1、什么是异常
异常就是程序运行时发生错误的信号(在程序出现错误时,则会产生一个异常,若程序没有处理它,则会抛出该异常,程序的运行也随之终止),在python中,错误触发的异常如下
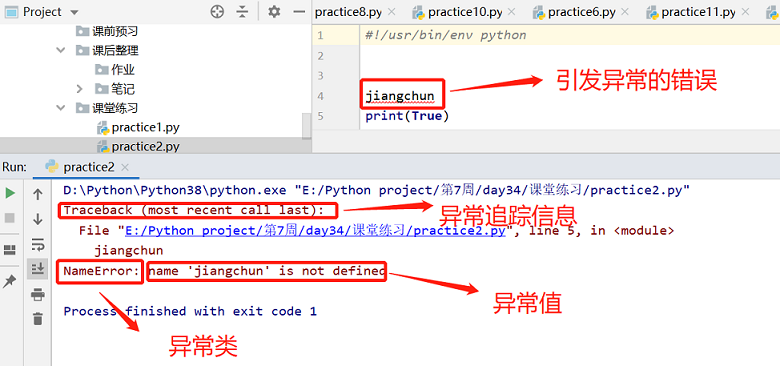
错误一般分为两种:
语法错误和逻辑错误
(1)语法错误

#!/usr/bin/env python class Beast(object): def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age @property def show(self): return f'[info]: name-->{self.name} age-->{self.age}' b = Beast('黄亮',26) if hasattr(b,'name') print(getattr(b,'name')) File "E:/Python project/第7周/day34/课堂练习/practice2.py", line 14 if hasattr(b,'name') ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax
(2)逻辑错误

lst = [1,2,3,4] print(lst[4]) IndexError: list index out of range name print(True) NameError: name 'name' is not defined float('我') ValueError: could not convert string to float: '我' int('1.01') ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: '1.01' dic = {'a':1111} dic['aaa'] KeyError: 'aaa' class Beast: pass Beast.name AttributeError: type object 'Beast' has no attribute 'name'
2、常用的异常种类

AttributeError 试图访问一个对象没有的树形,比如foo.x,但是foo没有属性x IOError 输入/输出异常;基本上是无法打开文件 ImportError 无法引入模块或包;基本上是路径问题或名称错误 IndentationError 语法错误(的子类) ;代码没有正确对齐 IndexError 下标索引超出序列边界,比如当x只有三个元素,却试图访问x[5] KeyError 试图访问字典里不存在的键 KeyboardInterrupt Ctrl+C被按下 NameError 使用一个还未被赋予对象的变量 SyntaxError Python代码非法,代码不能编译(个人认为这是语法错误,写错了) TypeError 传入对象类型与要求的不符合 UnboundLocalError 试图访问一个还未被设置的局部变量,基本上是由于另有一个同名的全局变量, 导致你以为正在访问它 ValueError 传入一个调用者不期望的值,即使值的类型是正确的
3、异常处理
为了保证程序的健壮性,即在遇到异常错误时,程序不会奔溃,需要在遇到异常时对其进行处理
(1)发生错误的条件是可以预知的,使用if
def register(): """注册函数""" while True: regisetr_name = input('请输入用户名:').strip() register_pwd = input('请输入密码:').strip() account_balance = input('请输入账号金额(元):').strip() if account_balance.isdigit(): flag, msg = user_interface.register(regisetr_name, register_pwd, account_balance) if flag: print(msg) break else: print(msg) else: print('请输入一个数字!')
(2)如果发生的条件是不可预知的,就使用try-except
基本语法结构:
try: 代码块1 代码块2 代码块3 except (异常类型1,异常类型2) as e: print(e) except 异常类型3 as e: print(f'异常信息如下: {e}') except Exception as e: print(f'我是万能异常:{e}') else: #代码段1,2,3 都没有异常执行该处代码 print('一切正常!') finally: # 无论是否捕捉到异常都执行该处代码 # 这里一般做回收系统资源的操作 f.close()
注意:

# 1、如果我们想多种类型的异常统一用一种逻辑处理,可以将多个异常放到一个元组内,用一个except匹配 #2、如果我们想捕获所有异常并用一种逻辑处理,Python提供了一个万能异常类型Exception #3、在多分支except之后还可以跟一个else(else必须跟在except之后,不能单独存在),只有在被检测的代码块没有触发任何异常的情况下才会执行else的子代码块 #4、此外try还可以与finally连用,从语法上讲finally必须放到else之后,但可以使用try-except-finally的形式,也可以直接使用try-finally的形式。无论被检测的代码块是否触发异常,都会执行finally的子代码块,因此通常在finally的子代码块做一些回收资源的操作,比如关闭打开的文件、关闭数据库连接等

f=None try: f=open(‘db.txt’,'r',encoding='utf-8') s=f.read().strip() int(s) # 若字符串s中包含非数字时则会触发异常ValueError # f.close() # 若上面的代码触发异常,则根本不可能执行到此处的代码,应该将关闭文件的操作放到finally中 finally: if f: # 文件存在则f的值不为None f.close()
在内置异常不够用的情况下,我们可以通过继承内置的异常类来自定义异常类
class PoolEmptyError(Exception): # 可以通过继承Exception来定义一个全新的异常 def __init__(self,value='The proxy source is exhausted'): # 可以定制初始化方法 super(PoolEmptyError,self).__init__() self.value=value def __str__(self): # 可以定义该方法用来定制触发异常时打印异常值的格式 return '< %s >' %self.value class NetworkIOError(IOError): # 也可以在特定异常的基础上扩展一个相关的异常 pass raise PoolEmptyError # __main__.PoolEmptyError: < The proxy source is exhausted > raise NetworkIOError('连接被拒绝') # __main__.NetworkIOError: 连接被拒绝
最后,Python还提供了一个断言语句assert expression,断定表达式expression成立,否则触发异常AssertionError,与raise-if-not的语义相同,如下
class Beast: def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age @property def show(self): return f'{self.name} {self.age}' b = Beast('黄亮',18) assert isinstance(b,Beast) assert isinstance('33',Beast)
assert isinstance(b,Beast)
等同于
if not isinstance(b,Beasr):
raise AssertionError
