在上一章内容中,详细的介绍了什么是Spring,Spring的历史与发展和Spring的一些特点。所以这一章我们来创建一个Spring的入门案例HelloSpring。
1、创建项目
首先我们创建一个名称为Hello_Spring的Maven项目。
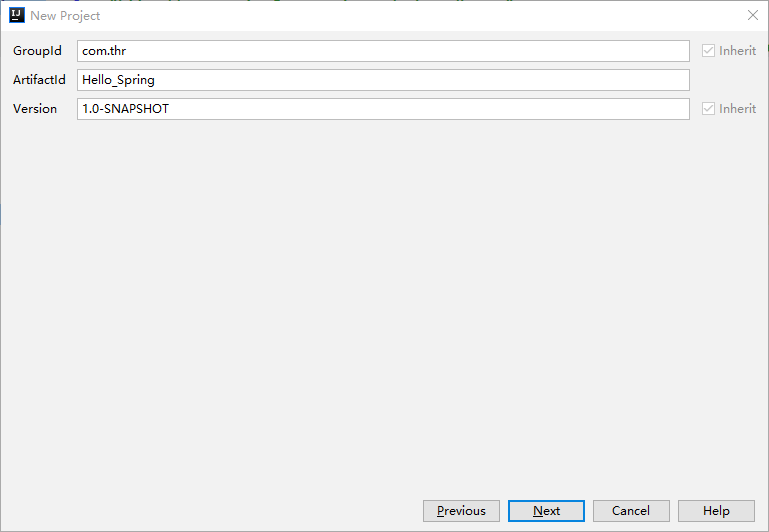
2、导入依赖
然后在pom.xml中导入spring依赖,我们暂时只导入一个,如下:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version>
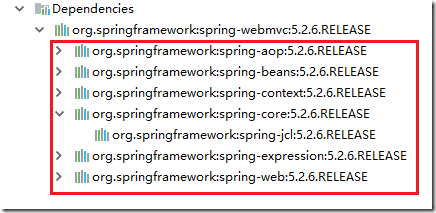
</dependency>因为这个依赖会自动关联很多jar,如下图:
3、创建Spring配置文件
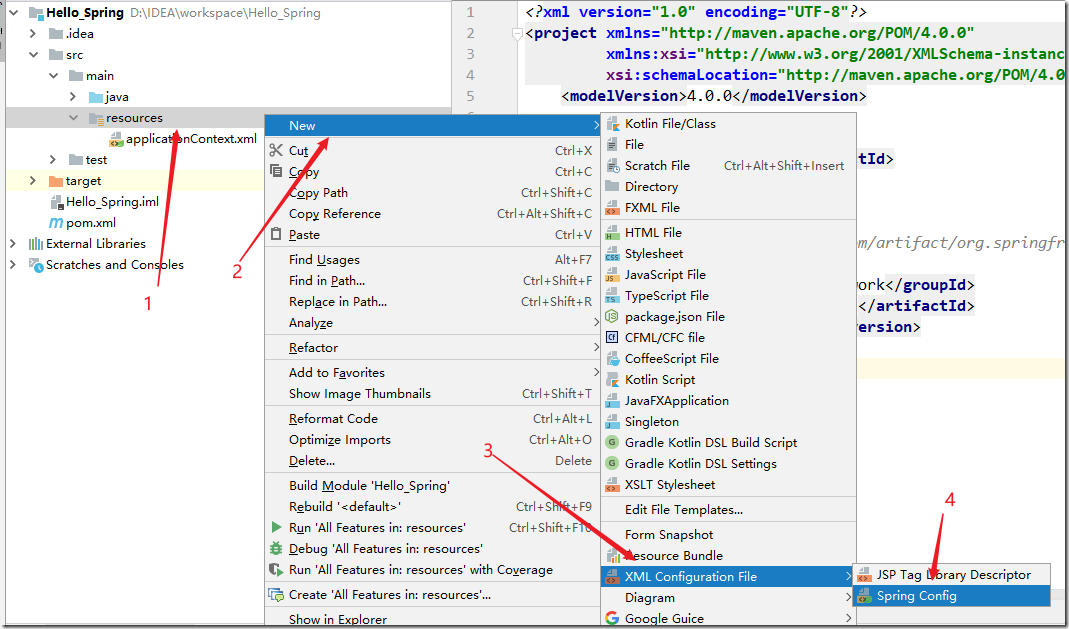
在src/mian/resources目录下创建一个applicationContext.xml文件。
【右击resources—>New—>选择XML Configuration File—>Spring Config】
注意:前提是要导入Spring的依赖,否则不会有Spring Config。
4、创建接口HelloSpring
在src/main/java目录下创建一个HelloSpring接口,并且定义一个sayHello()方法,代码如下所示。
package com.thr;
/**
* @author tanghaorong
* @desc HelloSpring接口
*/
public interface HelloSpring {
void sayHello();
}
5、创建接口实现类
实现上面创建的HelloSpring接口,并在方法中编写一条输出语句,代码如下所示。
package com.thr;
/**
* @author tanghaorong
* @desc HelloSpring实现类
*/
public class HelloSpringImpl implements HelloSpring {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello Spring");
}
}
6、配置applicationContext.xml
接下来配置我们在src/main/resources目录中创建的applicationContext.xml文件。
因为这是一个Spring入门的例子,所以用 xml 配置文件的方式来配置对象实例,我们要创建的对象实例要定义在 xml 的 <bean> 标签中。
其中<bean>标签表示配置一个对象实例。<bean>标签常用的两个参数 id 和 class ,id表示标识符(别名),class 表示对象实例类的全限定名。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!--将指定类配置给Spring,让Spring创建其对象的实例-->
