损失函数在机器学习中的模型非常重要的一部分,它代表了评价模型的好坏程度的标准,最终的优化目标就是通过调整参数去使得损失函数尽可能的小,如果损失函数定义错误或者不符合实际意义的话,训练模型只是在浪费时间。
所以先来了解一下常用的几个损失函数hinge loss(合页损失)、softmax loss、cross_entropy loss(交叉熵损失):
1:hinge loss(合页损失)
又叫Multiclass SVM loss。至于为什么叫合页或者折页函数,可能是因为函数图像的缘故。
s=WX,表示最后一层的输出,维度为(C,None),$L_i$表示每一类的损失,一个样例的损失是所有类的损失的总和。
$L_i=sum_{j!=y_i}left { ^{0 if s_{y_i}geq s_j+1}_{s_j-s_{y_i}+1 otherwise}
ight }$
$ =sum_{j!=y_i}max(0,s_{y_i}-s_j+1)$
函数图像长这样:
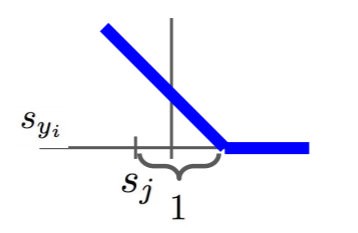
举个例子:

假设我们只有3个类别,上面的图片表示输入,下面3个数字表示最后一层每个类别的分数。
对于第一张猫的图片,$L_i$=max(0, 5.1 - 3.2 + 1) +max(0, -1.7 - 3.2 + 1)=2.9+0=2.9
对于第二张汽车的图片,$L_i$=max(0, 1.3 - 4.9 + 1) +max(0, 2.0 - 4.9 + 1)=0+0=0
可以看到对于分类错误的样例,最后有一个损失产生,对于正确分类的样例,其损失为0.
其实该损失函数不仅仅只是要求正确类别的分数最高,还要高出一定程度。也就是说即使分类正确了也有可能会产生损失,因为有可能正确的类别的分数没有超过错误类别一定的阈值(这里设为1)。但是不管阈值设多少,好像并没有什么太大的意义,只是对应着W的放缩而已。简单的理解就是正确类别的得分不仅要最高,而且要高的比较明显。
对于随机初始化的权重,最终输出应该也不叫均匀,loss应该能得到C-1,可以用这一点来检验自己的损失函数和前向传播的实现是否正确。
2:softmax
softmax操作的意图是把分数转换成概率,来看看怎么转换.
对于输入$x_i$最后会得到C个类别的分数s,每个类别的概率,$P(Y=k|X=x_i)=frac{e^{s_k}}{sum_j e^{s_j}}$。
首先取指数次幂,得到整数,然后用比值代替概率。
这样转换了之后我们定义似然函数(也就是损失函数)$L_i=-logP(Y=y_i|X=x_i)$,也就是说正确类别的概率越大越好,这也很好理解。
同样的我们来看一个例子:
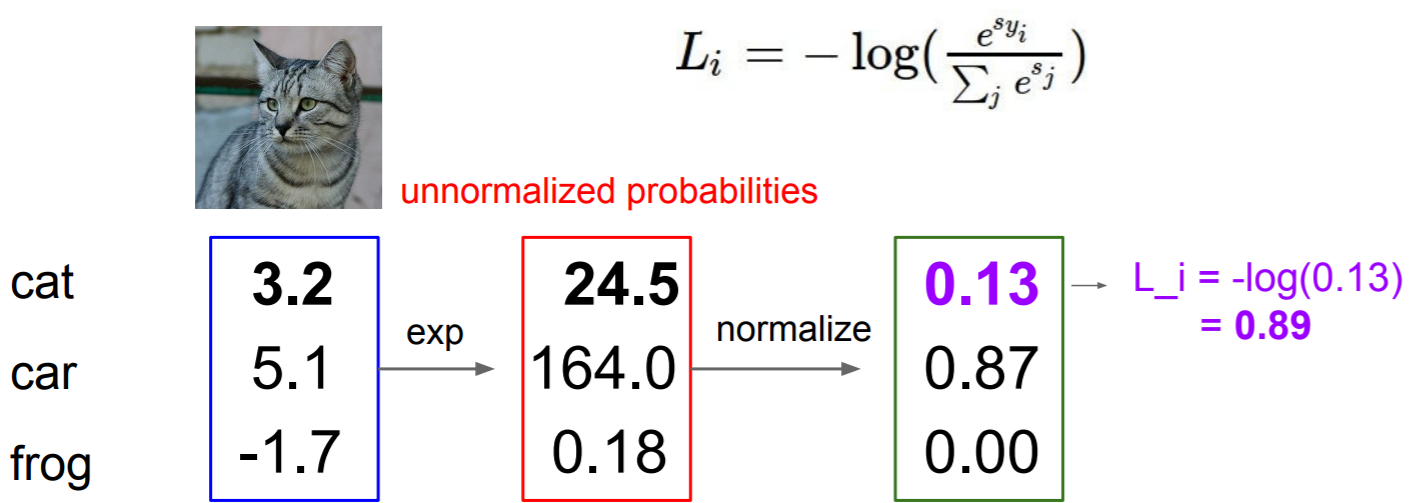
同样的,对于随机初始话的权重和数据,$L_i$应该=-log(1/c)。
3:cross_entrop loss
熵的本质是香农信息量的期望。
现有关于样本集的2个概率分布p和q,其中p为真实分布,q非真实分布。按照真实分布p来衡量识别一个样本的所需要的编码长度的期望(即平均编码长度)为:H(p)=-∑p(i)∗logp(i),如果使用错误分布q来表示来自真实分布p的平均编码长度,则应该是:H(p,q)=-∑p(i)∗logq(i)。H(p,q)=-∑p(i)∗logq(i)。因为用q来编码的样本来自分布p,所以期望H(p,q)中概率是p(i)。H(p,q)我们称之为“交叉熵”。
根据公式可以看出,对于正确分类只有一个情况,交叉熵H(p,q)=- ∑logq(i),其中q(i)为正确分类的预测概率,其余的项全部为0,因为除了正确类别,其余的真是概率p(i)都为0.在这种情况下,交叉熵损失与softmax损失其实就是同一回事。
python代码实现:
1 #首先是线性分类器的类实现 linear_classifier.py 2 3 import numpy as np 4 from linear_svm import * 5 from softmax import * 6 7 8 class LinearClassifier(object): 9 #线性分类器的基类 10 def __init__(self): 11 self.W = None 12 13 def train(self, X, y, learning_rate=1e-3, reg=1e-5, num_iters=100, 14 batch_size=200, verbose=False): 15 """ 16 使用SGD优化参数矩阵 17 18 Inputs: 19 - X (N, D) 20 - y (N,) 21 - learning_rate: 学习率. 22 - reg: 正则参数. 23 - num_iters: (int) 训练迭代的次数 24 - batch_size: (int) 每次迭代使用的样本数量. 25 - verbose: (boolean) 是否显示训练进度 26 27 Outputs: 28 返回一个list保存了每次迭代的loss 29 """ 30 num_train, dim = X.shape 31 num_classes = np.max(y) + 1 # 假设有k类,y的取值为【0,k-1】且最大的下标一定会在训练数据中出现 32 33 #初始化权重矩阵 34 if self.W is None: 35 self.W = 0.001 * np.random.randn(dim, num_classes) 36 37 38 loss_history = [] 39 for it in range(num_iters): 40 #在每次迭代,随机选择batch_size个数据 41 mask=np.random.choice(num_train,batch_size,replace=True) 42 X_batch = X[mask] 43 y_batch = y[mask] 44 45 # 计算损失和梯度 46 loss, grad = self.loss(X_batch, y_batch, reg) 47 loss_history.append(loss) 48 49 # 更新参数 50 self.W-=grad*learning_rate 51 52 if verbose and it % 100 == 0: 53 print('iteration %d / %d: loss %f' % (it, num_iters, loss)) 54 55 return loss_history 56 57 def predict(self, X): 58 """ 59 使用训练好的参数来对输入进行预测 60 61 Inputs: 62 - X (N, D) 63 64 Returns: 65 - y_pred (N,):预测的正确分类的下标 66 """ 67 68 y_pred=np.dot(X,self.W) 