Unit02-OOP-对象和类,数组(下)
1.方法的签名: 方法名+参数列表
2.方法的重载(Overload):
1)发生在一个类中,方法名称相同,参数列表不同
2)编译器在编译时自动根据签名绑定调用不同的方法
3.构造方法:
1)常常给成员变量赋初值
2)与类同名,没有返回值类型
3)在创建(new)对象时被自动调用
4)若自己不写构造方法,则编译器默认一个无参构造方法,
若自己写了构造方法,则编译器不再默认提供
5)构造方法可以重载
4.this:指代当前对象,哪个对象调指的就是哪个对象
只能用在方法中,方法中访问成员变量之前默认都有个this.
this的用法:
1)this.成员变量名------访问成员变量
2)this.方法名()--------调用方法
3)this()---------------调用构造方法
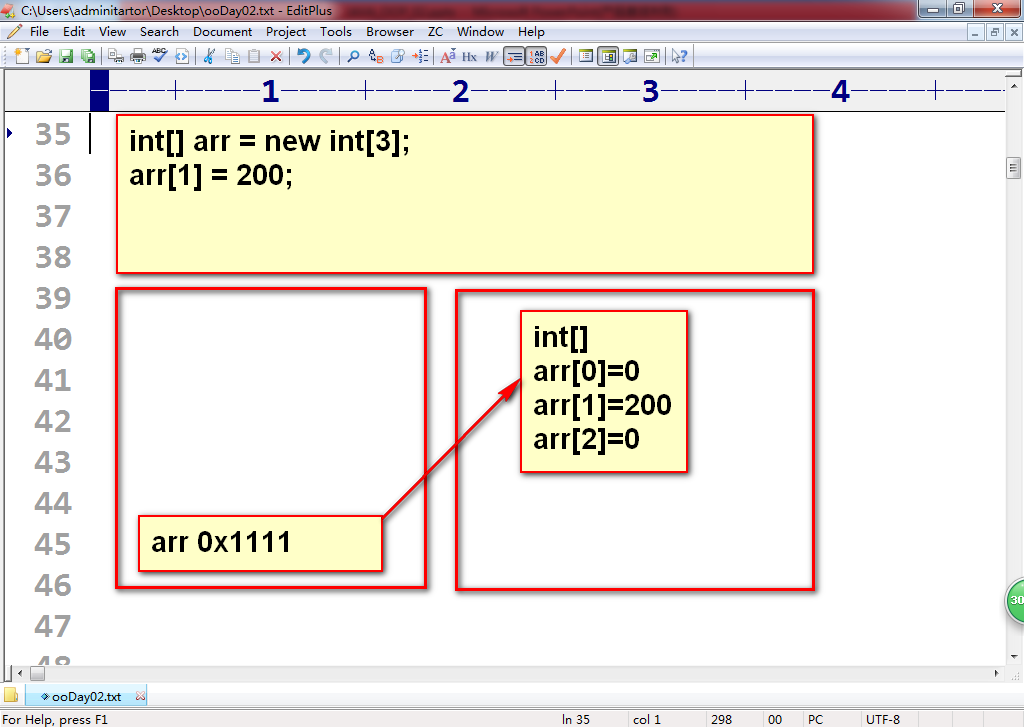
5.引用类型数组:
1)Cell[] cells = new Cell[4]; //创建格子数组对象
cells[0] = new Cell(2,5); //创建格子对象
cells[1] = new Cell(2,6);
cells[2] = new Cell(2,7);
cells[3] = new Cell(3,6);
2)Cell[] cells = new Cell[]{
new Cell(2,5),
new Cell(2,6),
new Cell(2,7),
new Cell(3,6)
};
3)int[][] arr = new int[3][];
arr[0] = new int[2];
arr[1] = new int[3];
arr[2] = new int[2];
arr[1][0] = 100; //arr中第2个元素中的第1个元素赋值为100
4)int[][] arr = new int[3][4]; //3行4列
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arr[i].length;j++){
arr[i][j] = 100;
}
}
嵌套数组:
3为arr的长度
4为arr中每个元素的长度
int[][] arr = new int[3][4]; //3行4列
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arr[i].length;j++){
arr[i][j] = 100;
}
}
i=1
j=0 arr10
j=1 arr11
j=2 arr12
j=3 arr13
//声明整型数组的数组arr,包含3个元素
//每个元素都是int[]型,默认值为null
int[][] arr = new int[3][];
arr[0] = new int[4];
arr[1] = new int[4];
arr[2] = new int[4];
//给arr中第2个元素中的第1个元素赋值为100
arr[1][0] = 100;
arr-----------------int[][]
arr[0]--------------int[]
arr[0][0]-----------int
//声明整型数组arr,包含4个元素
//每个元素都是int类型,默认值为0
int[] arr = new int[4];
//声明Cell型数组cells,包含4个元素
//每个元素都是Cell型,默认值为null
Cell[] cells = new Cell[4];
//声明Student数组stus,包含26个元素
//每个元素都是Student型,默认值为null
Student[] stus = new Student[26];
一个类,肯定有构造方法-----对
自己可不可以不写构造-------可以
写了更方便
成员变量:
class Student{
String name;
int age;
String address;
Student(){
}
//给成员变量赋初值
Student(String name1,int age1,String address1){
name = name1;
age = age1;
address = address1;
}
}
基本类型数组
引用类型数组

演示方法的重载
package oo.day02; /* * 补充: * 1.一个文件中可以包含多个类 * 2.public修饰的类只能有一个 * 3.public修饰的类必须与文件名相同 */ //演示方法的重载 public class OverloadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Aoo o = new Aoo(); o.say(); o.say("zhangsan"); o.say("zhangsan", 25); o.say(25, "zhangsan"); } } class Aoo{ void say(){} void say(String name){} void say(String name,int age){} void say(int age,String name){} //int say(){return 1;} //编译错误,重载与返回值类型无关 //void say(String address){} //编译错误,重载与参数名称无关 }
//引用类型数组
package oo.day02; //引用类型数组 public class RefArrayDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Cell[] cells = new Cell[4]; //创建格子数组对象 cells[0] = new Cell(2,5); //创建格子对象 cells[1] = new Cell(2,6); cells[2] = new Cell(2,7); cells[3] = new Cell(3,6); Cell[] cs = new Cell[]{ new Cell(2,5), new Cell(2,6), new Cell(2,7), new Cell(3,6) }; int[][] arr = new int[3][]; arr[0] = new int[2]; arr[1] = new int[3]; arr[2] = new int[2]; arr[1][0] = 100; //给arr中第2个元素中的第1个元素赋值为100 int[][] as = new int[3][4]; //3行4列 for(int i=0;i<as.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<as[i].length;j++){ as[i][j] = 100; } } } }
程序一:
Cell.java //格子类,演示构造方法
package oo.day02; public class Cell { int row; //声明行 int col; //声明列 Cell(){ //构造方法,默认值 this(0,0); } Cell(int n){ //构造方法,默认值 this(n,n); } Cell(int row,int col){ //构造方法,取值,赋值 this.row = row; this.col = col; } void drop(){ //下落一格 row++; //行号增1 } void drop(int n){ // 下降n格 row+=n; } void moveLeft() { // 左移1格 col--; } void moveLeft(int n){ // 左移n格 col -=n; } String getCellInfo(){ return row+","+col; } }
CellTest.java //格子类的测试类
package oo.day02; //格子类的测试类 public class CellTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //构建方法 Cell c1 = new Cell(); //0,0 System.out.println("---0------0-----"); printWall(c1); Cell c2 = new Cell(2); //2,2 System.out.println("---2------2-----"); printWall(c2); Cell c3 = new Cell(2,5); //2,5 System.out.println("---2------5-----"); printWall(c3); /* 方法一(不建议使用): Cell c = new Cell(); c.row = 2; c.col = 6; c.drop(); c.drop(3); c.moveLeft(); c.moveLeft(3); */ } //打墙+打格 public static void printWall(Cell cc){ for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ //行 for(int j=0;j<10;j++){ //列 if(i==cc.row && j==cc.col){ //行列匹配 System.out.print("* "); }else{ System.out.print("- "); } } System.out.println(); //换行 } } }
程序二:
Cell.java
package oo.day02; //格子类 public class Cell { int row; // 行号 int col; // 列号 Cell(){ this(0,0); } Cell(int n){ this(n,n); } Cell(int row,int col){ this.row = row; this.col = col; } String getCellInfo() { // 获取格子的行号和列号 return row + "," + col; // 返回行列号 } }
T.java
package oo.day02; //T型 public class T { Cell[] cells; //格子数组 T(){ this(0,0); } T(int row,int col){ this.cells = new Cell[4]; //创建格子数组对象 this.cells[0] = new Cell(row,col); //创建格子对象 this.cells[1] = new Cell(row,col+1); this.cells[2] = new Cell(row,col+2); this.cells[3] = new Cell(row+1,col+1); } void drop(){ //下落 for(int i=0;i<this.cells.length;i++){ this.cells[i].row++; } } void moveLeft(){ //左移 for(int i=0;i<cells.length;i++){ cells[i].col--; } } void moveRight(){ //右移 for(int i=0;i<cells.length;i++){ cells[i].col++; } } void print(){ //输出4个格子的行列号 for(int i=0;i<this.cells.length;i++){ String str = this.cells[i].getCellInfo(); System.out.println(str); } } }
J.java
package oo.day02; //J型 public class J { Cell[] cells; J(){ this(0,0); } J(int row,int col){ cells = new Cell[4]; cells[0] = new Cell(row,col); cells[1] = new Cell(row,col+1); cells[2] = new Cell(row,col+2); cells[3] = new Cell(row+1,col+2); } void drop(){ //下落 for(int i=0;i<cells.length;i++){ cells[i].row++; } } void moveLeft(){ //左移 for(int i=0;i<cells.length;i++){ cells[i].col--; } } void moveRight(){ //右移 for(int i=0;i<cells.length;i++){ cells[i].col++; } } void print(){ //输出4个格子的行列号 for(int i=0;i<cells.length;i++){ String str = cells[i].getCellInfo(); System.out.println(str); } } }
TJTest.java
package oo.day02; //T类与J类的测试类 public class TJTest { public static void main(String[] args) { T t = new T(2,5); t.print(); t.drop(); System.out.println("下落后:"); t.print(); t.moveLeft(); System.out.println("左移后:"); t.print(); } }
课后作业:
1 请描述下列代码的运行结果
public class ExerciseTest { public static void main(String[] args){ ExerciseTest f = new ExerciseTest(); System.out.println(f.add("4", "5")); } public int add(int x, int y) { return x + y; } public String add(String x,String y) { return x + y; } }
参考答案
上述代码运行后,将打印显示 45。这是因为,调用 add 方法时,传入的是 String 类型的变量,因此,执行第二个 add 方法,实现字符串的连接,得到字符串“45”。
2 关于构造方法,下面说法正确的是
A.构造方法不能带有参数
B.构造方法的名称必须和类名相同
C.构造方法可以定义返回值
D.构造方法不能重载
参考答案
B 选项的说法正确。
在Java语言中,可以通过构造方法实现对对象成员变量的初始化。构造方法是在类中定义的方法,但不同于其他的方法,构造方法的定义有如下规则:
1. 构造方法的名称必须与类名同名;
2. 构造方法没有返回值,但也不能写void,如果有返回值就是方法了。
另外,为了使用方便,可以对一个类定义多个构造方法,这些构造方法都有相同的名称,方法的参数不同,称之为构造方法的重载。在创建对象时,Java编译器会根据不同的参数调用不同构造方法。