2)、异步(Asynchronous)
使用异步方式接收消息的话,消息订阅者需注册一个消息监听者,类似于事件监听器,只要消息到达,JMS服务提供者会通过调用监听器的onMessage()递送消息。
5、JMS编程模型
- 管理对象(Administered objects)-连接工厂(Connection Factories)和目的地(Destination)
- 连接对象(Connections)
- 会话(Sessions)
- 消息生产者(Message Producers)
- 消息消费者(Message Consumers)
- 消息监听者(Message Listeners)
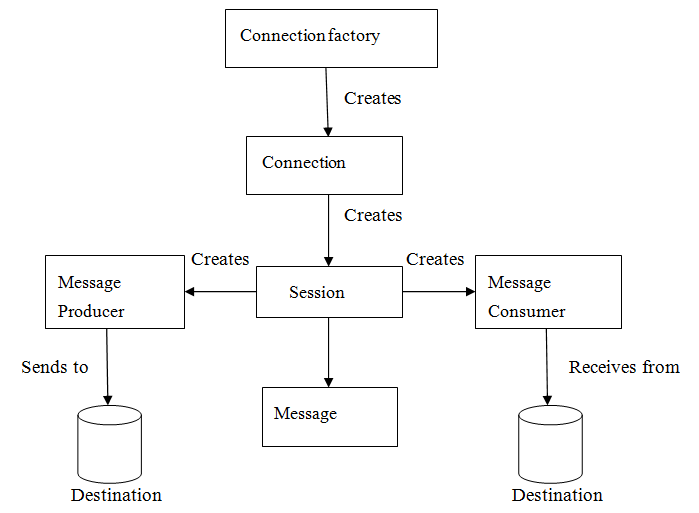
(1)、Connection Factories
创建Connection对象的工厂,针对两种不同的jms消息模型,分别有QueueConnectionFactory和TopicConnectionFactory两种。可以通过JNDI来查找ConnectionFactory对象。客户端使用一个连接工厂对象连接到JMS服务提供者,它创建了JMS服务提供者和客户端之间的连接。JMS客户端(如发送者或接受者)会在JNDI名字空间中搜索并获取该连接。使用该连接,客户端能够与目的地通讯,往队列或话题发送/接收消息。
QueueConnectionFactory queueConnFactory = (QueueConnectionFactory) initialCtx.lookup ("primaryQCF");
Queue purchaseQueue = (Queue) initialCtx.lookup ("Purchase_Queue");
Queue returnQueue = (Queue) initialCtx.lookup ("Return_Queue");
(2)、Destination
目的地指明消息被发送的目的地以及客户端接收消息的来源。JMS使用两种目的地,队列和话题。如下代码指定了一个队列和话题:
创建一个队列Session:
QueueSession ses = con.createQueueSession (false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //get the Queue object
Queue t = (Queue) ctx.lookup ("myQueue"); //create QueueReceiver
QueueReceiver receiver = ses.createReceiver(t);
创建一个Topic Session:
QueueSession ses = con.createQueueSession (false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); //get the Queue object
Queue t = (Queue) ctx.lookup ("myQueue"); //create QueueReceiver
QueueReceiver receiver = ses.createReceiver(t);
(3)、Connection
Connection表示在客户端和JMS系统之间建立的链接(对TCP/IP socket的包装)。Connection可以产生一个或多个Session。跟ConnectionFactory一样,Connection也有两种类型:QueueConnection和TopicConnection。
连接对象封装了与JMS提供者之间的虚拟连接,如果我们有一个ConnectionFactory对象,可以使用它来创建一个连接。
Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection();
(4)、Session
Session 是我们对消息进行操作的接口,可以通过session创建生产者、消费者、消息等。Session 提供了事务的功能,如果需要使用session发送/接收多个消息时,可以将这些发送/接收动作放到一个事务中。
我们可以在连接创建完成之后创建session:
Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
这里面提供了参数两个参数,第一个参数是是否支持事务,第二个是事务的类型
(5)、Producter
消息生产者由Session创建,用于往目的地发送消息。生产者实现MessageProducer接口,我们可以为目的地、队列或话题创建生产者;
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(dest); MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(queue); MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(topic);
(6)、Consumer
消息消费者由Session创建,用于接收被发送到Destination的消息。
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(dest); MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(queue); MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(topic);
(7)、MessageListener
消息监听器。如果注册了消息监听器,一旦消息到达,将自动调用监听器的onMessage方法。EJB中的MDB(Message-Driven Bean)就是一种MessageListener。
package com.sun.demo; import java.util.Date; import javax.jms.Connection; import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory; import javax.jms.DeliveryMode; import javax.jms.Destination; import javax.jms.JMSException; import javax.jms.MessageProducer; import javax.jms.Session; import javax.jms.TextMessage; import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnection; import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory; /** * @author sun 点对点模型 */ public class Sender { public static final int SEND_NUMBER = 5; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;// 连接工厂,JMS 用它创建连接 Connection connection = null;// JMS 客户端到JMS Provider 的连接 Session session = null;// 一个发送或接收消息的会话 Destination destination = null;// 消息的目的地;消息发送给谁 MessageProducer messageProducer = null;// 消息发送者 // 构造ConnectionFactory实例对象 connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_USER, // 默认为空 ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_PASSWORD, // 默认为空 "tcp://127.0.0.1:61616"); try { // 构造从工厂得到连接对象 connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); // 启动 connection.start(); // 获取操作连接 session = connection.createSession(Boolean.TRUE, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); // 获取session注意参数值zhan.huijing.Queue是一个服务器的queue,须在ActiveMq的console配置 destination = session.createQueue("zhan.huijing.Queue"); // 得到消息生成者【发送者】 messageProducer = session.createProducer(destination); // 设置不持久化,此处学习,实际根据项目决定 messageProducer.