> library(lattice)
> library(sp)
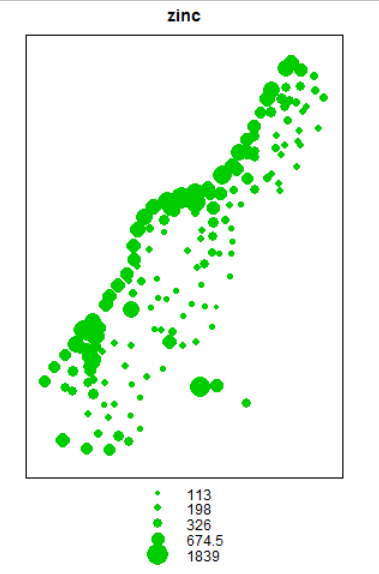
> data(meuse)
> coordinates(meuse) <- c("x","y")
> spplot(meuse, "zinc", do.log=T)
> bubble(meuse, "zinc", do.log=T, key.space="bottom")

> xyplot(log(meuse$zinc)~sqrt(meuse$dist), meuse, main="", xlab="dist", ylab="Zn")

> meuse$fitted.s <- predict(zn.lm, meuse) - mean(predict(zn.lm,meuse)) > meuse$residuals <- residuals(zn.lm) > spplot(meuse, c("fitted.s", "residuals")) > spplot(meuse, c("fitted.s", "residuals"))
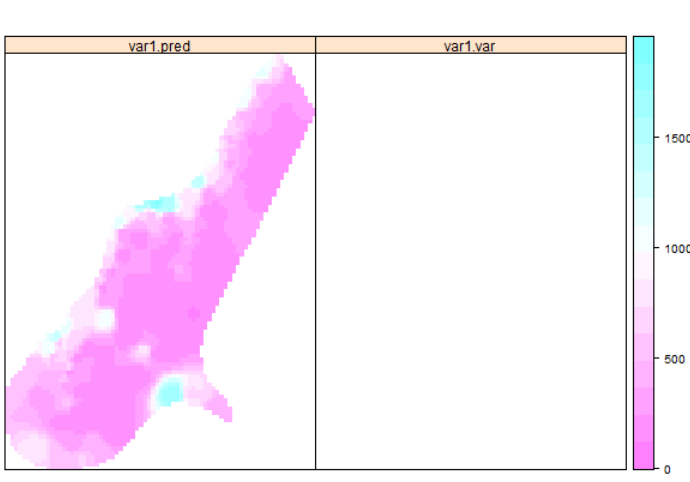
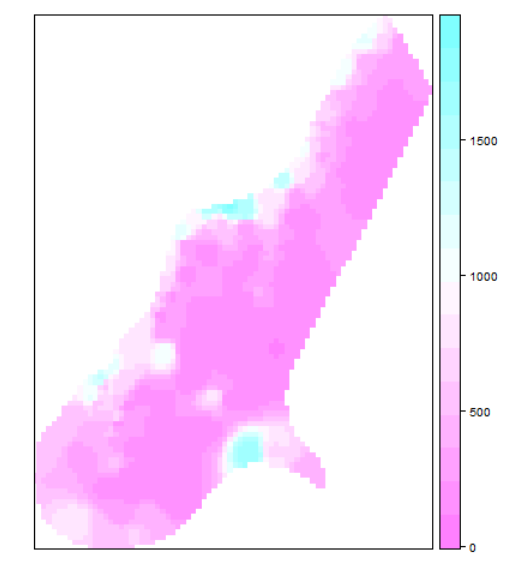
> library(gstat) > idw.out <- idw(zinc~1, meuse, meuse.grid, idp=1) [inverse distance weighted interpolation] > spplot(idw.out)
> spplot(idw.out, c("var1.pred"))
3、使用线性回归:
> zn.lm <- lm(log(zinc) ~ sqrt(dist), meuse) > meuse.grid$pred <- predict(zn.lm, meuse.grid) > meuse.grid$se.fit <- predict(zn.lm, meuse.grid, se.fit=TRUE)$se.fit
> spplot(meuse.lm)
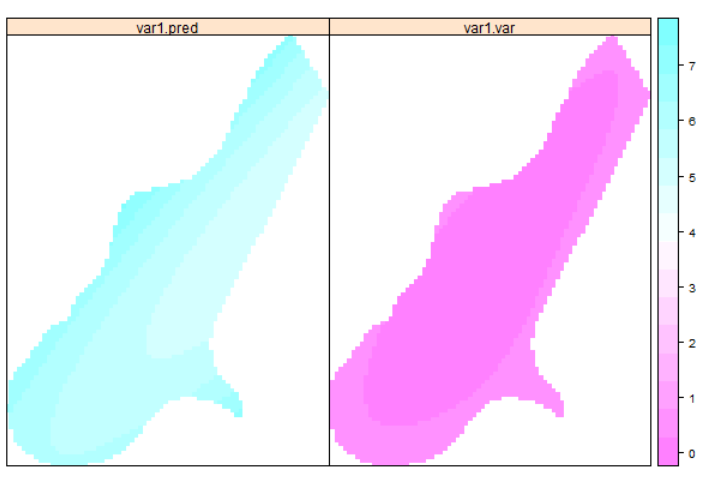
方式一、采用krige函数
> meuse.lm <- krige(log(zinc) ~ sqrt(dist), meuse, meuse.grid)
[ordinary or weighted least squares prediction]
> spplot(meuse.lm)

> meuse.lm <- krige(log(zinc)~1, meuse, meuse.grid, degree=2)
> spplot(meuse.lm)
方式二:采用lm函数
> lm(log(zinc)~I(x^2)+I(y^2)+I(x*y)+x+y, meuse)
> lm(log(zinc)~poly(x,y,degree=2), meuse)