函数fork
博文链接:
1. 代码示例:

1 #include "apue.h" 2 int glob = 6; 3 char buf[] = "a write to stdout "; 4 int main(void) 5 { 6 int var; 7 int pid; 8 var = 88; 9 if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1) != sizeof(buf) - 1) 10 { 11 err_sys("write error! "); 12 } 13 printf("before fork! "); 14 if ((pid = fork())<0) 15 { 16 err_sys("fork error! "); 17 } 18 else if (pid == 0) // this is child process for pid == 0 19 { 20 glob++; 21 var++; 22 } 23 else //this is parent process 24 { 25 sleep(2); //wait for child finishing 26 } 27 printf("pid= %d,glob= %d,var= %d ", getpid(), glob, var); 28 exit(0); 29 }
输出结果:

函数vfork
1. 代码示例

1 #include "apue.h" 2 int glob = 6; 3 char buf[] = "a write to stdout "; 4 int main(void) 5 { 6 int var; 7 int pid; 8 var = 88; 9 if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, sizeof(buf)-1)!= sizeof(buf)-1) 10 { 11 err_sys("write error! "); 12 } 13 printf("before fork! "); 14 if((pid = vfork())<0) 15 { 16 err_sys("fork error! "); 17 } 18 else if(pid == 0) // this is child process for pid == 0 19 { 20 glob++; 21 var++; 22 _exit(0); 23 } 24 25 printf("pid= %d,glob= %d,var= %d ",getpid(),glob,var); 26 exit(0); 27 }
输出结果:

函数wait和waitpid
博文链接:
函数原型: pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options);
pid:一共分为四种情况:
| pid 参数 | 解释 |
| < -1 | 等待组ID等于pid绝对值任一子进程 |
| == -1 | 为任意一个子进程收尸 |
| == 0 | 为与父进程同一个进程组中的任意一个子进程收尸 |
| > 0 | 为一个 PID 等于参数 pid 的子进程收尸 |
函数exec
进程程序替换
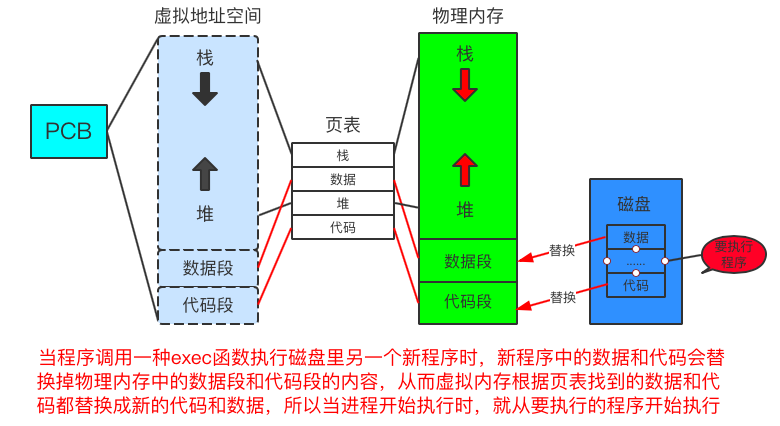
- 替换原理
fork创建子进程执行的是和父进程相同的程序(也有可能是某个分支),通常fork出的子进程是为了完成父进程所分配的任务,所以子进程通常会调用一种exec函数(六种中的任何一种)来执行另一个任务。当进程调用exec函数时,当前用户空间的代码和数据会被新程序所替换,该进程就会从新程序的启动历程开始执行。在这个过程中没有创建新进程,所以调用exec并没有改变进程的id。
- 替换图解
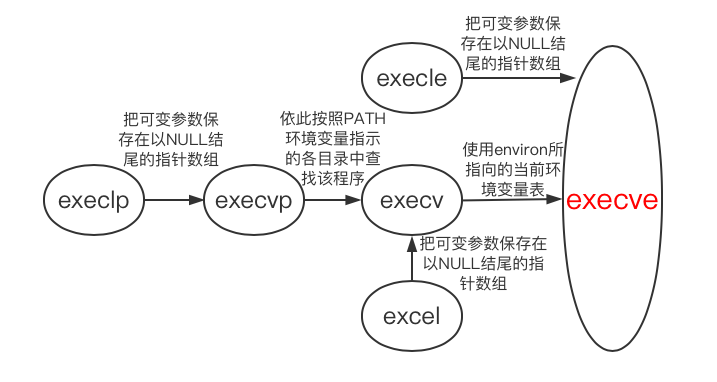
- 六个函数之间的关系
事实上,只有execve是系统调用,其他五个最终都调用execve。
#include "apue.h"
int glob = 6;
char buf[] = "a write to stdout
";
int main(void)
{
int var;
int pid;
var = 88;
if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, sizeof(buf)-1)!= sizeof(buf)-1)
{
err_sys("write error!
");
}
printf("before fork!
");
if((pid = vfork())<0)
{
err_sys("fork error!
");
}
else if(pid == 0) // this is child process for pid == 0
{
glob++;
var++;
_exit(0);
}
printf("pid= %d,glob= %d,var= %d
",getpid(),glob,var);
exit(0);
}
#include "apue.h"
int glob = 6;
char buf[] = "a write to stdout
";
int main(void)
{
int var;
int pid;
var = 88;
if(write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, sizeof(buf)-1)!= sizeof(buf)-1)
{
err_sys("write error!
");
}
printf("before fork!
");
if((pid = vfork())<0)
{
err_sys("fork error!
");
}
else if(pid == 0) // this is child process for pid == 0
{
glob++;
var++;
_exit(0);
}
printf("pid= %d,glob= %d,var= %d
",getpid(),glob,var);
exit(0);
}
