一.ServletConfig的使用
在学习servlet生命周期时我们讲过,Servlet在被web容器创建时要先调用其init方法传入一个ServletConfig类型的参数,什么是ServletConfig呢?ServletConfig顾名思义,就是Servlet的配置,我们在web.xml中定义的init-param标签的内容就是保存在ServletConfig这个对象中的。ServletConfig是一个接口,里面定义了如下的几个方法:
public interface ServletConfig { public String getServletName(); public ServletContext getServletContext(); public String getInitParameter(String name); public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames(); }
其中getServletName用于获取Servlet的名字;getInitParameter(String name)表示获取init-param的值;getInitParameterNames()表示获取所有配置在web.xml中的值,这三个方法都是比较的容易理解。这里我要着重介绍的是getServletContext()方法表示返回一个ServletContext对象,他代表应用的本身,那么在ServletConetxt中设置参数就会被所有的Servlet所共享而在initParamter参数只可以在配置的servlet中使用。下面我们来尝试获取一下配置在web.xml中的参数:
(1)定义web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <context-param> <param-name>test</param-name> <param-value>ServletContext</param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>testServletConfig</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.web.test.TestServletConfig</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>testServletConfig</param-name> <param-value>getFromServletConfig</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>encode</param-name> <param-value>utf-8</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>testServletConfig</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/testServletConfig</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
(2)获取参数
public class TestServletConfig extends HttpServlet{ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(req,resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletConfig servletConfig = this.getServletConfig(); String initParam = servletConfig.getInitParameter("testServletConfig"); System.out.println(initParam); Enumeration<String> inits = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames(); while(inits.hasMoreElements()){ System.out.println(servletConfig.getInitParameter(inits.nextElement())); } } } 输出: getFromServletConfig getFromServletConfig utf-8
二.ServletContext的使用
当web容器启动后会为每一个web容器创建一个ServletContext对象表示这个web应用本身,在我们刚才介绍的ServletConfig中保存着一个对ServletContext对象的引用。在同一个web应用中定义的Servlet共享一个ServletContext,所以我们也称ServletContext为域对象,使用ServletContext对象可以实现在不同的Servlet之间传递数据。
在ServletContext接口中定义了如下的几个方法:
public String getInitParameter(String name); public boolean setInitParameter(String name, String value); public Enumeration<String> getAttributeNames(); public void setAttribute(String name, Object object); public void removeAttribute(String name); public Object getAttribute(String name);
其中getInitParameter表示获取在web.xml中使用标签context-param定义的初始化参数,setInitParameter表示设置初始化参数,getAttribute和setAttribute分别表示从ServletContext获取值和向ServletContext设置值,removeAttribute表示移除ServletContext中对应的值。首先我们来尝试获取一下ServletContext的初始化参数:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <context-param> <param-name>test</param-name> <param-value>ServletContext</param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>testServletContext</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.web.test.TestServletContext</servlet-class> </servlet> </web-app>
先在web.xml中配置好servletContext的初始化参数,如上所示。在web.xml中定义的servlet中获取初始化参数:
package com.web.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class TestServletContext extends HttpServlet{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
String initName = servletContext.getInitParameter("test");
PrintWriter write = resp.getWriter();
write.print("initName:"+initName);
write.flush();
write.close();
}
}
浏览器页面输出:
initName:ServletContext
在ServletContext中设置值会被同一个web应用的其他Servlet所共享。首先我需要定义两个Servlet:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>testServletContext1</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.web.test.TestServletContext1</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>testServletContext1</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/testServletContext1</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet> <servlet-name>testServletContext2</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.web.test.TestServletContext2</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>testServletContext2</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/testServletContex2</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
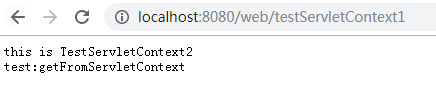
分别是TestServletContext1和TestServletContext2。在TestServletContext1中我们获取了ServletContext对象并且使用setAttribute方法往ServletContext中设置了值然后转发到了TestServletContext2,关于转发我在介绍HttpServletRequest对象在来介绍。在TestServletContext2中我们使用getAttribute方法来获取存放在ServletContext中的值。
public class TestServletContext1 extends HttpServlet{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(req,resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); servletContext.setAttribute("test","getFromServletContext"); servletContext.getRequestDispatcher("/testServletContex2").forward(req, resp); } }
public class TestServletContext2 extends HttpServlet{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(req,resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); String value = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("test"); PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter(); writer.print("this is TestServletContext2 "); writer.print("test:"+value); writer.flush(); writer.close(); } }
浏览器输出: