@
排序概述
- 排序是MapReduce框架中最重要的操作之一。
- Map Task和ReduceTask均会默认对数据按照key进行排序。该操作属于Hadoop的默认行为。任何应用程序中的数据均会被排序,而不管逻辑上是否需要。
- 黑默认排序是按照字典顺序排序,且实现该排序的方法是快速排序。
- 对于
MapTask,它会将处理的结果暂时放到一个缓冲区中,当缓冲区使用率达到一定阈值后,再对缓冲区中的数据进行一次排序,并将这些有序数据写到磁盘上,而当数据处理完毕后,它会对磁盘上所有文件进行一次合并,以将这些文件合并成一个大的有序文件。 - 对于
ReduceTask,它从每个MapTak上远程拷贝相应的数据文件,如果文件大小超过一定阑值,则放到磁盘上,否则放到内存中。如果磁盘上文件数目达到一定阈值,则进行一次合并以生成一个更大文件;如果内存中文件大小或者数目超过一定阈值,则进行一次合并后将数据写到磁盘上。当所有数据拷贝完毕后,ReduceTask统一对内存和磁盘上的所有数据进行一次归并排序。 - 排序器:排序器影响的是排序的速度(效率,对什么排序?),QuickSorter
- 比较器:比较器影响的是排序的结果(按照什么规则排序)
获取Mapper输出的key的比较器(源码)
public RawComparator getOutputKeyComparator() {
// 从配置中获取mapreduce.job.output.key.comparator.class的值,必须是RawComparator类型,如果没有配置,默认为null
Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR, null, RawComparator.class);
// 一旦用户配置了此参数,实例化一个用户自定义的比较器实例
if (theClass != null){
return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
}
//用户没有配置,判断Mapper输出的key的类型是否是WritableComparable的子类,如果不是,就抛异常,如果是,系统会自动为我们提供一个key的比较器
return WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), this);
}
案例实操(区内排序)
需求
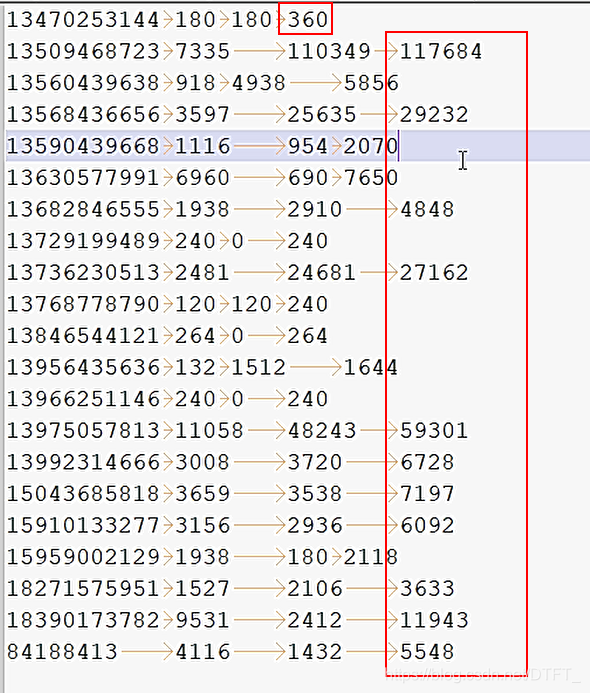
对每个手机号按照上行流量和下行流量的总和进行内部排序。
思考
因为Map Task和ReduceTask均会默认对数据按照key进行排序,所以需要把流量总和设置为Key,手机号等其他内容设置为value
FlowBeanMapper.java
public class FlowBeanMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, Text>{
private LongWritable out_key=new LongWritable();
private Text out_value=new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
//封装总流量为key
out_key.set(Long.parseLong(words[3]));//切分后,流量和的下标为3
//封装其他内容为value
out_value.set(words[0]+" "+words[1]+" "+words[2]);
context.write(out_key, out_value);
}
}
FlowBeanReducer.java
public class FlowBeanReducer extends Reducer<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>{
@Override
protected void reduce(LongWritable key, Iterable<Text> values,
Reducer<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(value, key);
}
}
}
FlowBeanDriver.java
public class FlowBeanDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Path inputPath=new Path("E:\mroutput\flowbean");
Path outputPath=new Path("e:/mroutput/flowbeanSort1");
//作为整个Job的配置
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//保证输出目录不存在
FileSystem fs=FileSystem.get(conf);
if (fs.exists(outputPath)) {
