16.1 更多集合接口
集合类(这里指IEnumerable层次结构)实现的接口层次结构
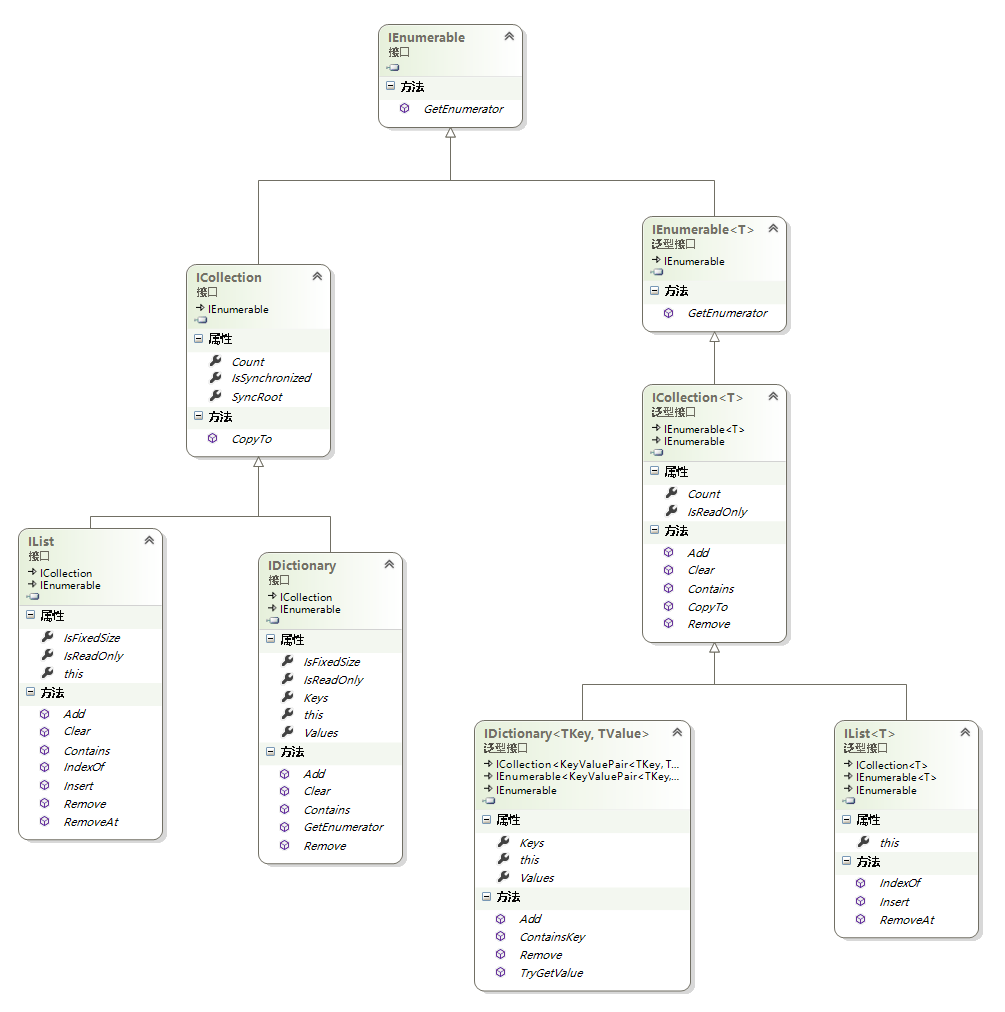
16.1.1 IList<T>与IDictionary<TKey,TValue>
IList<T>(侧重位置索引获取值)与 IDictionary<TKey,TValue>(侧重通过键来获取值)。16.1.2 ICompatable<T>
高级主题:用IComparer<T>排序
public static void Main()
{
Contact aaa = new Contact() { LastName = "bbb", FirstName = "ddd" };
Contact bbb = new Contact() { LastName = "aaa", FirstName = "ccc" };
//Console.WriteLine(new NameComparison().Compare(aaa, bbb));
List<Contact> contactlist = new List<Contact>();
contactlist.Add(aaa);
contactlist.Add(bbb);
foreach (var contact in contactlist)
{
Console.WriteLine(contact.LastName + " ");
}
//排序
contactlist.Sort(new NameComparison());
foreach (var contact in contactlist)
{
Console.WriteLine(contact.LastName + " ");
}
Console.Read();
}
class Contact
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
class NameComparison : IComparer<Contact>
{
public int Compare(Contact x, Contact y)
{
int result;
if (Contact.ReferenceEquals(x, y))
{
result = 0;
}
else
{
if (x == null)
{
result = 1;
}
else if (y == null)
{
result = -1;
}
else
{
result = StringCompare(x.LastName, y.LastName);
if (result == 0)
{
result =
StringCompare(x.FirstName, y.FirstName);
}
}
}
return result;
}
private static int StringCompare(string x, string y)
{
int result;
if (x == null)
{
if (y == null)
{
result = 0;
}
else
{
result = 1;
}
}
else
{
result = x.CompareTo(y);
}
return result;
}
}
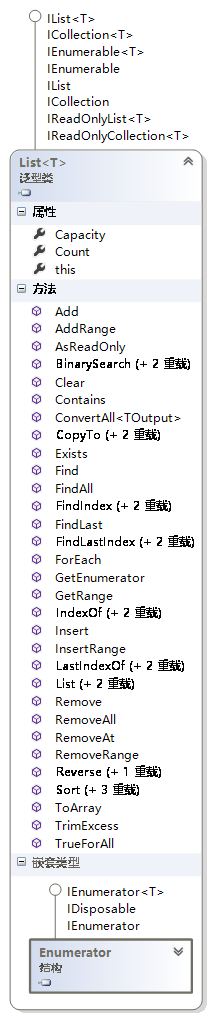
16.2.1 列表集合:List<T>
List<string> list = new List<string>();
// Lists automatically expand as elements
// are added.
list.Add("Sneezy");
list.Add("Happy");
list.Add("Dopey");
list.Add("Doc");
list.Add("Sleepy");
list.Add("Bashful");
list.Add("Grumpy");
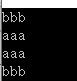
list.Sort();
Console.WriteLine(
"In alphabetical order {0} is the "
+ "first dwarf while {1} is the last.",
list[0], list[6]);
list.Remove("Grumpy");
16.2.3 搜索List<T>
List<string> list = new List<string>();
int search;
list.Add("public");
list.Add("protected");
list.Add("private");
list.Sort();
search = list.BinarySearch("protected internal");
if (search < 0)
{
list.Insert(~search, "protected internal");
}
foreach (string accessModifier in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(accessModifier);
}
高级主题:使用 FindAll() 查找多个数据项
public static void Main()
{
List<int> list = new List<int>();
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(4);
List<int> results = list.FindAll(Even);
foreach (int number in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
//2,2,4
Console.Read();
}
public static bool Even(int value)
{
return (value % 2) == 0;
}
16.2.4 字典集合:Dictonary<TKey,TValue>

Dictionary<Guid, string> dictionary =
new Dictionary<Guid, string>();
Guid key = Guid.NewGuid();
dictionary.Add(key, "object");
还有个选择是索引操作符
Dictionary<Guid, string> dictionary =
new Dictionary<Guid, string>();
Guid key = Guid.NewGuid();
dictionary[key] = "object";
dictionary[key] = "byte";
由于键和值都要添加到字典中,所以用于枚举字典中的元素的 foreach 循环的循环变量必须是 KeyValuePair<TKey,TValue> 。
Dictionary<string, string> dictionary = new
Dictionary<string, string>();
int index = 0;
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "object");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "byte");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "uint");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "ulong");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "float");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "char");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "bool");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "ushort");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "decimal");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "int");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "sbyte");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "short");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "long");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "void");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "double");
dictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "string");
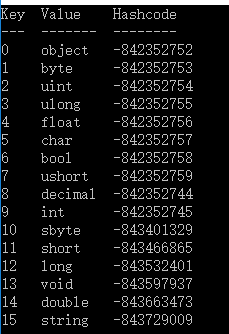
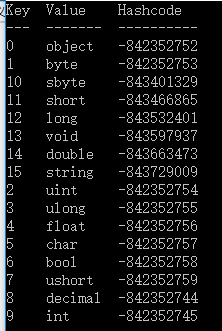
Console.WriteLine("Key Value Hashcode");
Console.WriteLine("--- ------- --------");
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, string> i in dictionary)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0,-5}{1,-9}{2}",
i.Key, i.Value, i.Key.GetHashCode());
}
16.2.5 已排序集合:SortedDictionary<TKey,TValue>和SortedList<T>
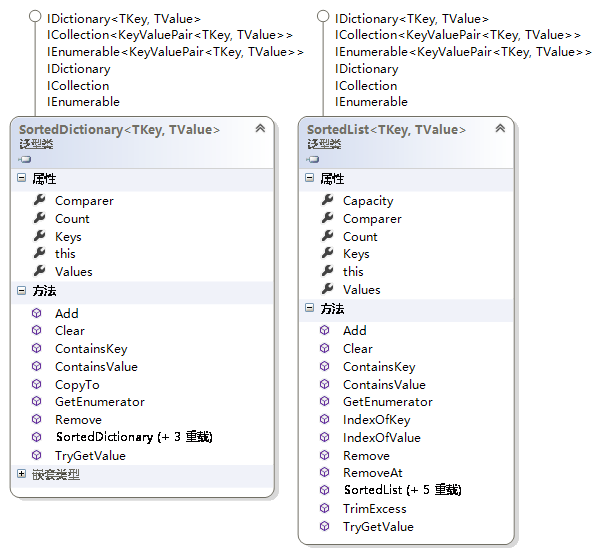
SortedDictionary<string, string> sortedDictionary =
new SortedDictionary<string, string>();
int index = 0;
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "object");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "byte");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "uint");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "ulong");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "float");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "char");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "bool");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "ushort");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "decimal");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "int");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "sbyte");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "short");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "long");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "void");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "double");
sortedDictionary.Add(index++.ToString(), "string");
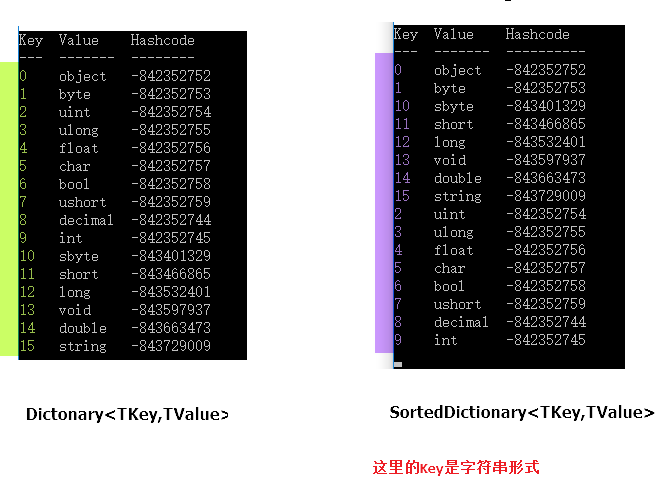
Console.WriteLine("Key Value Hashcode");
Console.WriteLine("--- ------- ----------");
foreach (
KeyValuePair<string, string> i in sortedDictionary)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0,-5}{1,-9}{2}",
i.Key, i.Value, i.Key.GetHashCode());
}
16.2.6 栈集合:Stack<T>
16.2.7队列集合:Queue<T>
16.2.8 链表:LinkedList<T>
16.5.1 迭代器定义
16.5.2 迭代器语法
public IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator()
{
//...
return new List<T>.Enumerator();//This will be implimented in 16.16
}