1,指针:
未初始化的指针通常会使得程序崩溃;
在C ++中,有几种使用其零参数构造函数创建对象的方法。
m = new IntCell( ); // OK
m = new IntCell{ }; // C++11
m = new IntCell; // Preferred in this text
通常使用最后一种;
为避免内存泄漏,通常在局部变量使用完之后删除;
地址运算符&;
int main(void) { IntCell *m; m=new IntCell{0}; m->write(5); cout<<"Cell contents: "<<m->read()<<endl; delete m; system("pause"); return 0; }
IntCell具体定义 见上章
2,引用:
在C ++ 11中,我们可以有两种类型的引用:左值引用和右值引用。
右值引用作用并不明显,
string str = "hell";
string & rstr = str; // rstr is another name for str
rstr += ’o’; // changes str to "hello"
bool cond = (&str == &rstr); // true; str and rstr are same object
string & bad1 = "hello"; // illegal: "hello" is not a modifiable lvalue
string & bad2 = str + ""; // illegal: str+"" is not an lvalue
string & sub = str.substr( 0, 4 ); // illegal: str.substr( 0, 4 ) is not an lvalue
string str = "hell";
string && bad1 = "hello"; // Legal
string && bad2 = str + ""; // Legal
string && sub = str.substr( 0, 4 ); // Legal
类型后边 && 表示右值引用,一个&表左值引用;
左值引用的使用:
#1:给复杂名字重命名
学散列时用:
auto & whichList = theLists[ myhash( x, theLists.size( ) ) ];
if( find( begin( whichList ), end( whichList ), x ) !=end( whichList ) )
return false;
whichList.push_back( x );
用whichlist替代一长串,接下来就不用被写入四次
auto whichList = theLists[ myhash( x, theLists.size( ) ) ];
不会有上边那种效果,它只会copy一下theLists[ myhash( x, theLists.size( ) ) ]里的内容,然后push_back只会改变现有的,而不是原来的;
#2:循环范围的使用
给vector中的每个值+1,
for( int i = 0; i < arr.size( ); ++i )
++arr[ i ];
原始写法:x是假定向量中每个值的copy
for( auto x : arr )// broken
++x;
我们真正想要的是x是向量中每个值的另一个名称,如果x是引用,这很容易做到:
for(auto&x:arr)//适用于
++ x;
#3:避免复制
找vector中最大值:
auto x = findMax( arr );
很多情况下,只需要值而不做改变,那么引用显然会比直接复制好,
auto & x = findMax( arr );
3,参数传递:
#1:按值调用 (Call-by-value )
按值调用无法进行交换(具体原理参照c)
double average( double a, double b ); // returns average of a and b
void swap( double a, double b ); // swaps a and b; wrong parameter types
string randomItem( vector<string> arr ); // returns a random item in arr; inefficient
比如:
double z = average( x, y );
按值调用将x复制到a,将y复制到b,然后执行在其他地方完全指定的平均函数定义的代码。
void swap( double & a, double & b ); // swaps a and b; correct parameter types(左值引用)
#2:按常量引用调用( Call-by-constant-reference )
string randomItem( const vector<string> & arr ); // returns a random item in arr
#3:按引用调用(Call-by-reference )
左值引用:
void swap( double & a, double & b ); // swaps a and b; correct parameter types
右值引用:( call-byrvalue-reference. )
string randomItem( vector<string> && arr );
例:
string randomItem( const vector<string> & arr ); // returns random item in lvalue arr
string randomItem( vector<string> && arr ); // returns random item in rvalue arr
引用;
vector<string> v { "hello", "world" };
cout << randomItem( v ) << endl; // invokes lvalue method
cout << randomItem( { "hello", "world" } ) << endl; // invokes rvalue method
注*:
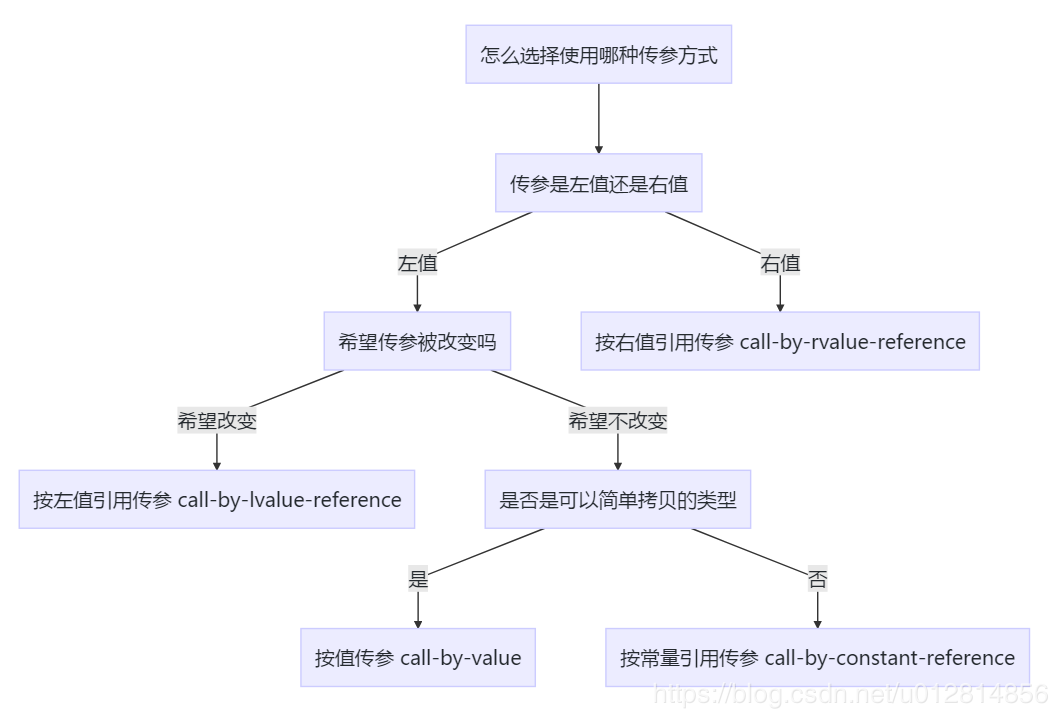
1.按值调用适用于不应由函数更改的小对象。
2.按常量引用调用适用于不应由函数更改且复制成本昂贵的大型对象。
3.按引用调用适用于该函数可能更改的所有对象。
下图百度找的,加深理解;
4,返回类型:
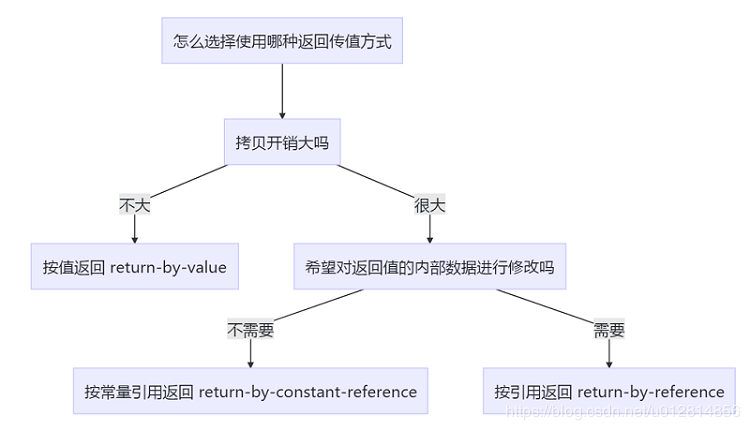
#1:按值返回
double average( double a, double b ); // returns average of a and b
LargeType randomItem( const vector<LargeType> & arr ); // potentially inefficient
vector<int> partialSum( const vector<int> & arr ); // efficient in C++11
LargeType randomItem1 (const vector<LargeType> & arr)
{
return arr[randomInt(0, arr.size() - 1)];
}
vector<LargeType> vec;
LargeType item1 = randomItem1 (vec);
#2:按引用常量返回
vector<int>partialSum(const vector<int>&arr) { vector<int>result(arr.size()); result[0]=arr[0]; for(int i=1;i<arr.size();++i) result[i]=result[i-1]+arr[i]; return result; } vector<int>vec; vector<int>sums=partialSum(vec);//copy in old C++; move in c++11;
const LargeType & randomItem2(const vector<LargeType> & arr)
{
return arr[randomInt(0, arr.size() - 1)];
}
vector<LargeType> vec;
// copy
LargeType item1 = randomItem2(vec);
// no copy
const LargeType & item2 = randomItem2(vec);
#3:按引用返回
既不产生拷贝,并且还能对其值进行修改(这种情况虽然少见,但是也有存在)
5,std::swap,std::move
在进行元素交换时,我们通常使用一个缓存变量temp来临时保存数据;而对temp直接进行=的赋值操作时,实际上temp复制了一次原有对象的内存,但我们需要只是对象之间的移动而不是复制,而C++STL中的std::move函数便可以达成这一操作
void swap(double &x,double &y) { double tmp=x; x=y; y=tmp; } //replace expensive copies with moves; void swap(vector<string> &x,vector<string> &y) { vector<string>tmp=static_cast<vector<string>&&>(x); x=static_cast<vector<string>&&>(y); y=static_cast<vector<string>&&>(tmp); } //The syntax of a static cast is daunting; void swap(vector<string>&x,vector<string>&y) { vector<string>tmp=std::move(x); x=std::move(y); y=std::move(tmp); } //move function.
6,动态内存分配