<!--id:标识符(别名) class:需要实例化的类路径-->
<bean id="helloSpring" class="com.thr.HelloSpringImpl"></bean>
</beans>这样HelloSpringImpl的实例对象就由Spring给我们创建了,名称为helloSpring,当然我们也可以创建多个对象实例,如下:
<bean id="helloSpring" class="com.thr.HelloSpringImpl"></bean>
<bean id="helloSpring1" class="com.thr.HelloSpringImpl"></bean>
<bean id="helloSpring2" class="com.thr.HelloSpringImpl"></bean>7、配置测试类
在src/test/java下,创建测试类TestHelloSpring,代码如下:
package com.thr;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author tanghaorong
* @desc 测试类
*/
public class TestHelloSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//传统方式:new 对象() 紧密耦合
HelloSpring helloSpring = new HelloSpringImpl();
helloSpring.sayHello();
//Spring方式:XML解析+反射+工厂模式
//1.初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.通过容器获取helloSpring实例,getBean()方法中的参数是bean标签中的id
HelloSpring helloSpring1 = (HelloSpring) applicationContext.getBean("helloSpring");
//3.调用实例中的方法
helloSpring1.sayHello();
}
}因为这里是测试使用,所以需要初始化Spring容器,并且加载配置文件,实际开发中这一步不需要。
8、项目整体目录结构
以上全部创建完成后,项目的整体目录结构如下图:
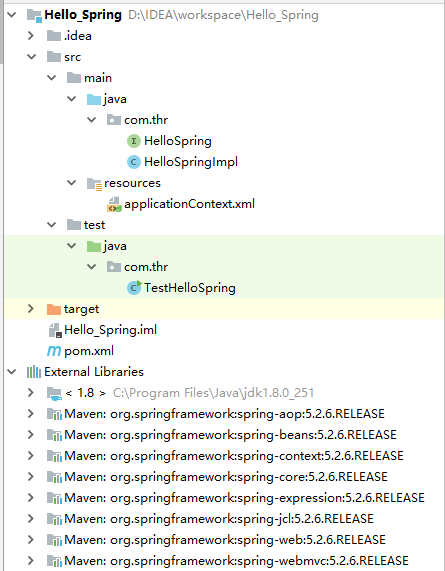
9、运行测试
运行的结果会打印两遍Hello Spring,第一步是传统 new对象的方式,第二种是使用Spring IOC的方式,结果如下图:
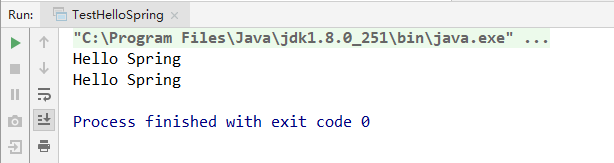
可以发现两种方式都创建了HelloSpring的对象实例,但是Spring IOC方式更加方便,而且低耦合,这样更有利于后期的维护。
这篇文章只是一个简单的入门案例,所以例子非常简单,也希望大家多多指点,谢谢!