Springboot中可以用@Validated来校验数据,如果数据异常则会统一抛出异常,方便异常中心统一处理。
我们这里来写个注解让我们的name不能为空@NotBlank(message="名字不能为空")
要用@Validated,需要在pom.xml中加入引用,@NotBlank需要用到import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;(注意不要引错包,报错了会报红)
<!--引入校验-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
package com.example.springstudy.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
/**
* @author pu2qmb
*/
@Data
//注册bean
@Component
/*
@ConfigurationProperties作用:
将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;
告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
参数 prefix = “hello” : 将配置文件中的hello下面的所有属性一一对应
如果没有@Component注解,@ConfigurationProperties会出现红色波浪线
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")
@Validated //数据校验
public class HelloEntity {
@NotBlank(message="名字不能为空")
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
yaml配置
hello:
name:
age: 13
用测试类进行测试
package com.example.springstudy.controller;
import com.example.springstudy.entity.HelloEntity;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
HelloEntity helloEntity;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(helloEntity);
}
}
测试结果:
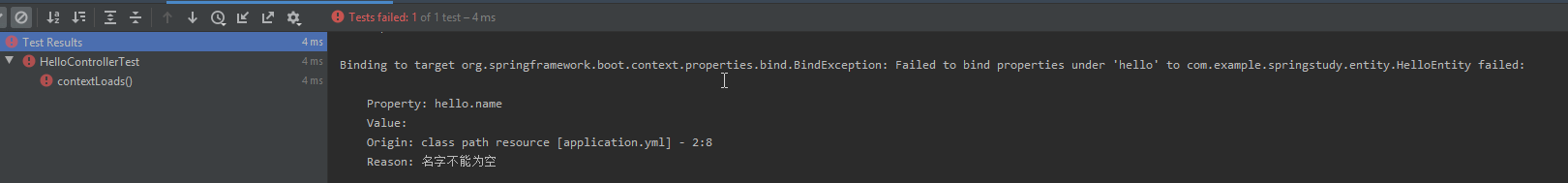
常见参数
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
.......等等
除此以外,我们还可以自定义一些数据校验规则