1. 从函数重载到运算符重载
1.1 多态性
◼ 使用一致的接口(uniform interface)处理不同类型的数据
◼例子:运算符重载(+)
3.14 + 0.0015 = 3.1415
[1, 2, 3] + [4, 5, 6] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[3+4i] + [1+5i] = [4+9i]
"coffee" + " tea" = "coffee tea"
1.2 函数重载
一个名字,却可以有好几个函数,根据参数的个数和种类区分
1.3 运算符重载
一个运算符,保留功能,对象可能不同
1.4 复数类(Complex)的实现:(a+bi)+(c+di) = (a+c) + (b+d)i
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Complex { float real, imag; //实部和虚部 public: Complex(float r=0,float i=0) { real = r; imag = i; } Complex operator+(Complex other) //+运算符的重载 { Complex r; r.real = real + other.real; r.imag = imag + other.imag; return r; } void Output() { if(imag>0) cout << real << "+" << imag << "i" << endl; else cout << real << imag << "i" << endl; } }; int main() { Complex a(2,3), b(3, 4), c; c = a + b; c.Output(); return 0; }
2.运算符重载规则
2.1 入选
◼可重载
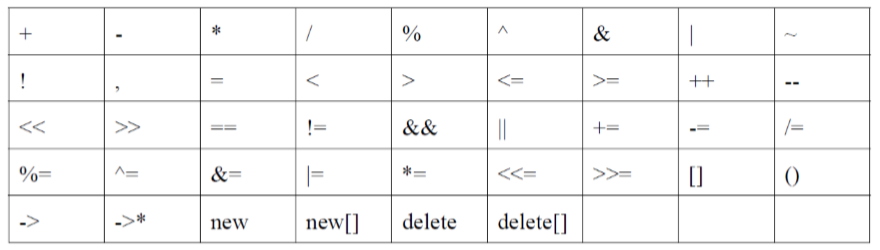
◼不可重载
①. ② .* ③:: ④?:
2.2 重载规则
◼ 重载后运算符的优先级和结合性不变
◼ 运算符操作数的个数不能改变
◼ 不能重载C++中不支持的运算符 (@、#、$等,emmmm,拒绝创新喽)
◼ 保持运算符的语义(加号不能当作减号用,这样别人会误会的)
3.重载方式
3.1 重载为类的成员函数
◼ 定义
返回类型 [类名::]operator 运算符(形参表) {}
Complex operator + (Complex op2);
一般是一个对象 可以省略一个形参,另一个参数通过this指针隐式传递
class Complex { public: Complex(double=0.0,double=0.0);//constructor Complexoperator+(const Complex &);//addition private: double real; //real part double imaginary;//imaginary part }; Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex &operand2)
{ return Complex(real+operand2.real, imaginary+operand2.imaginary); }
重载为成员函数时,参数个数为运算符目数-1
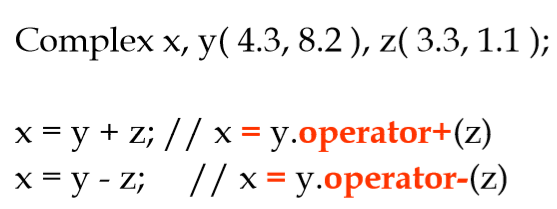
Complex Complex::operator=(Complex c2) { real = c2.real; imag = c2.imag; return *this; //指针的使用 }
◼前缀与后缀运算符

// Overload postfix ++ for Complex. Complex Complex::operator++(int x) //后缀的话要传入一个参数加以区分 { Complex r = *this; //要新建一个指针 real++; imag++; return r; } // Overload prefix ++ for Complex. Complex Complex::operator++() //前缀的话就是普通的,默认是前缀的 { ++real; ++imag; return *this; //直接返回就行 } int main() { Complex a(2,3), b(3, 4), c; c = a * b; Complex d = ++c; //但是可以看到在使用的时候没有区别 Complex e = d++; //后缀并不需要传递那个int d.Output(); e.Output(); return 0; }
3.2 重载为类的非成员函数(一般为友元函数)
◼ 定义
friend 返回类型 operator 运算符(形参表) {}
friend Complex operator + (Complex op1, Complex op2);
◼ 友元函数没有this指针,需给出所有传递参数
◼ 友元函数的操作灵活性
当运算符左右为不同类型数据时,比如a = 3 + b;,重载为类的成员函数无法实现
friend Complex operator+(float x, Complex c) { Complex r; r.real = x+c.real; r.imag = c.imag; return r; }
3.3 重载为普通函数
class Complex {
public:
Complex( double r = 0.0, double i= 0.0 ){
real = r;
imaginary = i;
}
double real; // real part
double imaginary; // imaginary part
};
Complex operator+( const Complex & a ,const Complex & b)
{
return Complex( a.real+b.real,a.imaginary+b.imaginary);
}
Complex a(1,2), b(2,3),c;
// “类名(参数表)”就代表个对象
c = a + b; // 等效于c = operator+(a,b);
重载为普通函数时,参数个数为运算符目数
注意:类的成员变量要为public(故用得少)
3.4 第一二种方式的比较
◼一般,单目运算符(只接收一个操作数的运算符,如++)重载是类的成员函数,双目运算符(俩操作数,如a=b+c)重载为类的友元函数(另一个可以是数字)
4.典型运算符重载
4.1 输入输出流:“<<”和“>>”只能以友元函数的方式重载
int main() { Complex a, b, c; cin >> a >> b; //实现直接输入输出 c = a * b; Complex d = ++c; Complex e = d++; d = d+1.01; e = 1.01+e; cout << d << e; return 0; } friend istream &operator>>(istream &in, Complex &c)//因为要改变值所以有引用 { in >> c.real >> c.imag; return in; } friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Complex c) { if(c.imag>0) out << c.real << "+" << c.imag << "i" << endl; else out << c.real << c.imag << "i" << endl; return out; }
4.2 “=”
类似于浅拷贝&深拷贝

4.3 “[ ]” :防止数组越界
float &Complex::operator[](int i) //要修改时,就要用引用 { if (i==0) //实部是啥 return real; else if(i==1) return imag; else { cout << "Out of boundary" << endl; exit(1); } } int main() { Complex c(3, 4); cout << c[0] << endl; //输出实部 c[1] = 5; cout << c; c[2] = 6; //一共就俩数,超了 }
4.4 “()”:自动执行和表达式中的使用
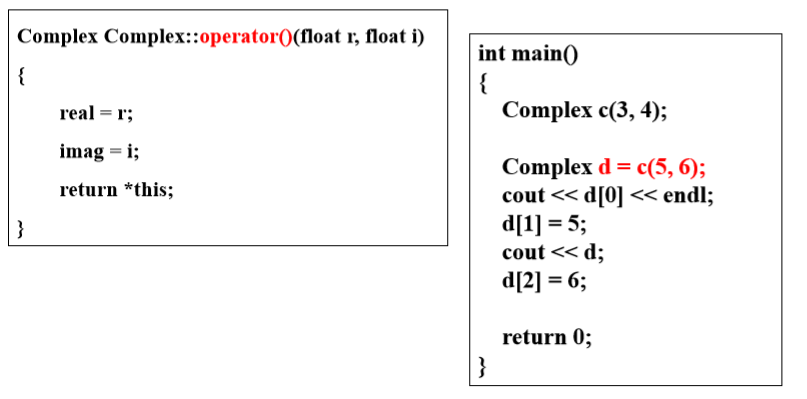
4.5 类型转换运算符:强制类型转化类的对象

5.运算符函数参数/返回类型