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.NON_PERSISTENT); // 构造消息,此处写死,项目就是参数,或者方法获取 sendMessage(session, messageProducer); session.commit(); } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (null != connection) try { connection.close(); } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @param session * @param messageProducer * @throws JMSException */ private static void sendMessage(Session session, MessageProducer messageProducer) throws JMSException { for (int i = 1; i <= SEND_NUMBER; i++) { TextMessage message = session.createTextMessage(new Date() + " 学习ActiveMq"); String msg = message.getText(); // 发送消息到目的地方 System.out.println("发送消息:" + i + ":" + msg); messageProducer.send(message); } } }
package com.sun.demo; import javax.jms.Connection; import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory; import javax.jms.Destination; import javax.jms.JMSException; import javax.jms.Message; import javax.jms.MessageConsumer; import javax.jms.MessageListener; import javax.jms.Session; import javax.jms.TextMessage; import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnection; import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory; /** * @author sun * */ public class ReceiverListener { public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;// 连接工厂,JMS 用它创建连接 Connection connection = null;// JMS 客户端到JMS Provider 的连接 Session session = null;// 一个发送或接收消息的会话 Destination destination = null;// 消息的目的地;消息发送给谁 MessageConsumer consumer;// 消费者,消息接收者 // 构造ConnectionFactory实例对象 connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_USER, // 默认为空 ActiveMQConnection.DEFAULT_PASSWORD, // 默认为空 "tcp://127.0.0.1:61616"); boolean flag = false;// 标记 try { // 构造从工厂得到连接对象 connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); // 启动 connection.start(); // 获取操作连接 session = connection.createSession(Boolean.FALSE, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); // 获取session注意参数值zhan.huijing.Queue是一个服务器的queue,须在在ActiveMq的console配置 destination = session.createQueue("zhan.huijing.Queue"); // 从消息队列destination中抓取消息 consumer = session.createConsumer(destination); //监听器监听 consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() { public void onMessage(Message message) { TextMessage tm = (TextMessage) message; try { System.out.println("收到消息:" + tm.getText()); } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); while (!flag) { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (null != connection) try { connection.close(); } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
JMS Topic模型代码实现:
将上述代码中出现的queueDestination改为topicDestination即可。
5、ActiveMQ的特性
5.1 ActiveMq 的特性
- 多种语言和协议编写客户端。语言: Java, C, C++, C#, Ruby, Perl, Python, PHP。应用协议: OpenWire,Stomp REST,WS Notification,XMPP,AMQP
- 完全支持JMS1.1和J2EE 1.4规范 (持久化,XA消息,事务)
- 对Spring的支持,ActiveMQ可以很容易内嵌到使用Spring的系统里面去,而且也支持Spring2.0的特性
- 通过了常见J2EE服务器(如 Geronimo,JBoss 4, GlassFish,WebLogic)的测试,其中通过JCA 1.5 resource adaptors的配置,可以让ActiveMQ可以自动的部署到任何兼容J2EE 1.4 商业服务器上
- 支持多种传送协议:in-VM,TCP,SSL,NIO,UDP,JGroups,JXTA
- 支持通过JDBC和journal提供高速的消息持久化
- 从设计上保证了高性能的集群,客户端-服务器,点对点
- 支持Ajax
- 支持与Axis的整合
- 可以很容易得调用内嵌JMS provider,进行测试
5.2 什么情况下使用ActiveMQ?
- 多个项目之间集成
(1) 跨平台
(2) 多语言
(3) 多项目 - 降低系统间模块的耦合度,解耦
(1) 软件扩展性 - 系统前后端隔离
(1) 前后端隔离,屏蔽高安全区