子查询:
含义:
出现在其他语句中(不仅仅是放在select语句中,在其它增删改中都可以用,只是用在查询中是最多的)的select语句,称为子查询或内查询
外部的查询语句,称为主查询语句,称为主查询或外查询。
示例: SELECT first_name FROM employees WHERE
department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM departments
WHERE location_id=1700)
分类:
按子查询出现的位置:
select后面:
仅仅只支持标量子查询
from 后面:
支持表子查询(只要是个结果集就行)
where或having后面:♦ --侧重点
标量子查询 ♣
列子查询 ♣
行子查询(用的较少)
exists后面(称为:相关子查询):
表子查询(结果集)
按结果集的行列数不同:
标量子查询(又称为:单行子查询)(结果只有一行一列):
列子查询(又称:多行子查询)(结果集只有一列多行):
行子查询(结果集有一行多列):
表子查询(结果集一般为多行多列):
一.where或having后面
1.标量子查询(单行子查询)
2.列子查询(单行子查询)
3.行子查询(有很多列,很多行)
特点:
1.子查询放在小括号内
2.子查询一般放在条件的右侧
3.标量子查询,一般搭配着单行操作符,其实就是条件运算符(> < >= <= = <>)使用
列子查询,一般搭配着多行操作符(常见的有:IN,ANY/SOME,ALL)使用
4.子查询的执行优先于主查询执行,主查询的条件用到了子查询的结果
#1.标量子查询
#案列1:谁的工资比Abel高?
#(1)查询Abel的工资
select salary
from employees
where last_name = 'Abel'
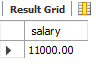
#(2)查询员工的信息,满足salary>(1结果)
select *
from employees
where salary>( #直接放where salary > 11000。这种被称为硬编码,如果(1)中Abel的工资变了,这种情况就不对了,还得修改
select salary
from employees
where last_name = 'Abel');

#案列2:返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary比 143号员工多的员工 姓名,job_id和工资
#(1)查询141号员工的job_id
select job_id
from employees
where employee_id = 141
#(2)查询员工号为143号的员工的工资
select salary
from employees
where employee_id = 143
#(3)查询员工 姓名,job_id和工资
select concat(first_name,'-',last_name) as 姓名,job_id,salary
from employees
where job_id = (
select job_id #这里只能select job_id这一个columns。多了会报错:Error Code:1241.Operand should contain 1 columns(1) . 如果查询的不是job_id 这个
from employees #column,不会报错,但查不到任何内容如图:这里是将job_id改为first_name得到的结果: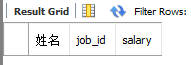
where employee_id = 141)
and salary > (
select salary
from employees
where employee_id = 143
);
#案例3:返回工资最少的员工的last_name,job_id和salary
#(1)查询工资最少的员工的工资
select min(salary)
from employees
#(2)查询员工的last_name,job_id和salar
select last_name,job_id,salary
from employees
where salary = (
select min(salary)
from employees
);

#案例4:查询最低工资大于50号部门最低工资的部门和其最低工资
#(1)50号部门的最低工资
select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = 50

#(2)查询每个部门的最低工资
select min(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id;

#(3) 在(2)基础上筛选,满足min(salary)>(1)
select min(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
having min(salary)>(
select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = 50
);
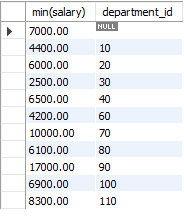
#非法使用标量子查询
select min(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
having min(salary)>(
select min(salary) #如果是select salary。因为50号部门的员工的工资有很多。明明这儿应该用标量子查询,但是这儿用到了列子查询(多行子查询)。报错:Error Code:1242.Subquery returns more than 1 row.(子查询返回超过1row)
from employees
where department_id = 50 #如果选择一个不存在的部门:where department_id = 250(不存在值为250的department_id)。不报错,但这也属于非法使用。结果:
);
#2.列子查询(多行子查询) #因为他的结果是一列多行
#案列1:返回location_id是1400或1700的部门中的所有员工姓名
#(1)查询location_id是1400或1700的部门编号
select department_id
from departments
where location_id in (1400,1700);
#(2)查询员工姓名,要求部门编号是(1)列表中的某一个
子查询实现:
select concat(first_name,'-',last_name) as name,distinct department_id
from employees
where department_id in (
select department_id
from departments
where location_id in (1400,1700)
);
join实现:
select concat(employees.first_name,'-',employees.last_name) as name,employees.department_id
from employees
inner join departments
on employees.department_id = departments.department_id
where location_id in (1400,1700)
#案列2:返回其它工种中(不包括'IT_PROG')比job_id为'IT_PROG'任一工资低的员工的:工号,姓名,job_id,及salary
#(1)查询job_id为'IT_PROG'部门任一工资
select distinct salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG';

#(2)查询员工号,姓名,job_id以及salary,salary<any((1))的任意一个
select last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary
from employees
where salary<any(
select distinct salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
) and job_id <> 'IT_PROG';
#或
select last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary
from employees
where salary<any(
select max(salary)
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
) and job_id <> 'IT_PROG';

#案列3:返回其它工种中(不包括'IT_PROG')比job_id为'IT_PROG'所有工资低的员工的:工号,姓名,job_id,及salary
select last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary
from employees
where salary < all(
select distinct salary
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
) and job_id <> 'IT_PROG';

#或
select last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary
from employees
where salary < (
select min(salary)
from employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
) and job_id <> 'IT_PROG';
#3.行子查询(结果集一行多列或多行多列)
select * #行子查询:将多个字段(employee_id和salary),当成了一个虚拟的字段((employee_id,salary))来用
from employees
where (employee_id,salary) = ( #用得不多,有局限性,要求两个筛选条件,或者更多的筛选条件都用的是=
select min(employee_id),max(salary)
from employees
)
#(1)查询最小的员工编号
select min(employee_id)
from employee
#(2)查询最高工资
select max(salary)
from employees
#(3)查询员工信息
select *
from employees
where employee_id = (
select min(employee_id)
from employees
) and salary = (
select max(salary)
from employees
);

#二,放在select后面的子查询
#案例:查询每个部门的员工个数
select d.*,(
select count(*)
from employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id
) as 个数
from departments d;

#案例2:查询员工号=102的部门名
select (
select department_name
from departments d
inner join employees e
on d.department_id = e.department_id
where e.employee_id = 102
) as 部门名;

#三,from后面
将子查询结果充当一张表,要求必须其别名
#案例:查询每个部门的平均工资的工资等级
#(1)查询每个部门的平均工资
select avg(salary),department_id
from employees
group by department_id
select * from job_grades;
#(2)连接(1)的结果集和job_grades表,筛选条件平均工资between lowest_sal and highest
select ag_dep.*,g.grade_level
from (
select avg(salary) ag,department_id
from employees
group by department_id
) ag_dep
inner join job_grades g
on ag_dep.ag between lowest_sal and highest_sal
#四、exists后面的子查询(相关子查询)
/*
语法:
exists(完整的查询语句)
结果:
1或0
*/
select exists(select empooyee_id from employees); #exists(是否存在,bool类型)只关心(select empooyee_id from employees)中是否有值,有值为1,没有值为0
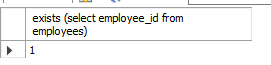
select exists(select employee_id from employees where salary = 300000);

#案例1:查询有员工名的部门名
select department_name
from departments d
where exists(
select *
from employees e
where d.department_id = e.department_id
);
#案例2:查询没有女朋友的男神信息
#in
select bo.*
from boys bo
where bo.id not in(
select boyfriend_id
from beauty
);
#exists
select bo.*
from boys bo
where not exists(
select boyfriend_id
from beauty b
where bo.id = b.boyfriend_id
);
