说明
本题可以使用quickSelect,PriorityQueue,或者自己构建堆。
对于要排序的总数是确定的情况下,可以使用quickSelect,对于总数不确定的情况下,可以使用堆排序。
对于前两种方法本文不说明,本文主要说明堆排序。图片来自于这个up
堆排序
堆排序要求整棵树是一个完全二叉树(平衡的),它的数组实现方式对空间利用率很高。
堆排序的最佳,平均,最坏时间复杂度都是o(nlogn)的,在平均情况下,它比快速排序慢一个常数因子,但是堆排序更适合外部排序,处理那些数据集太大而不适合在内存中排序的情况。
基于大根堆的排序算法的过程:
- 建堆
- 取出堆顶元素(最大值),放到数组的末尾
- 将堆的最末尾元素放到堆顶,重新构建堆
- 如此重复,直到堆为空
建堆
- 对于数组中index为i的元素的建堆过程是:先判断2i + 1和2i + 2是否越界,如果不越界,找到这两个index中对应的值最大(最大的值的索引记为max)的和i处的值做交换,同时由于交换了索引对应的值,没法保证索引max的子树还是最大堆,所以要对索引max再次建堆(如果都比i处的值小,就不交换)
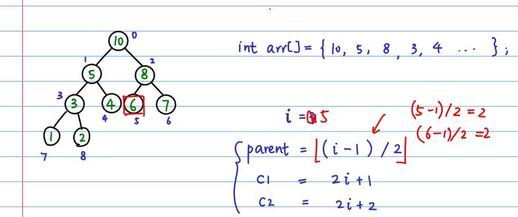
上述过程对应的代码:
public void heapify(int[] nums, int i, int heapSize){
int leftChild = 2 * i + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * i + 2;
int maxIndex = i;
if (leftChild < heapSize && nums[leftChild] > nums[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < heapSize && nums[rightChild] > nums[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = rightChild;
}
if (maxIndex != i){
swap(nums, maxIndex, i);
heapify(nums, maxIndex, heapSize);
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
- 从最后一个非叶子节点往前倒退,分别对这些节点做heapify,就可以构建出整个堆
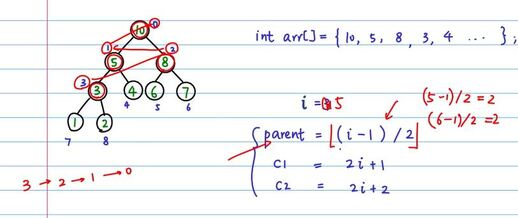
上述过程的代码:
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] nums, int heapSize){
for (int i = (heapSize - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){
heapify(nums, i, heapSize);
}
}
取出堆顶元素,放到数组末尾。并将堆末尾元素放到堆顶,重新建堆
执行过程是:交换数组中第一个元素(最大值)和最后一个元素,堆长度-1,对剩下元素重新调整堆。
代码如下:
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize);
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; i--){
swap(nums, 0, i);
heapSize--;
heapify(nums, 0, heapSize);
}
return nums[0];
}
总结
本题完整代码如下:
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize);
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; i--){
swap(nums, 0, i);
heapSize--;
heapify(nums, 0, heapSize);
}
return nums[0];
}
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] nums, int heapSize){
for (int i = (heapSize - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){
heapify(nums, i, heapSize);
}
}
public void heapify(int[] nums, int i, int heapSize){
int leftChild = 2 * i + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * i + 2;
int maxIndex = i;
if (leftChild < heapSize && nums[leftChild] > nums[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < heapSize && nums[rightChild] > nums[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = rightChild;
}
if (maxIndex != i){
swap(nums, maxIndex, i);
heapify(nums, maxIndex, heapSize);
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
补充:堆排序(leetcode 912)
代码如下:
public void heapSort(int[] nums) {
int heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize);
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){
swap(nums, 0, i);
heapSize--;
heapify(nums, 0, heapSize);
}
}
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] nums, int heapSize){
for (int i = (heapSize - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){
heapify(nums, i, heapSize);
}
}
public void heapify(int[] nums, int i, int heapSize){
int leftChild = 2 * i + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * i + 2;
int maxIndex = i;
if (leftChild < heapSize && nums[leftChild] > nums[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < heapSize && nums[rightChild] > nums[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = rightChild;
}
if (maxIndex != i){
swap(nums, maxIndex, i);
heapify(nums, maxIndex, heapSize);
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
heapSort(nums);
return nums;
}