题目:
A clique is a complete graph, in which there is an edge between every pair of the vertices. Given a graph with N vertices and M edges, your task is to count the number of cliques with a specific size S in the graph.
Input:
The first line is the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains 3 integers N,M and S (N ≤ 100,M ≤ 1000,2 ≤ S ≤ 10), each of the following M lines contains 2 integers u and v (1 ≤ u < v ≤ N), which means there is an edge between vertices u and v. It is guaranteed that the maximum degree of the vertices is no larger than 20.
Output:
For each test case, output the number of cliques with size S in the graph.
题意:
给出一个图有n个点、m条边,给出子图的大小s,要求求出子图是一个完全图,而且图中需要有s个点。
PS:
我竟然把这个题目读成了求图中点数为s的环的个数,这个锅背的很强,,,,
首先回顾一下完全图的性质:完全图中任意一个点与其他的所有的点都有连边。如下:
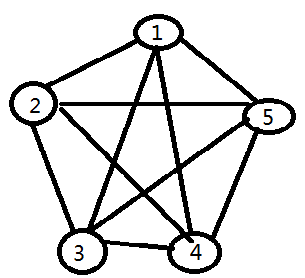
所以有n个点的完全图会有n*(n-1)/2条边。
思路:这个题如果双向建图,然后遍历求点数为s的完全图,铁定TLE,因为同一个图会被多次搜索。要避免重复搜索,可以单向建图,从小到大dfs遍历,同时在path数组中记录已经在完全图中的点,只要当前的点和之前path中的点都有边(这样path中所有的点才能构成完全图),就将该点记录到path中,点数达到s,答案ans++。
代码:

#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <set> #include <vector> using namespace std; const int maxn = 100+10; int m,n,s,ans; int mp[maxn][maxn]; int path[maxn]; vector<int> G[maxn]; int read() { int res = 0; char op = getchar(); if(op>='0' && op<='9') { res = op-'0'; op = getchar(); } while(op>='0' && op<='9') { res = res*10 + op-'0'; op = getchar(); } return res; } void init() { ans = 0; memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp)); memset(path,0,sizeof(path)); for(int i = 0; i<maxn; i++) G[i].clear(); } void dfs(int i,int cnt) { if(cnt == s) { ans++; return; } for(int j = 0; j<G[i].size(); j++) { int u = G[i][j],f = 0; for(int k = 1; k<=cnt; k++)//看点u是否和path中的点是否都有边相连 { if(mp[u][path[k]] == 0) { f = 1; break; } } if(!f)//都想连就存入path继续遍历 { path[cnt+1] = u; dfs(u, cnt+1); path[cnt+1] = 0; } } } int main() { int T; T = read(); //scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { init(); n = read(),m = read(),s= read(); //scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); for(int i = 0; i<m; i++) { int st,en; st = read(),en = read(); //scanf("%d%d",&st,&en); if(st>en)//单向建图,避免重复遍历 G[en].push_back(st); else G[st].push_back(en); mp[st][en] = 1,mp[en][st] = 1;//在遍历的时候用来检查是否能构成完全图 } for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++) { path[1] = i;//记录拿出的可以构成完全图的点 dfs(i,1); path[1] = 0; } printf("%d ",ans); } return 0; }