69 y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred, axis = 1) 70 71 return y_pred 72 73 def loss(self, X_batch, y_batch, reg): 74 """ 75 这只是一个线性分类器的基类 76 不同的线性分类器loss的计算方式不同 77 所以需要在子类中重写 78 """ 79 pass 80 81 82 class LinearSVM(LinearClassifier): 83 """ 使用SVM loss """ 84 85 def loss(self, X_batch, y_batch, reg): 86 return svm_loss_vectorized(self.W, X_batch, y_batch, reg) 87 88 89 class Softmax(LinearClassifier): 90 """ 使用交叉熵 """ 91 92 def loss(self, X_batch, y_batch, reg): 93 return softmax_loss_vectorized(self.W, X_batch, y_batch, reg)
1 #svm loss 的实现 softmax.py 2 3 import numpy as np 4 from random import shuffle 5 6 def softmax_loss_naive(W, X, y, reg): 7 """ 8 用循环实现softmax损失函数 9 D,C,N分别表示数据维度,标签种类个数和数据批大小 10 Inputs: 11 - W (D, C):weights. 12 - X (N, D):data. 13 - y (N,): labels 14 - reg: (float) regularization strength 15 16 Returns : 17 - loss 18 - gradient 19 """ 20 21 loss = 0.0 22 dW = np.zeros_like(W) 23 24 num_classes = W.shape[1] 25 num_train = X.shape[0] 26 27 for i in range(num_train): 28 scores=np.dot(X[i],W) 29 shift_scores=scores-max(scores) 30 dom=np.log(np.sum(np.exp(shift_scores))) 31 loss_i=-shift_scores[y[i]]+dom 32 loss+=loss_i 33 for j in range(num_classes): 34 softmax_output = np.exp(shift_scores[j])/sum(np.exp(shift_scores)) 35 if j == y[i]: 36 dW[:,j] += (-1 + softmax_output) *X[i].T 37 else: 38 dW[:,j] += softmax_output *X[i].T 39 loss /= num_train 40 loss += reg * np.sum(W * W) 41 dW = dW/num_train + 2*reg* W 42 43 44 return loss, dW 45 46 47 def softmax_loss_vectorized(W, X, y, reg): 48 """ 49 无循环的实现 50 """ 51 52 loss = 0.0 53 dW = np.zeros_like(W) 54 num_classes = W.shape[1] 55 num_train = X.shape[0] 56 57 scores=np.dot(X,W) 58 shift_scores=scores-np.max(scores,axis=1).reshape(-1,1) 59 softmax_output = np.exp(shift_scores)/np.sum(np.exp(shift_scores), axis = 1).reshape(-1,1) 60 loss=np.sum(-np.log(softmax_output[range(num_train),y])) 61 loss=loss/num_train+reg * np.sum(W * W) 62 63 dW=softmax_output.copy() 64 dW[range(num_train),y]-=1 65 dW=np.dot(X.T,dW) 66 dW = dW/num_train + 2*reg* W 67 68 69 return loss, dW
1 #svm loss的实现 linear_svm.py 2 3 import numpy as np 4 from random import shuffle 5 6 def svm_loss_naive(W, X, y, reg): 7 """ 8 用循环实现的SVM loss计算 9 这里的loss函数使用的是margin loss 10 11 Inputs: 12 - W (D, C): 权重矩阵. 13 - X (N, D): 批输入 14 - y (N,) 标签 15 - reg: 正则参数 16 17 Returns : 18 - loss float 19 - W的梯度 20 """ 21 dW = np.zeros(W.shape) 22 num_classes = W.shape[1] 23 num_train = X.shape[0] 24 loss = 0.0 25 26 for i in range(num_train): 27 scores = X[i].dot(W) 28 correct_class_score = scores[y[i]] 29 for j in range(num_classes): 30 if j == y[i]: 31 continue 32 margin = scores[j] - correct_class_score + 1 33 if margin > 0: 34 loss += margin 35 dW[:,j]+=X[i].T 36 dW[:,y[i]]-=X[i].T 37 38 39 loss /= num_train 40 dW/=num_train 41 loss += reg * np.sum(W * W) 42 dW+=2* reg * W 43 44 45 return loss, dW 46 47 48 def svm_loss_vectorized(W, X, y, reg): 49 """ 50 不使用循环,利用numpy矩阵运算的特性实现loss和梯度计算 51 """ 52 loss = 0.0 53 dW = np.zeros(W.shape) 54 55 #计算loss 56 num_classes = W.shape[1] 57 num_train = X.shape[0] 58 scores=np.dot(X,W)#得到得分矩阵(N,C) 59 correct_socre=scores[range(num_train), list(y)].reshape(-1,1)#得到每个输入的正确分类的分数 60 margins=np.maximum(0,scores-correct_socre+1) 61 margins[range(num_train), list(y)] = 0 62 loss=np.sum(margins)/num_train+reg * np.sum(W * W) 63 64 #计算梯度 65 mask=np.zeros((num_train,num_classes)) 66 mask[margins>0]=1 67 mask[range(num_train),list(y)]-=np.sum(mask,axis=1) 68 dW=np.dot(X.T,mask) 69 dW/=num_train 70 dW+=2* reg * W 71 72 return loss, dW
1 #最后是测试文件,看看实现的线性分类器在CIFAR10上的分类效果如何 2 3 # coding: utf-8 4 5 #实现hinge_loss和sotfmax_loss 6 7 import random 8 import numpy as np 9 from cs231n.data_utils import load_CIFAR10 10 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 11 from cs231n.classifiers.linear_svm import svm_loss_naive,svm_loss_vectorized 12 from cs231n.classifiers.softmax import softmax_loss_naive,softmax_loss_vectorized 13 import time 14 from cs231n.classifiers import LinearSVM,Softmax 15 %matplotlib inline 16 plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 8.0) # set default size of plots 17 plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest' 18 plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray' 19 20 21 ####################################################################################### 22 ####################################################################################### 23 ###################################第一部分 载入数据并处理############################### 24 ####################################################################################### 25 ####################################################################################### 26 27 # 载入CIFAR10数据. 28 cifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py' 29 X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir) 30 31 print('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape) 32 print('Training labels shape: ', y_train.shape) 33 print('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape) 34 print('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape) 35 36 #每个分类选几个图片显示观察一下 37 classes = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'] 38 num_classes = len(classes) 39 samples_per_class = 7 40 for y, cls in enumerate(classes): 41 idxs = np.flatnonzero(y_train == y) 42 idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, samples_per_class, replace=False) 43 for i, idx in enumerate(idxs): 44 plt_idx = i * num_classes + y + 1 45 plt.subplot(samples_per_class, num_classes, plt_idx) 46 plt.imshow(X_train[idx].astype('uint8')) 47 plt.axis('off') 48 if i == 0: 49 plt.title(cls) 50 plt.show() 51 52 #把数据分为训练集,验证集和测试集。 53 #用一个小子集做测验,运行更快。 54 num_training = 49000 55 num_validation = 1000 56 num_test = 1000 57 num_dev = 500 58 59 #数据集本身没有给验证集,需要自己把训练集分成两部分 60 mask = range(num_training, num_training + num_validation) 61 X_val = X_train[mask] 62 y_val = y_train[mask] 63 64 mask = range(num_training) 65 X_train = X_train[mask] 66 y_train = y_train[mask] 67 68 69 mask = np.random.choice(num_training, num_dev, replace=False) 70 X_dev = X_train[mask] 71 y_dev = y_train[mask] 72 73 mask = range(num_test) 74 X_test = X_test[mask] 75 y_test = y_test[mask] 76 77 print('Train data shape: ', X_train.shape) 78 print('Train labels shape: ', y_train.shape) 79 print('Validation data shape: ', X_val.shape) 80 print('Validation labels shape: ', y_val.shape) 81 print('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape) 82 print('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape) 83 84 85 X_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], -1)) 86 X_val = np.reshape(X_val, (X_val.shape[0], -1)) 87 X_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0], -1)) 88 X_dev = np.reshape(X_dev, (X_dev.shape[0], -1)) 89 90 print('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape) 91 print('Validation data shape: ', X_val.shape) 92 print('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape) 93 print('dev data shape: ', X_dev.shape) 94 95 96 # 预处理: 把像素点数据化成以0为中心 97 # 第一步: 在训练集上计算图片像素点的平均值 98 mean_image = np.mean(X_train, axis=0) 99 print(mean_image.shape) 100 plt.figure(figsize=(4,4)) 101 plt.imshow(mean_image.reshape((32,32,3)).astype('uint8')) # 可视化一下平均值 102 plt.show() 103 104 # 第二步: 所有数据都减去刚刚得到的均值 105 X_train -= mean_image 106 X_val -= mean_image 107 X_test -= mean_image 108 X_dev -= mean_image 109 110 111 # 第三步: 给所有的图片都加一个位,并设为1,这样在训练权重的时候就不需要b了,只需要w 112 # 相当于把b的训练并入了W中 113 X_train = np.hstack([X_train, np.ones((X_train.shape[0], 1))]) 114 X_val = np.hstack([X_val, np.ones((X_val.shape[0], 1))]) 115 X_test = np.hstack([X_test, np.ones((X_test.shape[0], 1))]) 116 X_dev = np.hstack([X_dev, np.ones((X_dev.shape[0], 1))]) 117 118 print(X_train.shape, X_val.shape, X_test.shape, X_dev.shape) 119 120 121 ####################################################################################### 122 ####################################################################################### 123 ###################################第二部分 定义需要用到的函数########################### 124 ####################################################################################### 125 ####################################################################################### 126 127 def cmp_naiveANDvectorized(naive,vectorized): 128 ''' 129 每个损失函数都用两种方式实现:循环和无循环(即利用numpy的特性) 130 ''' 131 132 W = np.random.randn(3073, 10) * 0.0001 133 134 #对比两张实现方式的计算时间 135 tic = time.time() 136 loss_naive, grad_naive = naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005) 137 toc = time.time() 138 print('Naive computed in %fs' % ( toc - tic)) 139 140 tic = time.time() 141 loss_vectorized, grad_vectorized = vectorized(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005) 142 toc = time.time() 143 print('Vectorized computed in %fs' % ( toc - tic)) 144 145 # 检验损失的实现是否正确,对于随机初始化的数据的权重, 146 # softmax_loss应该约等于-log(0.1),svm_loss应该约等于9 147 print('loss %f %f' % (loss_naive , loss_vectorized)) 148 149 # 对比两种实现方式得到的结果是否相同 150 print('difference loss %f ' % (loss_naive - loss_vectorized)) 151 difference = np.linalg.norm(grad_naive - grad_vectorized, ord='fro') 152 print('difference gradient: %f' % difference) 153 154 def cross_choose(Linear_classifier,learning_rates,regularization_strengths): 155 ''' 156 选择超参数 157 ''' 158 159 results = {} # 存储每一对超参数对应的训练集和验证集上的正确率 160 best_val = -1 # 最好的验证集上的正确率 161 best_model = None # 最好的验证集正确率对应的svm类的对象 162 best_loss_hist=None 163 for rs in regularization_strengths: 164 for lr in learning_rates: 165 classifier = Linear_classifier 166 loss_hist = classifier.train(X_train, y_train, lr, rs, num_iters=3000) 167 y_train_pred = classifier.predict(X_train) 168 train_accuracy = np.mean(y_train == y_train_pred) 169 y_val_pred = classifier.predict(X_val) 170 val_accuracy = np.mean(y_val == y_val_pred) 171 if val_accuracy > best_val: 172 best_val = val_accuracy 173 best_model = classifier 174 best_loss_hist=loss_hist 175 results[(lr,rs)] = train_accuracy, val_accuracy 176 177 for lr, reg in sorted(results): 178 train_accuracy, val_accuracy = results[(lr, reg)] 179 print ('lr %e reg %e train accuracy: %f val accuracy: %f' % ( 180 lr, reg, train_accuracy, val_accuracy)) 181 182 print('best validation accuracy achieved during cross-validation: %f' % best_val) 183 # 可视化loss曲线 184 plt.plot(best_loss_hist) 185 plt.xlabel('Iteration number') 186 plt.ylabel('Loss value') 187 plt.show() 188 return results,best_val,best_model 189 190 def show_weight(best_model): 191 # 看看最好的模型的效果 192 # 可视化学到的权重 193 194 y_test_pred = best_model.predict(X_test) 195 test_accuracy = np.mean(y_test == y_test_pred) 196 print('final test set accuracy: %f' % test_accuracy) 197 198 w = best_model.W[:-1,:] # 去掉偏置参数 199 w = w.reshape(32, 32, 3, 10) 200 w_min, w_max = np.min(w), np.max(w) 201 classes = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'] 202 for i in range(10): 203 plt.subplot(2, 5, i + 1) 204 205 # 把权重转换到0-255 206 wimg = 255.0 * (w[:, :, :, i].squeeze() - w_min) / (w_max - w_min) 207 plt.imshow(wimg.astype('uint8')) 208 plt.axis('off') 209 plt.title(classes[i]) 210 plt.show() 211 212 ####################################################################################### 213 ####################################################################################### 214 ##########################第三部分 应用和比较svm_loss和softmax_loss###################### 215 ####################################################################################### 216 ####################################################################################### 217 218 cmp_naiveANDvectorized(svm_loss_naive,svm_loss_vectorized) 219 learning_rates = [(1+i*0.1)*1e-7 for i in range(-3,5)] 220 regularization_strengths = [(5+i*0.1)*1e3 for i in range(-3,3)] 221 #正则参数的选择要根据正常损失和W*W的大小的数量级来确定,初始时正常loss大概是9,W*W大概是1e-6 222 #可以观察最后loss的值的大小来继续调整正则参数的大小,使正常损失和正则损失保持合适的比例 223 results,best_val,best_model=cross_choose(LinearSVM(),learning_rates,regularization_strengths) 224 show_weight(best_model) 225 226 print("--------------------------------------------------------") 227 228 cmp_naiveANDvectorized(softmax_loss_naive,softmax_loss_vectorized) 229 learning_rates = [(2+i*0.1)*1e-7 for i in range(-2,2)] 230 regularization_strengths = [(7+i*0.1)*1e3 for i in range(-3,3)] 231 results,best_val,best_model=cross_choose(Softmax(),learning_rates,regularization_strengths) 232 show_weight(best_model)
1 #获取数据的部分 2 3 from six.moves import cPickle as pickle 4 import numpy as np 5 import os 6 from scipy.misc import imread 7 import platform 8 9 def load_pickle(f): 10 version = platform.python_version_tuple() 11 if version[0] == '2': 12 return pickle.load(f) 13 elif version[0] == '3': 14 return pickle.load(f, encoding='latin1') 15 raise ValueError("invalid python version: {}".format(version)) 16 17 def load_CIFAR_batch(filename): 18 """ CIRAR的数据是分批的,这个函数的功能是载入一批数据 """ 19 with open(filename, 'rb') as f: 20 datadict = load_pickle(f) #以二进制方式打开文件 21 X = datadict['data'] 22 Y = datadict['labels'] 23 X = X.reshape(10000, 3, 32, 32).transpose(0,2,3,1).astype("float") 24 Y = np.array(Y) 25 return X, Y 26 27 def load_CIFAR10(ROOT): 28 """ load 所有的数据 """ 29 xs = [] 30 ys = [] 31 for b in range(1,6): 32 f = os.path.join(ROOT, 'data_batch_%d' % (b, )) 33 X, Y = load_CIFAR_batch(f) 34 xs.append(X) 35 ys.append(Y) 36 Xtr = np.concatenate(xs) 37 Ytr = np.concatenate(ys) 38 del X, Y 39 Xte, Yte = load_CIFAR_batch(os.path.join(ROOT, 'test_batch')) 40 return Xtr, Ytr, Xte, Yte 41 42 43 def get_CIFAR10_data(num_training=49000, num_validation=1000, num_test=1000, 44 subtract_mean=True): 45 """ 46 Load the CIFAR-10 dataset from disk and perform preprocessing to prepare 47 it for classifiers. These are the same steps as we used for the SVM, but 48 condensed to a single function. 49 """ 50 # Load the raw CIFAR-10 data 51 cifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py' 52 X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir) 53 54 # Subsample the data 55 mask = list(range(num_training, num_training + num_validation)) 56 X_val = X_train[mask] 57 y_val = y_train[mask] 58 mask = list(range(num_training)) 59 X_train = X_train[mask] 60 y_train = y_train[mask] 61 mask = list(range(num_test)) 62 X_test = X_test[mask] 63 y_test = y_test[mask] 64 65 # Normalize the data: subtract the mean image 66 if subtract_mean: 67 mean_image = np.mean(X_train, axis=0) 68 X_train -= mean_image 69 X_val -= mean_image 70 X_test -= mean_image 71 72 # Transpose so that channels come first 73 X_train = X_train.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2).copy() 74 X_val = X_val.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2).copy() 75 X_test = X_test.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2).copy() 76 77 # Package data into a dictionary 78 return { 79 'X_train': X_train, 'y_train': y_train, 80 'X_val': X_val, 'y_val': y_val, 81 'X_test': X_test, 'y_test': y_test, 82 }