重载new和delete
1. 测试代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<new> 3 using namespace std; 4 class A { 5 public: 6 A() { cout << "A constructor" << endl; } 7 8 void* operator new(size_t size) 9 { 10 cout << "this is A's new" << endl; 11 return ::operator new(size); 12 } 13 14 void operator delete(void* ptr) 15 { 16 cout << "this is A's delete" << endl; 17 return ::operator delete(ptr); 18 } 19 20 ~A() { cout << "A destructor" << endl; } 21 }; 22 23 int main() 24 { 25 A *a = new A; 26 delete a; 27 return 0; 28 }
运行结果:

虽然我们不能改变new/delete的行为,但是通过重载operator new() 和 operator delete()我们可以实现自己想要的内存管理方式,这在内存池的实现中十分关键。关于operator new有几点要注意:
(1)当无法满足所要求分配的空间时,则如果有new_handler,则调用new_handler,否则如果没要求不抛出异常(以nothrow参数表达),则执行bad_alloc异常,否则返回0
(2)重载时,返回类型必须声明为void*
(3)重载时,第一个参数类型必须为表达要求分配空间的大小(字节),类型为size_t
(4)重载时,可以带除(3)以外的其它参数
2.测试代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <new> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void* operator new(size_t size) 7 { 8 cout << "global Override operator new: " << size << endl; 9 void * ptr = malloc(size); 10 return ptr; 11 } 12 13 void* operator new(size_t size, int flag) 14 { 15 cout << "global Override operator new: " << size << " " << flag << endl; 16 return (::operator new(size)); 17 } 18 19 void operator delete (void* ptr) 20 { 21 cout << "global Override operator delete" << endl; 22 free(ptr); 23 ptr = nullptr; 24 } 25 26 void operator delete (void* ptr, int flag) 27 { 28 cout << "Override operator delete: " << flag << endl; 29 ::operator delete(ptr); 30 ptr = nullptr; 31 } 32 int main() { 33 int * ptr = new int(10); 34 delete ptr; 35 cout << endl << "*********************" << endl << endl; 36 ptr = new(20) int(10); 37 delete ptr; 38 return 0; 39 }
输出结果:

定位new表达式
1. 测试代码:

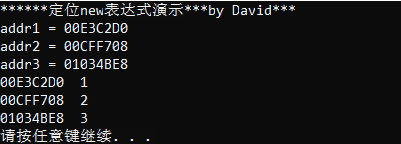
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 char addr1[100]; 4 int main() 5 { 6 cout << "******定位new表达式演示***by David***" << endl; 7 char addr2[100]; 8 char *addr3 = new char[100]; 9 cout << "addr1 = " << (void*)addr1 << endl; 10 cout << "addr2 = " << (void*)addr2 << endl; 11 cout << "addr3 = " << (void*)addr3 << endl; 12 int *p = nullptr; 13 14 p = new(addr1)int; ////把内存分配到静态区 15 *p = 1; 16 cout << (void*)p << " " << *p << endl; 17 18 p = new(addr2)int; ////把内存分配到栈区 19 *p = 2; 20 cout << (void*)p << " " << *p << endl; 21 22 p = new(addr3)int; //把内存分配到堆区 23 *p = 3; 24 cout << (void*)p << " " << *p << endl; 25 return 0; 26 }
运行结果:
2.测试代码
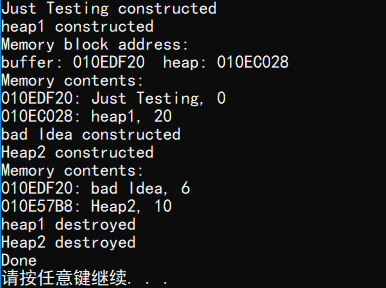
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <new> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 const int BUF = 512; 7 8 class JustTesting { 9 private: 10 string words; 11 int number; 12 public: 13 JustTesting(const string &s = "Just Testing", int n = 0) 14 { 15 words = s; 16 number = n; 17 cout << words << " constructed "; 18 } 19 20 ~JustTesting() { cout << words << " destroyed "; } 21 void Show() const { cout << words << ", " << number << endl; } 22 }; 23 24 int main(void) 25 { 26 char *buffer = new char[BUF]; // get a block of memory 27 JustTesting *pc1, *pc2; 28 29 pc1 = new (buffer)JustTesting; // place object in buffer 30 pc2 = new JustTesting("heap1", 20); // place object on heap 31 32 cout << "Memory block address: " << "buffer: " 33 << (void *)buffer << " heap: " << pc2 << endl; 34 cout << "Memory contents: "; 35 cout << pc1 << ": "; 36 pc1->Show(); 37 cout << pc2 << ": "; 38 pc2->Show(); 39 40 JustTesting *pc3, *pc4; 41 pc3 = new (buffer) JustTesting("bad Idea", 6); 42 pc4 = new JustTesting("Heap2", 10); 43 44 cout << "Memory contents: "; 45 cout << pc3 << ": "; 46 pc3->Show(); 47 cout << pc4 << ": "; 48 pc4->Show(); 49 50 delete pc2; // free heap1 51 delete pc4; // free heap2 52 delete[] buffer; // free buffer 53 cout << "Done "; 54 55 return 0; 56 }
运行结果: