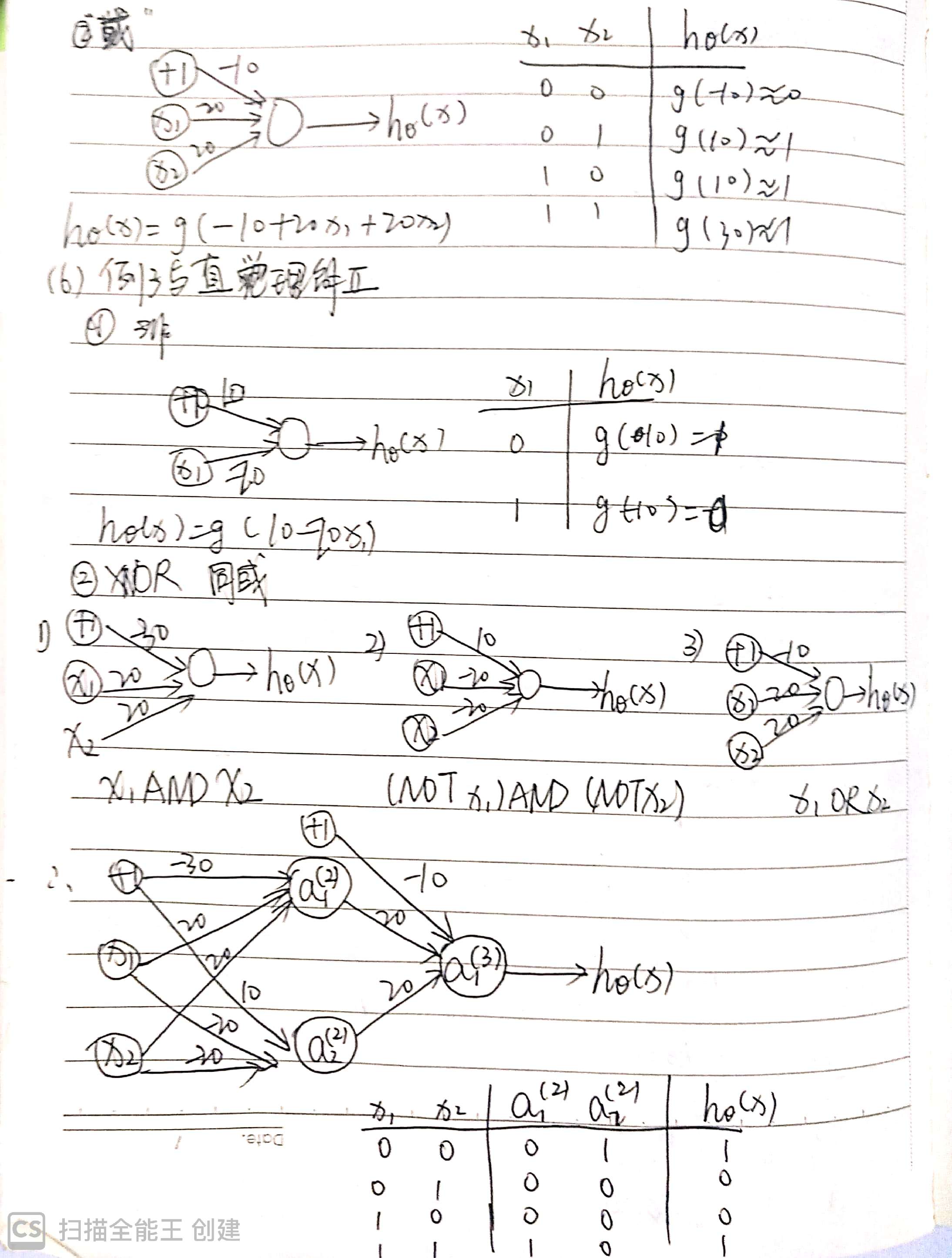
一、一组神经元
θ是模型权重(模型的参数)。

二、模型展示

三、多元分类

四、编程作业(多元分类)
1.lrCostFunction.m
在这部分是对上节作业的for循环进行矢量化,在上节作业中已经矢量化了。从代码中可以看出用到了costfunction函数,所以把该函数放到同一文件夹中。
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda) %LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with %regularization % J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using % theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the % gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly J = 0; grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta. % You should set J to the cost. % Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial % derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta % % Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be % efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation % % sigmoid(X * theta) % % Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the % prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize % the cost function and gradient computations. % % Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function, % there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution % looks like: % grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression) % temp = theta; % temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0 % grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable) % h = sigmoid(X*theta); [J, grad] = costFunction(theta,X,y); J = J + lambda*(theta'*theta-theta(1).^2)/2/m; grad = X'*(h-y)/m+lambda*theta/m; temp =(X(:,1))'*(h-y)/m; grad(1,1) = temp; % ============================================================= grad = grad(:); end
2.oneVsAll.m
一对多分类问题中,找到每组的 θ 值(用高级优化fminunc),利用for循环,组成模型权重。
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i
% Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell you
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
%
for c = 1:num_labels
%对于每类都寻找最优的
options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',50);
initial_theta = zeros(n+1,1);
[theta] = ...
fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)),initial_theta, options);
all_theta(c,:) = theta';
% =========================================================================
end
3.predictOneVsAll.m
预测函数。即从输入层,利用模型权重得到输出层h。
h是5000x10的矩阵,每行代表输入值在每类的相似度,取每行的最大值即属于这类的可能性最大,利用max函数得到最大的相似度值及其所在的列数(分类类别数)。
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X) %PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels %are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1). % p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions % for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in % rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic % regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector % of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2 % for 4 examples) m = size(X, 1); num_labels = size(all_theta, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using % your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all). % You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to % num_labels). % % Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function. % In particular, the max function can also return the index of the % max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples % are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max % for each row. % h = sigmoid(X*all_theta') [Z,p] = max(h,[],2); % ========================================================================= end
五、编程作业(神经网络)
1.predict.m
这部分的目的在于理解神经网络学习。

function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X) %PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network % p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the % trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2) % Useful values m = size(X, 1); num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using % your learned neural network. You should set p to a % vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels. % % Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max % function can also return the index of the max element, for more % information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you % can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row. % %给输入加一个偏置位 a1 = [ones(m,1) X]; %第一个隐藏层A1 z2 = a1*Theta1'; %隐藏层的值,加一个偏置位 a2 = sigmoid(z2); a2 = [ones(m,1) a2]; %输出层z3 z3 = a2*Theta2'; a3 = sigmoid(z3); [Z,p] = max(a3,[],2); % ========================================================================= end