大致可以分为三类:数值、日期/时间和字符串(字符)类型。
学习链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12b411K7Zu?p=118
一、数值类型
| 类型 | 大小 | 范围(有符号) | 范围(无符号) | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TINYINT | 1 byte | (-128,127) | (0,255) | 小整数值 |
| SMALLINT | 2 bytes | (-32 768,32 767) | (0,65 535) | 大整数值 |
| MEDIUMINT | 3 bytes | (-8 388 608,8 388 607) | (0,16 777 215) | 大整数值 |
| INT或INTEGER | 4 bytes | (-2 147 483 648,2 147 483 647) | (0,4 294 967 295) | 大整数值 |
| BIGINT | 8 bytes | (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808,9 223 372 036 854 775 807) | (0,18 446 744 073 709 551 615) | 极大整数值 |
| FLOAT | 4 bytes | (-3.402 823 466 E+38,-1.175 494 351 E-38),0,(1.175 494 351 E-38,3.402 823 466 351 E+38) | 0,(1.175 494 351 E-38,3.402 823 466 E+38) | 单精度 浮点数值 |
| DOUBLE | 8 bytes | (-1.797 693 134 862 315 7 E+308,-2.225 073 858 507 201 4 E-308),0,(2.225 073 858 507 201 4 E-308,1.797 693 134 862 315 7 E+308) | 0,(2.225 073 858 507 201 4 E-308,1.797 693 134 862 315 7 E+308) | 双精度 浮点数值 |
| DECIMAL | 对DECIMAL(M,D) ,如果M>D,为M+2否则为D+2 | 依赖于M和D的值 | 依赖于M和D的值 | 小数值 |
1.1什么是有符号和无符号
有符号,即有正、0、负数,无符号,就是没有负数。
1.2 如何设置有符号和无符号
CREATE TABLE test(
t1 int,
t2 int UNSIGNED
);
desc test;
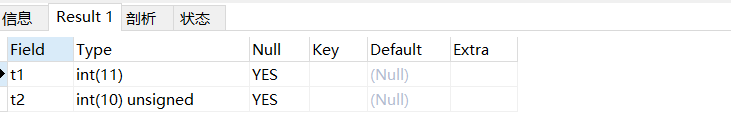
1、int没有指定长度,默认长度是11位,默认是有符号数
2、指定无符号数需要使用关键字UNSIGNED
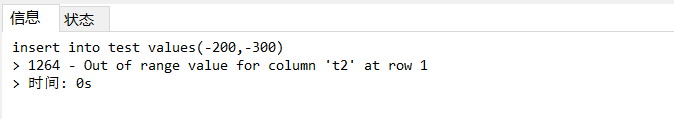
3、如果在无符号的字段,插入一个有符号数,数据插入不了
insert into test values(-200,-300);
commit;
4、创建表,指定int的长度,并不是这个字段实际的int长度,实际的int长度,由int数据类型的范围决定的,如果指定int长度,一般和填充(ZEROFILL)一起使用。
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t3 int(5)
)
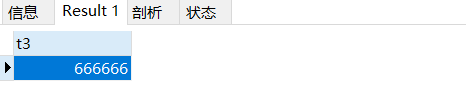
insert into test02 values(666666)
select * from test02;
上面的sql虽然超过长度5,但是能执行成功:
那么,这个int长度5的作用是什么呢?
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t3 int(5) ZEROFILL
);
insert into test02 values(11);
select * from test02;
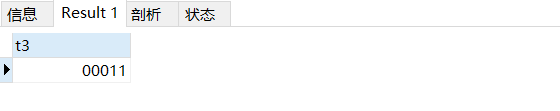
由上面的结果可见,长度不够时,填充了0
1.3 float、double、decimal
decimal是定点型。如果保存精度要求比较高,使用这个。
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t1 float(5,2),
t2 double(5,2),
t3 decimal(5,2)
);
insert into test02 values(123.45,123.45,123.45);
select * from test02;
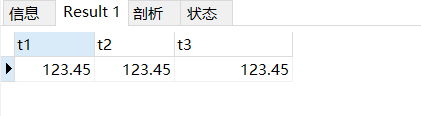
从上面的执行结果来看,没有什么区别。
注意(5,2) 5代表的是总长度,2代表的是小数点后的位数
如果小数位数过多,会四舍五入
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t1 float(5,2),
t2 double(5,2),
t3 decimal(5,2)
);
insert into test02 values(123.45,123.45,123.45);
insert into test02 values(123.456,123.456,123.456);
insert into test02 values(123.4,123.4,123.4);
select * from test02;
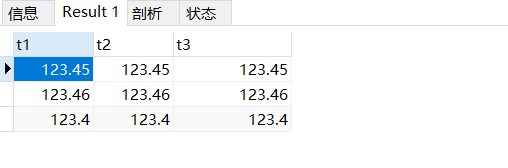
如果再插入一下的数据,数据插不进去,因为整数的长度是3
insert into test02 values(1523.4,1523.4,1523.4);
长度都可以省略:
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t1 float,
t2 double,
t3 decimal
);
desc test02;
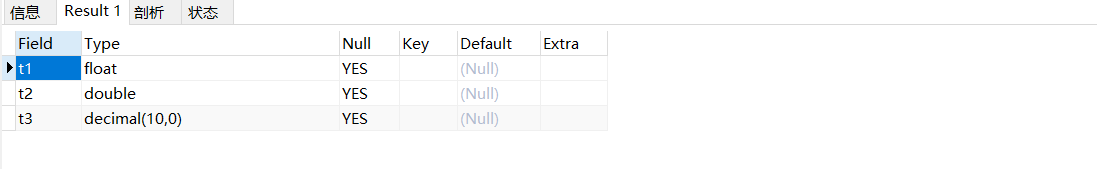
由上面的结果可知,如果是decimal,默认是(10,0),如果是float和double,则会根据插入数值的精度来决定精度
二、字符串类型
| 类型 | 大小 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR | 0-255 bytes | 定长字符串 |
| VARCHAR | 0-65535 bytes | 变长字符串 |
| TINYBLOB | 0-255 bytes | 不超过 255 个字符的二进制字符串 |
| TINYTEXT | 0-255 bytes | 短文本字符串 |
| BLOB | 0-65 535 bytes | 二进制形式的长文本数据 |
| TEXT | 0-65 535 bytes | 长文本数据 |
| MEDIUMBLOB | 0-16 777 215 bytes | 二进制形式的中等长度文本数据 |
| MEDIUMTEXT | 0-16 777 215 bytes | 中等长度文本数据 |
| LONGBLOB | 0-4 294 967 295 bytes | 二进制形式的极大文本数据 |
| LONGTEXT | 0-4 294 967 295 bytes | 极大文本数据 |
2.1char和varchar
char:固定长度的字符,空间相对消耗大,效率相对高,长度可以省略,默认为1
varchar:可变长度的字符,空间相对消耗小,效率相对低,长度不可省略
2.2枚举(了解)
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t1 ENUM('a','b','c')
);
insert into test02 values('a');
2.3集合(了解)
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t1 SET('a','b','c')
);
insert into test02 values('a');
insert into test02 values('a,b');
三、日期与时间类型
| 类型 | 大小 ( bytes) | 格式 | 范围 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATE | 3 | YYYY-MM-DD | 1000-01-01/9999-12-31 | 日期值 |
| TIME | 3 | HH:MM:SS | '-838:59:59'/'838:59:59' | 时间值或持续时间 |
| YEAR | 1 | YYYY | 1901/2155 | 年份值 |
| DATETIME | 8 | YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS | 1000-01-01 00:00:00/9999-12-31 23:59:59 | 混合日期和时间值 |
| TIMESTAMP | 4 | YYYYMMDD HHMMSS | 1970-01-01 00:00:00/2038结束时间是第 2147483647 秒,北京时间 2038-1-19 11:14:07,格林尼治时间 2038年1月19日 凌晨 03:14:07 | 混合日期和时间值,时间戳 |
3.1timestamp和datetime
timestamp和时区有关
drop table if exists test02
CREATE TABLE test02(
t1 TIMESTAMP,
t2 DATETIME
);
insert into test02 values(NOW(),NOW());
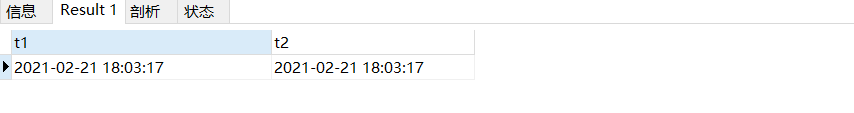
上面的结果看不出两者都何区别
修改时区,改成了东九区:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "time_zone"
SET time_zone ='+09:00'
修改时区之后,再执行上面的SQL,结果:
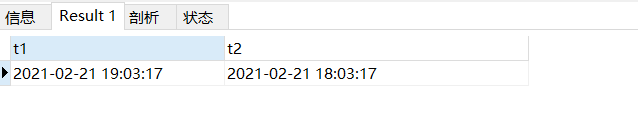
可见,两者时间相差一个小时。