一.将读取文件夹内容,变为字典保存,代码如下:
def read_class_names(class_file_name):
'''loads class name from a file'''
names = {}
with open(class_file_name, 'r') as data:
for ID, name in enumerate(data):
names[ID] = name.strip(' ')
return names
a=read_class_names( "C:/Users/10107472/Desktop/repetition/data/classes/coco.names")
print(a)
print(type(a))
print(len(a))
结果如下:
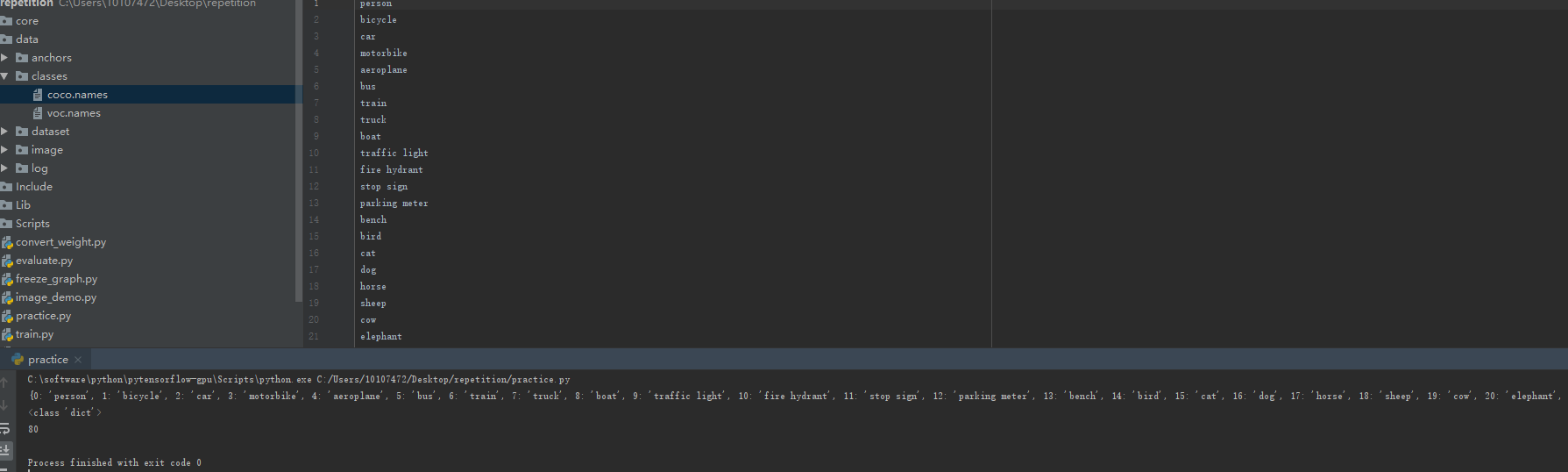
二.读取文件变为矩阵,代码如下:
def get_anchors(anchors_path):
'''loads the anchors from a file'''
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = np.array(anchors.split(','), dtype=np.float32)
return anchors.reshape(3, 3, 2)
a=get_anchors( "C:/Users/10107472/Desktop/repetition/data/anchors/coco_anchors.txt")
print(a)
print(type(a))
print(len(a))
结果如下:
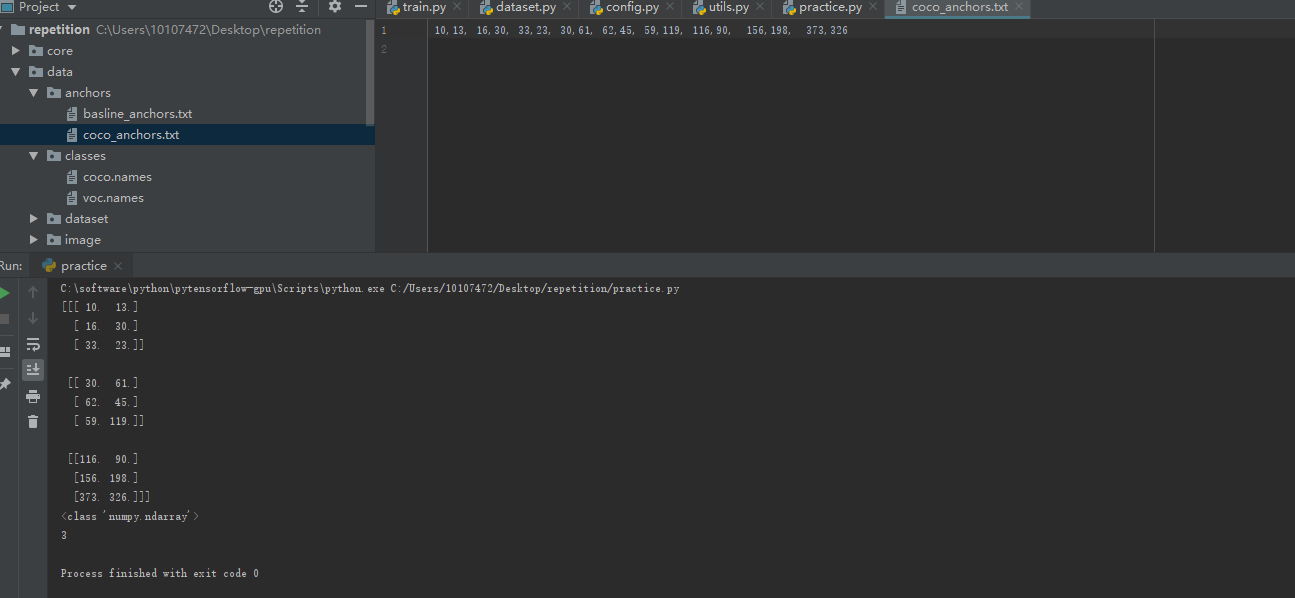
三 .将文件数据变成列表,代码如下:
with open("C:/Users/10107472/Desktop/repetition/data/dataset/voc_train.txt", 'r') as f:
txt = f.readlines() # 已经读取了文件所有数据,并以列表形式保存,每个换行符为界,组成该列表的元素,但有一个
的符号
annotations = [line.strip() for line in txt if len(line.strip().split()[1:]) != 0] # 此代码去掉
的符号
np.random.shuffle(annotations) # 直接将annotations进行随机位置变换
print(annotations)
print(type(annotations))
print(len(annotations))
结果如下:
