call_onced
简介 - 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xijiacun/article/details/71023777
#include <mutex> template <class Fn, class... Args> void call_once(once_flag &flag, Fn &&fn, Args &&... args);
第一个参数是std::once_flag的对象(once_flag是不允许修改的,其拷贝构造函数和operator=函数都声明为delete),第二个参数可调用实体,即要求只执行一次的代码,后面可变参数是其参数列表。
call_once保证函数fn只被执行一次,如果有多个线程同时执行函数fn调用,则只有一个活动线程(active call)会执行函数,其他的线程在这个线程执行返回之前会处于”passive execution”(被动执行状态)——不会直接返回,直到活动线程对fn调用结束才返回。对于所有调用函数fn的并发线程,数据可见性都是同步的(一致的)。
如果活动线程在执行fn时抛出异常,则会从处于”passive execution”状态的线程中挑一个线程成为活动线程继续执行fn,依此类推。一旦活动线程返回,所有”passive execution”状态的线程也返回,不会成为活动线程。(实际上once_flag相当于一个锁,使用它的线程都会在上面等待,只有一个线程允许执行。如果该线程抛出异常,那么从等待中的线程中选择一个,重复上面的流程)
注意: once_flag的生命周期,它必须要比使用它的线程的生命周期要长。所以通常定义为全局变量。
1. 示例
1 #include <thread> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <mutex> 4 #include <vector> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 once_flag gOnceFlag; 9 10 void initializeSharedResources() { 11 cout << "Shared resources initialized." << endl; 12 } 13 14 void processingFunction() { 15 call_once(gOnceFlag, initializeSharedResources); 16 cout << "Processing" << endl; 17 } 18 19 int main() { 20 vector<thread> threads(3); 21 for (auto &t : threads) { 22 t = thread{processingFunction}; 23 } 24 25 for (auto &t : threads) { 26 t.join(); 27 } 28 29 return 0; 30 }
std::future 介绍
1. future图解
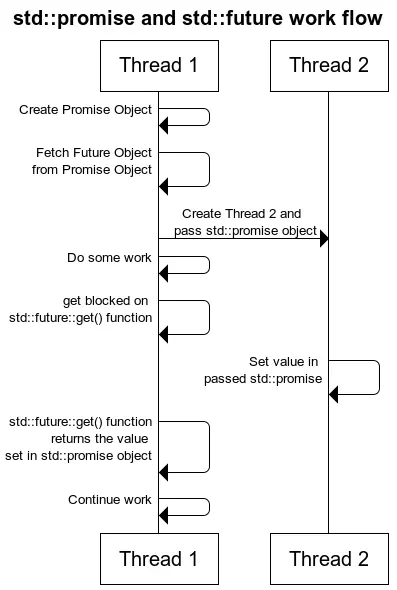
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <thread> 3 #include <future> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void DoWork(promise<int> thePromise) 8 { 9 thePromise.set_value(42); 10 } 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 promise<int> myPromise; 15 std::future<int> theFuture = myPromise.get_future(); 16 thread theThread{DoWork, std::move(myPromise)}; 17 int result = theFuture.get(); 18 19 cout << "Result: " << result << endl; 20 theThread.join(); 21 22 return 0; 23 }
std::packaged_task
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <thread> 3 #include <future> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int CalculateSum(int a, int b) 7 { 8 return a + b; 9 } 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 packaged_task<int(int, int)> task(CalculateSum); 14 std::future<int> theFuture = task.get_future(); 15 thread theThread{ std::move(task), 39, 3 }; 16 int result = theFuture.get(); 17 cout << result << endl; 18 theThread.join(); 19 return 0; 20 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <thread> 3 #include <future> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void DoWork(promise<int> thePromise) 8 { 9 thePromise.set_value(42); 10 } 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 promise<int> myPromise; 15 std::future<int> theFuture = myPromise.get_future(); 16 thread theThread{DoWork, std::move(myPromise)}; 17 int result = theFuture.get(); 18 19 cout << "Result: " << result << endl; 20 theThread.join(); 21 22 return 0; 23 }