一、Logistic回归——分类
对于分类问题,采用线性回归是不合理的。
1.假设函数(logistic函数/Sigmoid函数):
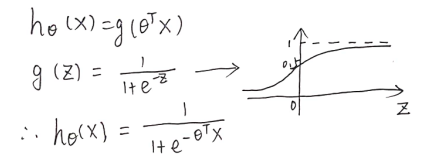
注:假设函数 h 的值,看作结果为y=1的概率估计。决策界限可以看作是 h=0.5 的线。
2.代价函数
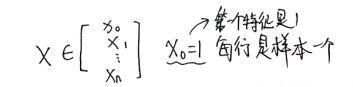
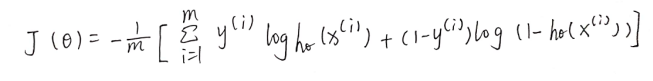
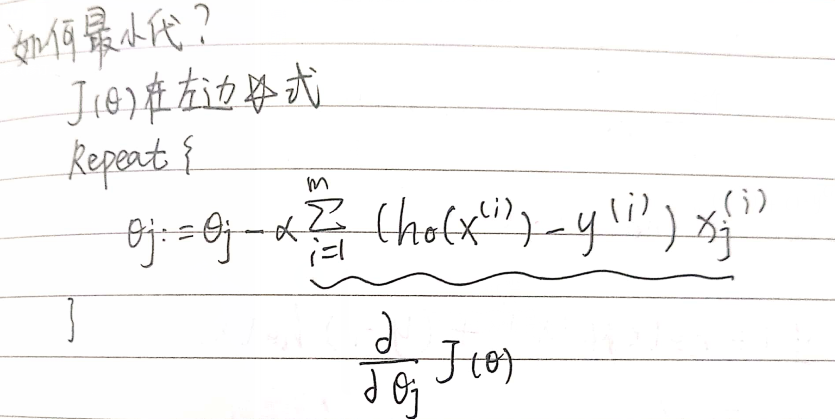
3.高级优化 fminunc
在上文优化过程中需要提供α值,而高级优化α是自动选择。
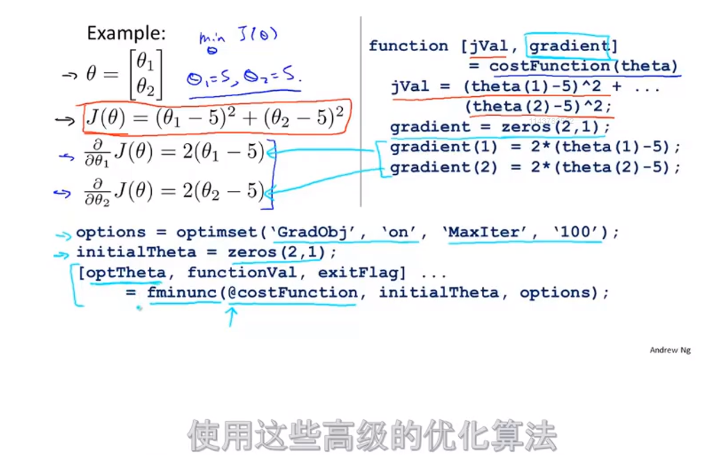
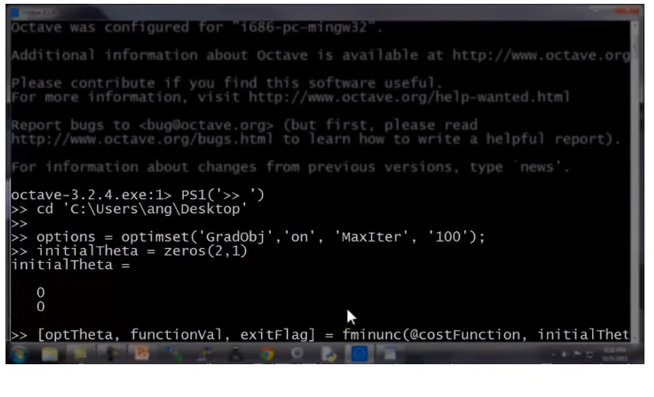
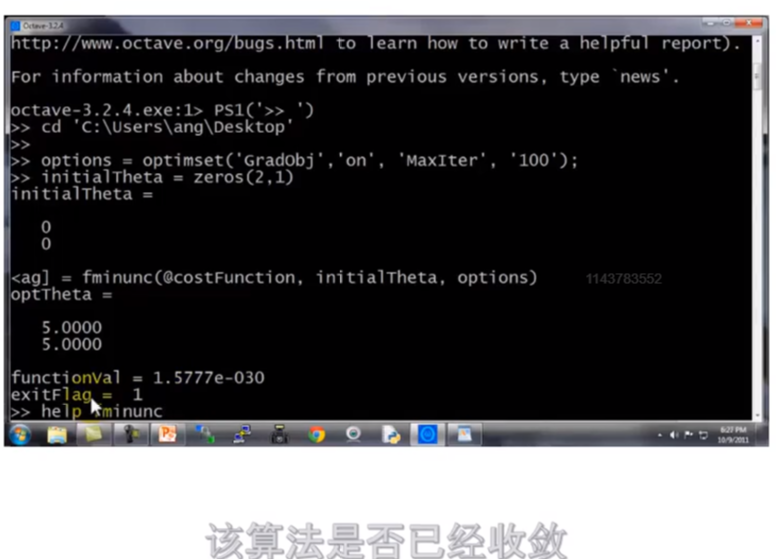
优化结果
二、Logistic回归——多元分类(一对多种类别)
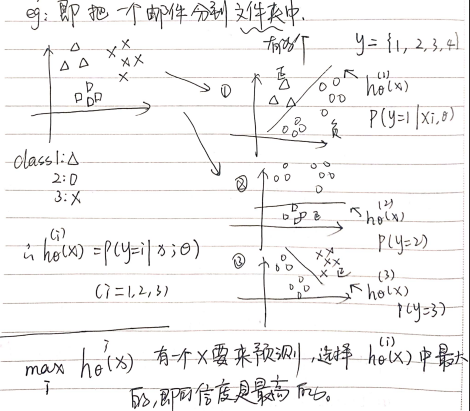
三、编程作业
1.sigmoid.m 写假设函数
function g = sigmoid(z) %SIGMOID Compute sigmoid function % g = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z. % You need to return the following variables correctly g = zeros(size(z)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix, % vector or scalar). g = 1./(1+ exp(-z)); % ============================================================= end
2.plotDate.m 数据可视化
function plotData(X, y) %PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure % PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples % and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix. % Create New Figure figure; hold on; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a % 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive % examples and 'ko' for the negative examples. % axis([30 100 30 100]); pos = find( y==1 ); neg = find( y==0 ); plot(X(pos, 1), X(pos, 2), 'k+','LineWidth', 2, ... 'MarkerSize', 7); plot(X(neg, 1), X(neg, 2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', ... 'MarkerSize', 7);
3.costFunction.m 写代价函数和梯度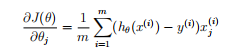
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y) %COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression % J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the % parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost % w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly J = 0; grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta. % You should set J to the cost. % Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial % derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta % % Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta % h =sigmoid(X*theta); costfun = y.*log(h)+(1-y).*log(1-h); J = -1/m*sum(costfun); grad = X'*(h-y)/m; % ============================================================= end
4.fminunc高级优化
命令行:
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial theta, options);
5.predict.m
对每个样本预测分类结果(根据假设函数),将分类结果存到向量 v 中,与实际的分类结果 y 比较,得到正确率。
function p = predict(theta, X) %PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic %regression parameters theta % p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a % threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1) m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly p = zeros(m, 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using % your learned logistic regression parameters. % You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's % h = sigmoid(X*theta); h(h>=0.5)=1; h(h<0.5)=0; p = h; % ========================================================================= end