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
}
// ①创建Job
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// ②设置Job
// 设置Job运行的Mapper,Reducer类型,Mapper,Reducer输出的key-value类型
job.setMapperClass(FlowBeanMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowBeanReducer.class);
// Job需要根据Mapper和Reducer输出的Key-value类型准备序列化器,通过序列化器对输出的key-value进行序列化和反序列化
// 如果Mapper和Reducer输出的Key-value类型一致,直接设置Job最终的输出类型
//由于Mapper和Reducer输出的Key-value类型不一致(maper输出类型是long-text,而reducer是text-value)
//所以需要额外设定
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
// 设置输入目录和输出目录
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 默认升序排,可以设置使用自定义的比较器
//job.setSortComparatorClass(DecreasingComparator.class);
// ③运行Job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
运行结果(默认升序排)
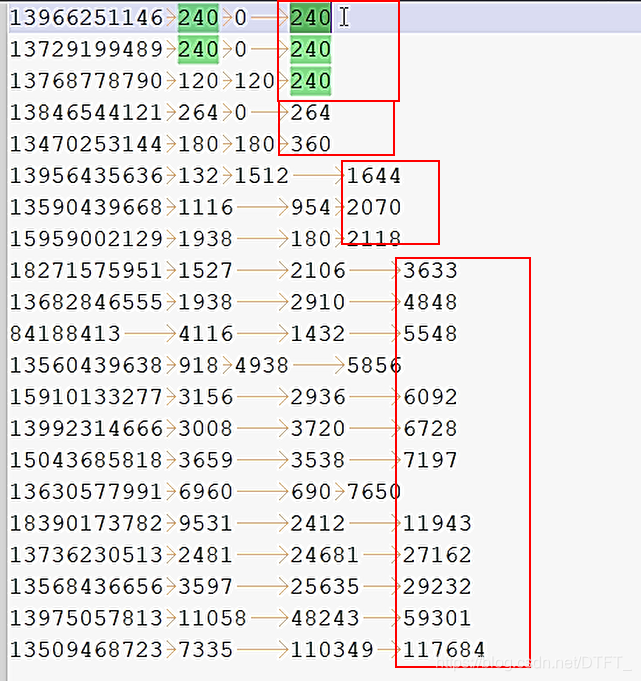
自定义排序器,使用降序
-
方法一:自定义类,这个类必须是
RawComparator类型,通过设置mapreduce.job.output.key.comparator.class自定义的类的类型。
自定义类时,可以继承WriableComparator类,也可以实现RawCompartor
调用方法时,先调用RawCompartor. compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2),再调用RawCompartor.compare() -
方法二:定义Mapper输出的key,让key实现
WritableComparable,实现CompareTo()
MyDescComparator.java
public class MyDescComparator extends WritableComparator{
@Override
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1,byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
long thisValue = readLong(b1, s1);
long thatValue = readLong(b2, s2);
//这里把第一个-1改成1,把第二个1改成-1,就是降序排
return (thisValue<thatValue ? 1 : (thisValue==thatValue ? 0 : -1));
}
}
运行结果
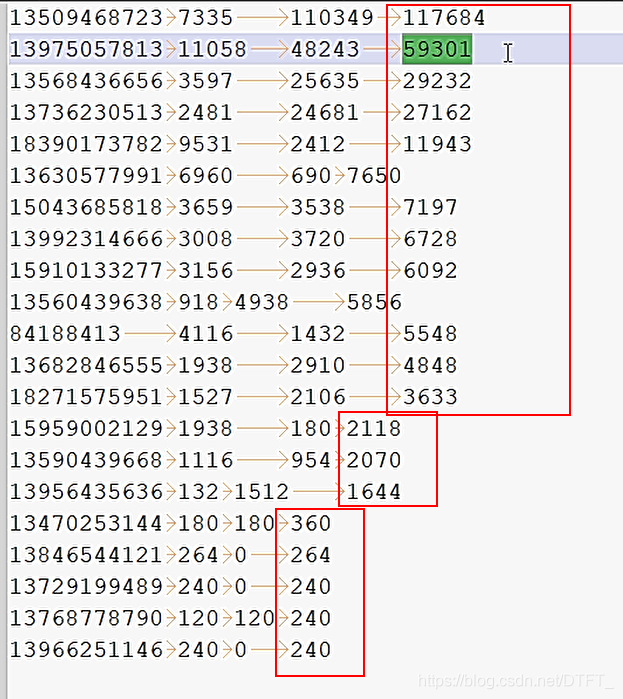
Key实现Comparable进行比较
思路二:把map输出时的key封装为一个bean,这个key包含上行流量、下行流量、总流量,value只有手机号
FlowBean.java
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean>{
private long upFlow;
private long downFlow;
private Long sumFlow;
public FlowBean() {
}
public long getUpFlow() {
return upFlow;
}
public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) {
this.upFlow = upFlow;
}
public long getDownFlow() {
return downFlow;
}
public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
}
public long getSumFlow() {
return sumFlow;
}
public void setSumFlow(long sumFlow) {
this.sumFlow = sumFlow;
}
// 序列化 在写出属性时,如果为引用数据类型,属性不能为null
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(upFlow);
out.writeLong(downFlow);
out.writeLong(sumFlow);
}
//反序列化 序列化和反序列化的顺序要一致
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
upFlow=in.readLong();
downFlow=in.readLong();
sumFlow=in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return upFlow + " " + downFlow + " " + sumFlow;
}
// 系统封装的比较器在对比key时,调用key的compareTo进行比较
// 降序比较总流量
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean o) {
return -this.sumFlow.compareTo(o.getSumFlow());
}
}
FlowBeanMapper.java
public class FlowBeanMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, Text>{
private FlowBean out_key=new FlowBean();
private Text out_value=new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
//封装总流量为key
out_key.setUpFlow(Long.parseLong(words[1]));
out_key.setDownFlow(Long.parseLong(words[2]));
out_key.setSumFlow(Long.parseLong(words[3]));
out_value.set(words[0]);
context.write(out_key, out_value);
}
}
FlowBeanReducer.java
public class FlowBeanReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean>{
@Override
protected void reduce(FlowBean key, Iterable<Text> values,
Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(value, key);
}
}
}
FlowBeanDriver.java
public class FlowBeanDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Path inputPath=new Path("E:\mroutput\flowbean");
Path outputPath=new Path("e:/mroutput/flowbeanSort2");
//作为整个Job的配置
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//保证输出目录不存在
FileSystem fs=FileSystem.get(conf);
if (fs.exists(outputPath)) {
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
}
// ①创建Job
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// ②设置Job
// 设置Job运行的Mapper,Reducer类型,Mapper,Reducer输出的key-value类型
job.setMapperClass(FlowBeanMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowBeanReducer.class);
// Job需要根据Mapper和Reducer输出的Key-value类型准备序列化器,通过序列化器对输出的key-value进行序列化和反序列化
// 如果Mapper和Reducer输出的Key-value类型一致,直接设置Job最终的输出类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
// 设置输入目录和输出目录
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// ③运行Job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
总结
- 如果用户自定义了比较器,MR就使用用户自定义的比较器(
RawComparator类型) - 如果用户没有自定义,那么Mapper输出的Key需要实现
WriableComparable接口,系统会自动提供比较器 - 不管是自己提供比较器还是实现WriableComparable接口,最后在比较时,都是调用
自己实现的CompareTo()方法