认证的使用
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from api import models
# 认证类
class TokenAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.query_params.get('token')
user_object = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if user_object:
return (user_object, token)
return (None, None)
# 认证类的应用
# 单独的视图认证应用
class OrderView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication, ] #设置成空列表代表没有权限
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
print(request.user)
print(request.auth)
return Response('order')
# 认证的全局应用
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES"=["api.views.auth.MyAuthentication",]
}
认证的源码分析
执行流程
1.请求进来执行dispatch方法中的initialize_request方法
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request)
return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
)
#会对request对象进行重新封装,把老的request封装成新的request
执行self.get_authenticators()
def get_authenticators(self):
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes] # 循环自定义的认证类,生成认证对象列表封装到request中
authentication_classes
settings中的认证配置
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":["api.views.auth.MyAuthentication]
2.执行inital
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
.......略过的代码
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
self.perform_authentication(request) #认证函数
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request)
3.执行perform_authentication(request)认证函数
def perform_authentication(self, request):
request.user# 调用request的user方法
4.
@property
def user(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._user
5.执行_authenticate()方法
def _authenticate(self):
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self) #每个认证对象(authenticator)中的authenticate方法,可以重写该方法进行定制,之前已经封装到request中了
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return
self._not_authenticated()
#返回元祖(user,auth)代表认证成功
#抛出异常代表认证失败
#返回None继续下个认证
看张图吧!

.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
正经点......
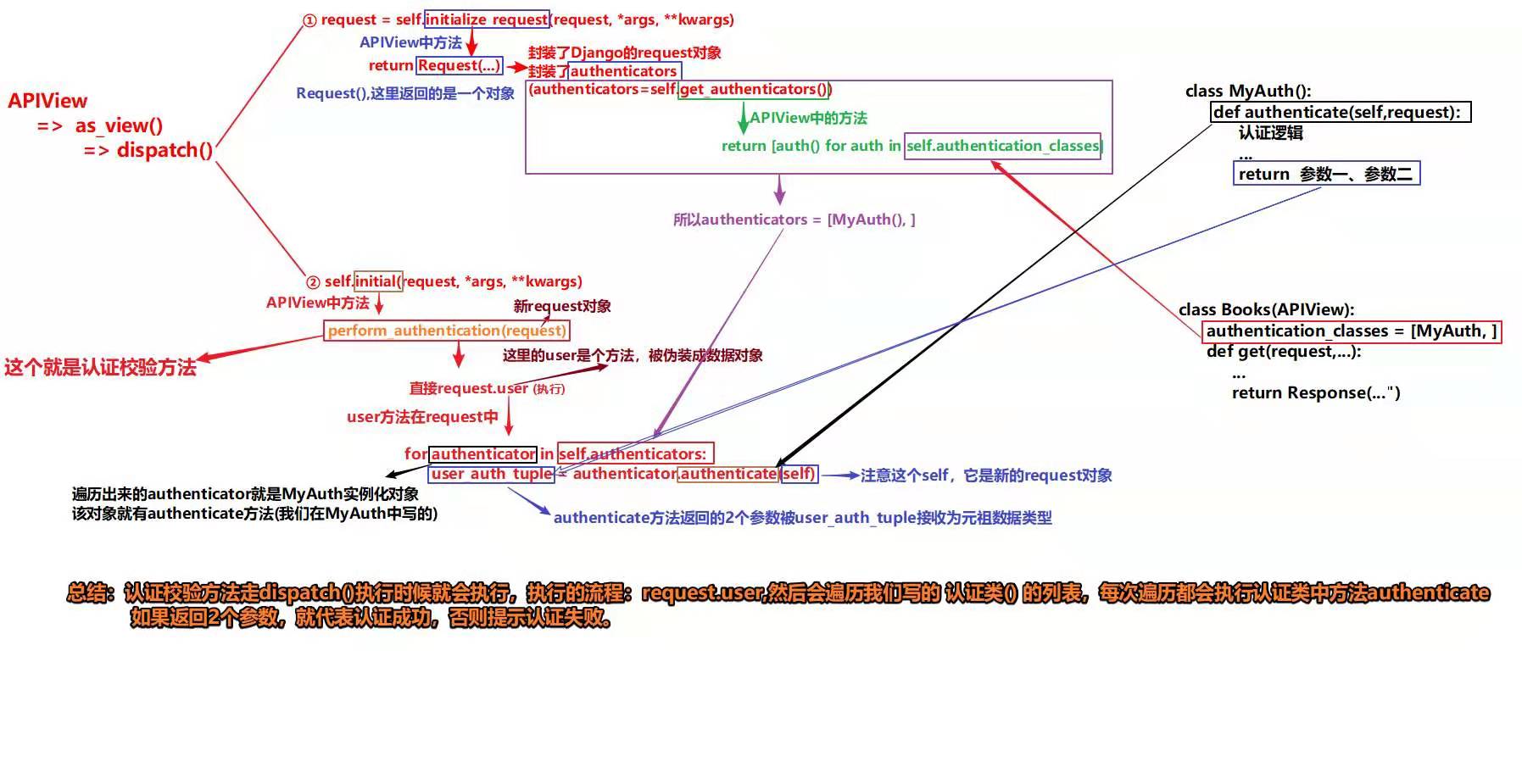
概括
1.请求进来时,先执行dispatch方法,对的request进行重新封装
2.执行get_authenticators(),循环authentication_classes得到这个认证类的对象,把对象也封装进去
3.执行initial中的perform_authentication(request),调用request.user,调用request的user方法(静态属性)
4.执行 _authenticate,循环authentication对象,调用authenticate方法返回元祖(user,auth)代表认证成功或者抛出异常代表认证失败或返回None继续下个认证