运行类型识别
一、使用RTTI
dynamic_cast运算符的调用形式如下所示:
dynamic_cast<type*>(e) //e是指针 dynamic_cast<type&>(e) //e是左值 dynamic_cast<type&&>(e) //e是右值
e能成功转换为type*类型的情况有三种:
1)e的类型是目标type的公有派生类:派生类向基类转换一定会成功。
2)e的类型是目标type的基类,当e是指针指向派生类对象,或者基类引用引用派生类对象时,类型转换才会成功,当e指向基类对象,试图转换为派生类对象时,转换失败。
3)e的类型就是type的类型时,一定会转换成功。
1. 测试代码:

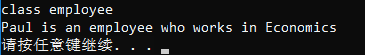
1 class Rect : public Shape { 2 public: 3 void fun() {}; 4 void prin() { cout << "我是方形" << endl; } 5 }; 6 7 class Circle : public Shape { 8 public: 9 void fun() {}; 10 void prin() { cout << "我是圆形" << endl; } 11 }; 12 13 void fun(Shape *p) 14 { 15 if (typeid(*p) == typeid(Rect)) 16 { 17 Rect *r = dynamic_cast<Rect *>(p); 18 r->prin(); 19 } 20 if (typeid(*p) == typeid(Circle)) 21 { 22 Circle *c = dynamic_cast<Circle *>(p); 23 c->prin(); 24 } 25 } 26 int main() 27 { 28 Rect r; 29 cout << "第一次执行fun函数:"; 30 fun(&r); 31 32 Circle c; 33 cout << "第二次执行fun函数:"; 34 fun(&c); 35 36 return 0; 37 }
输出结果:
二、type_info类
1. 测试代码:

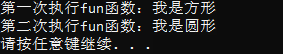
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <typeinfo.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Base { 6 public: 7 virtual void vvfunc() {} 8 }; 9 10 class Derived : public Base {}; 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 Derived* pd = new Derived; 15 Base* pb = pd; 16 cout << typeid(pb).name() << endl; //prints "class Base *" 17 cout << typeid(*pb).name() << endl; //prints "class Derived" 18 cout << typeid(pd).name() << endl; //prints "class Derived *" 19 cout << typeid(*pd).name() << endl; //prints "class Derived" 20 delete pd; 21 }
输出结果:
2. 代码示例
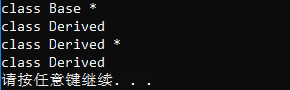
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <typeinfo> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 if (typeid(int).before(typeid(char))) 7 std::cout << "int goes before char in this implementation. "; 8 else 9 std::cout << "char goes before int in this implementation. "; 10 }
运行结果:
3. 代码示例

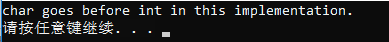
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <typeinfo> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <utility> 5 6 class person 7 { 8 public: 9 10 person(std::string&& n) : _name(n) {} 11 virtual const std::string& name() const { return _name; } 12 13 private: 14 15 std::string _name; 16 }; 17 18 class employee : public person 19 { 20 public: 21 22 employee(std::string&& n, std::string&& p) : 23 person(std::move(n)), _profession(std::move(p)) {} 24 25 const std::string& profession() const { return _profession; } 26 27 private: 28 std::string _profession; 29 }; 30 31 void somefunc(const person& p) 32 { 33 if (typeid(employee) == typeid(p)) 34 { 35 std::cout << typeid(p).name() << std::endl; 36 std::cout << p.name() << " is an employee "; 37 auto& emp = dynamic_cast<const employee&>(p); 38 std::cout << "who works in " << emp.profession() << ' '; 39 } 40 } 41 42 int main() 43 { 44 employee paul("Paul", "Economics"); 45 somefunc(paul); 46 }
运行结果: