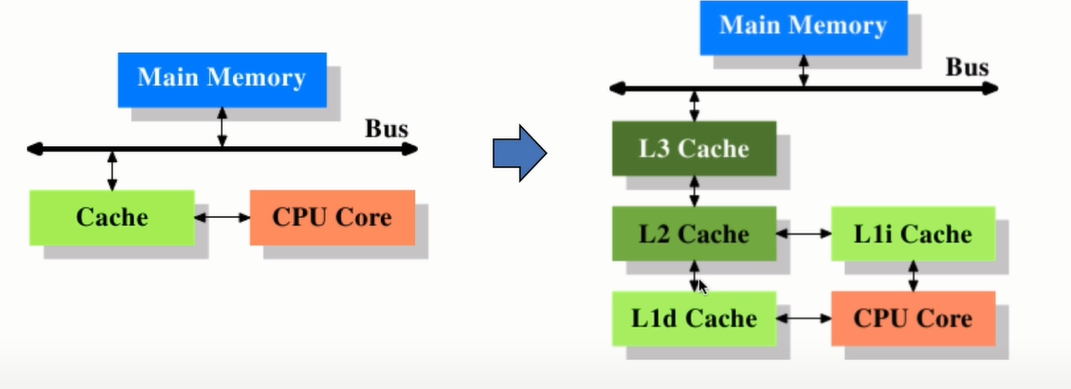
CPU多级缓存:






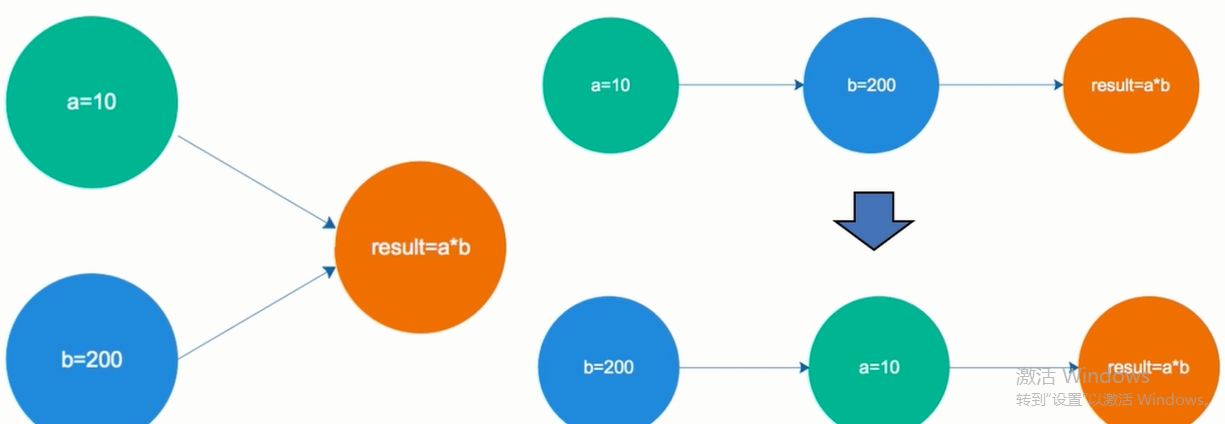
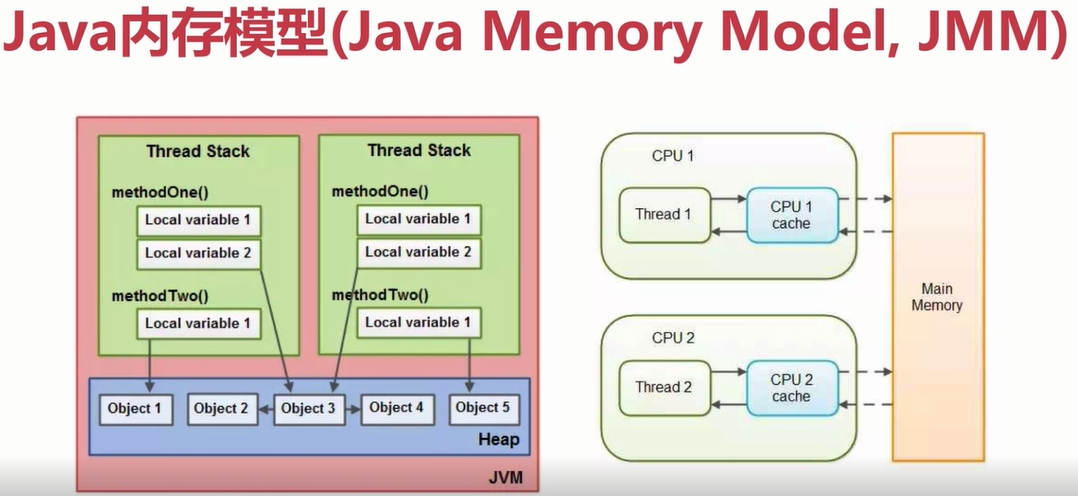

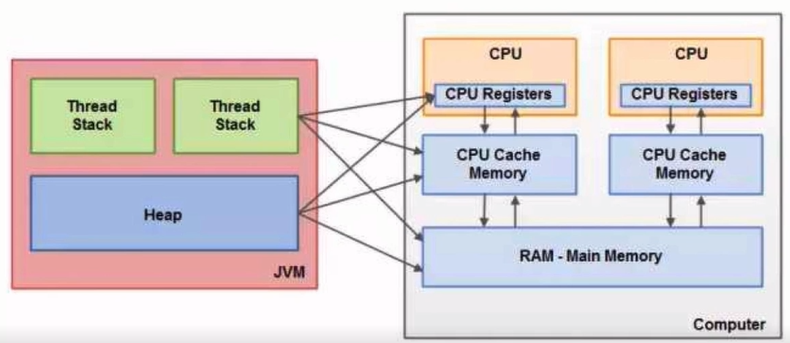
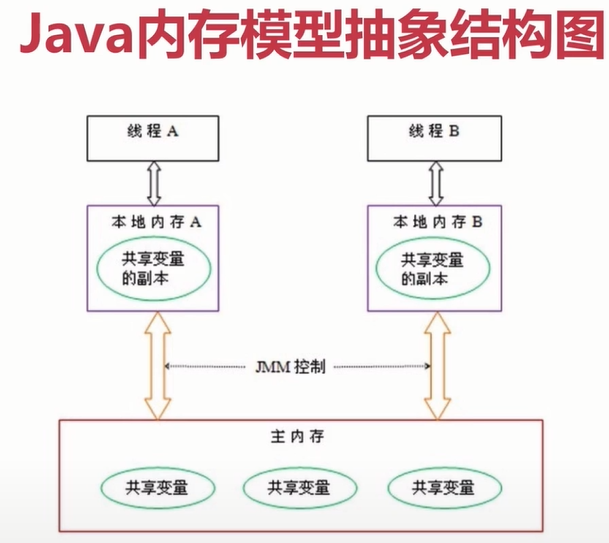



read(读取):作用于主内存的变量,把一个变量值从主内存传输到线程的工作内存中,以便随后的load动作使用
load(载入):作用于工作内存的变量,它把read操作从主内存中得到的变量值放到工作内存中的变量副本中

write(写入):作用于主内存的变量,他把store操作从工作内存中一个变量的值,传送到主内存的变量中

不允许一个线程丢弃它的最近assign的操作,即变量在工作内存中改变了之后必须同步到内存中


如果对一个变脸执行lock操作,将会清空工作内存中此变量的值,在执行引擎使用这个变量前需要重新执行load或assign操作初始变量的值。



可以阻塞线程,并保证线程在满足特定的条件下继续执行,线程执行完成之后,在进行其他的处理
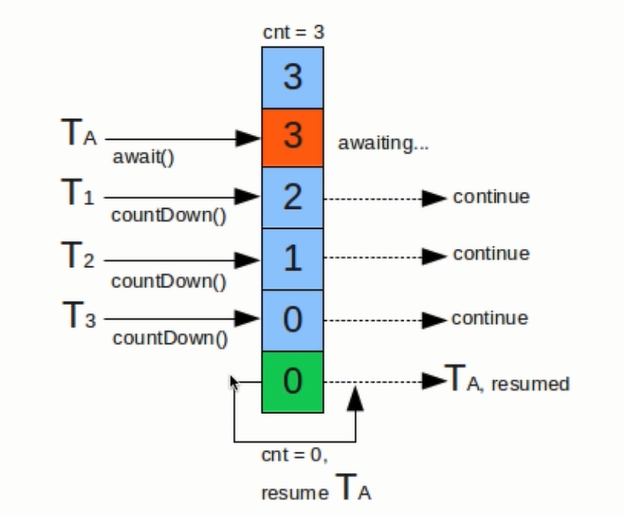
 阻塞进程,并同一时间控制请求的并发量,控制同时的并发数
阻塞进程,并同一时间控制请求的并发量,控制同时的并发数
添加几个注解:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
//用来标记【不推荐】的类或者写法
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface NotRecommend {
String value() default "";
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
//用来标记【线程安全】的类或者写法
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface NotThreadSafe {
String value() default "";
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
//用来标记【推荐】的类或者写法
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Recommend {
}
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
//用来标记【线程安全】的类或者写法
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface ThreadSafe {
String value() default "";
}
线程不安全:
import com.example.annoations.NotThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
@Slf4j
@NotThreadSafe
public class ConcurrencyTest {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal=5000;
//同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal=200;
public static int count=0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire(); //是否允许被执行
add();
semaphore.release(); //释放信号量
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("count:{}",count);
}
private static void add(){
count++;
}
}
线程安全性:






import com.example.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class CountExample2 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal=5000;
//同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal=200;
public static AtomicInteger count= new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire(); //是否允许被执行
add();
semaphore.release(); //释放信号量
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("count:{}",count.get());
}
private static void add(){
count.incrementAndGet();
}
}

import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import com.example.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample2 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal=5000;
//同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal=200;
public static AtomicLong count= new AtomicLong(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire(); //是否允许被执行
add();
semaphore.release(); //释放信号量
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("count:{}",count.get());
}
private static void add(){
count.incrementAndGet();
}
}
import com.example.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample6 {
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal=5000;
//同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal=200;
public static LongAdder count= new LongAdder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire(); //是否允许被执行
add();
semaphore.release(); //释放信号量
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("count:{}",count);
}
private static void add(){
count.increment();
}
}

import com.example.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample7 {
private static AtomicReference<Integer> count=new AtomicReference<>(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
count.compareAndSet(0,2);
count.compareAndSet(0,1);
count.compareAndSet(1,3);
count.compareAndSet(2,4);
count.compareAndSet(3,5);
log.info("count:{}",count.get());
}
}
import com.example.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample8 {
//更新指定的类的某个字段的值,字段用volatile 非static 描述的字段
private static AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AtomicExample8> updater=
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AtomicExample8.class,"count");
@Getter
public volatile int count=100;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicExample8 example8=new AtomicExample8();
if(updater.compareAndSet(example8,100,200)){
log.info("update success 1,{}",example8.getCount());
}
if(updater.compareAndSet(example8,100,200)){
log.info("update success 2,{}",example8.getCount());
}
else{
log.info("update failed,{}",example8.getCount());
}
}
}


import com.example.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicExample9 {
private static AtomicBoolean isHappened=new AtomicBoolean(false);//默认是是否发生
//请求总数
public static int clientTotal=5000;
//同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal=200;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executorService.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire(); //是否允许被执行
test();
semaphore.release(); //释放信号量
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("exception",e);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executorService.shutdown();
log.info("isHappened:{}",isHappened.get());
}
private static void test(){
if(isHappened.compareAndSet(false,true));
log.info("execute");
}

 同步锁。
同步锁。




import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@Slf4j
public class SynchronizedExample1 {
//修饰一个代码块,不同调用对象之间是互相不影响的,
public void test1(int j){
synchronized (this){
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
log.info("test1{}-{}",j,i);
}
}
}
//修饰一个方法 不同调用对象之间是互相不影响的,不属于方法声明的一部分
public synchronized void test2(int j){
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
log.info("test2{}-{}",j,i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronizedExample1 example1=new SynchronizedExample1();
SynchronizedExample1 example2=new SynchronizedExample1();
ExecutorService excutorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
excutorService.execute(()->{
example1.test2(1);
});
excutorService.execute(()->{
example2.test2(1);
});
}
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@Slf4j
public class SynchronizedExample2 {
//修饰一个类
public void test1(int j){
synchronized (this){
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
log.info("test1{}-{}",j,i);
}
}
}
//修改一个静态方法
public static synchronized void test2(int j){
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
log.info("test2{}-{}",j,i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronizedExample1 example1=new SynchronizedExample1();
SynchronizedExample1 example2=new SynchronizedExample1();
ExecutorService excutorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
excutorService.execute(()->{
example1.test2(1);
});
excutorService.execute(()->{
example2.test2(1);
});
}
}
原子性对比:













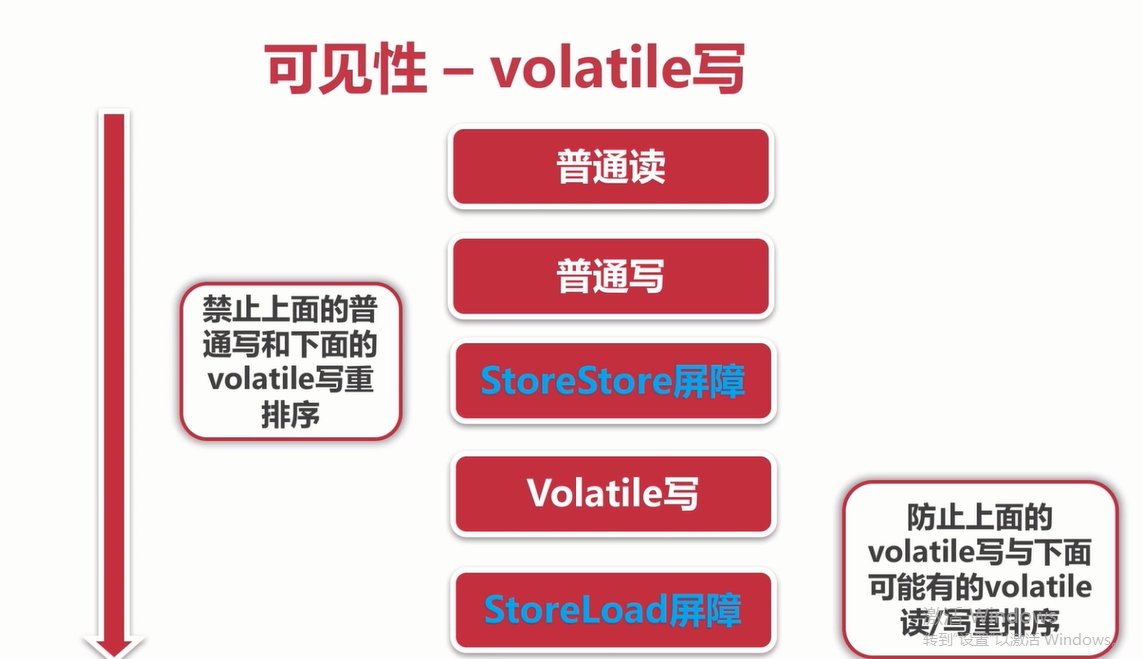
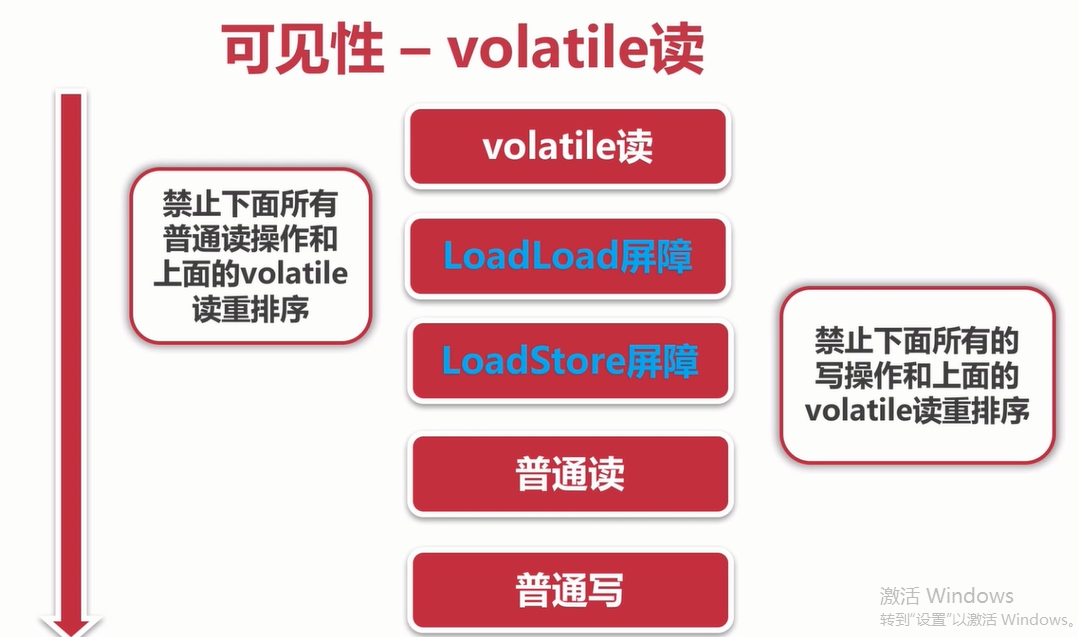
无法保证线程安全:(不具有原子性)



适用场景:作为状态标识量












线程安全性总结:


