最近研究了一下C++线程池,在网上看了一下别人的代码,写的很不错,参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/3328646.html
其中,他用了STL的set容器管理线程池中的线程,在线程池运行的过程中需要频繁的进行插入、查找和删除的操作,我个人觉得这些操作会是线程池中的很大的时间开销,想起了大学老师讲过的一个TireTree(字典树)的数据结构,利用多叉树
可以快速的实现元素的插入、查找和删除,稍加改动也可以支持自动排序,唯一的缺点就是多叉树的结构空间开销较大,所以要控制好内存操作,防止内存泄露。
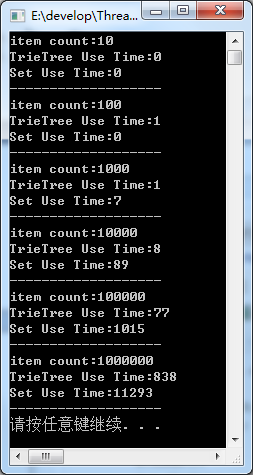
经测试,再插入元素和删除元素的方面,TrieTree比set有明显优势,在相同的元素数量下,内存开销也不过是set的1.5~2倍,时间却是1/10左右。
1 #ifndef _MY_TRIE_TREE 2 #define _MY_TRIE_TREE 3 4 template<class T,class K> 5 class TrieTree{ 6 public: 7 TrieTree(); 8 virtual ~TrieTree(); 9 bool insert(T *data,K key,bool overwrite = false); 10 bool remove(K key,bool free_memory = false); 11 bool find(K key,T *& pData); 12 private: 13 enum 14 { 15 Dimension = 10, 16 }; 17 typedef struct tagNode 18 { 19 tagNode *child[Dimension]; 20 T *data; 21 tagNode() 22 { 23 for(int i = 0;i < Dimension;i++) 24 { 25 child[i] = NULL; 26 } 27 data = NULL; 28 } 29 ~tagNode() 30 { 31 if(child == NULL) 32 { 33 delete[] child; 34 } 35 if(data != NULL) 36 { 37 delete data; 38 } 39 } 40 }Node; 41 Node *m_pHead; 42 unsigned int m_nElementCnt; 43 unsigned int m_nNodeCnt; 44 void destory(Node *p_head); 45 public: 46 void free(); 47 void dump(); 48 void trival( Node *pNode,int &nodeCnt ); 49 }; 50 51 template<class T,class K> 52 bool TrieTree<T, K>::find( K key,T *& pData ) 53 { 54 int m = 0; 55 Node **p_find = NULL; 56 if(m_pHead == NULL) 57 { 58 return false; 59 } 60 p_find = &m_pHead; 61 while( key > 0 ) 62 { 63 m = key%10; 64 if((*p_find) != NULL) 65 { 66 p_find = &(*p_find)->child[m]; 67 } 68 else 69 { 70 break; 71 } 72 key /= 10; 73 } 74 if((*p_find) != NULL) 75 { 76 // 数据为空 77 if((*p_find)->data == NULL) 78 { 79 return false; 80 } 81 pData = (*p_find)->data; 82 return true; 83 } 84 else 85 { 86 return false; 87 } 88 } 89 90 template<class T,class K> 91 void TrieTree<T, K>::free() 92 { 93 destory(m_pHead); 94 } 95 96 template<class T,class K> 97 void TrieTree<T, K>::destory( Node *p_head ) 98 { 99 if(p_head != NULL) 100 { 101 for(int i = 0;i < Dimension;i++) 102 { 103 destory(p_head->child[i]); 104 } 105 delete p_head; 106 m_nNodeCnt--; 107 } 108 } 109 110 111 template<class T,class K> 112 void TrieTree<T, K>::trival( Node *pNode,int &nodeCnt ) 113 { 114 if(pNode != NULL) 115 { 116 nodeCnt++; 117 if(pNode->data != NULL) 118 { 119 //cout<<*(pNode->data)<<" "; 120 } 121 for(int i = 0;i < Dimension;i++) 122 { 123 trival(pNode->child[i],nodeCnt); 124 } 125 } 126 } 127 128 template<class T,class K> 129 void TrieTree<T, K>::dump() 130 { 131 int nodeCnt = 0; 132 trival(m_pHead,nodeCnt); 133 cout<<endl; 134 //cout<<endl<<"size = "<<sizeof(Node)<< " * "<<nodeCnt<<" = "<<sizeof(Node)*nodeCnt<<endl; 135 //cout<<endl<<"data = "<<sizeof(T)<< " * "<<m_nElementCnt<<" = "<<sizeof(T)*m_nElementCnt<<endl; 136 //cout<<endl<<"rate = "<<((double)sizeof(T) * m_nElementCnt)/(sizeof(Node)*nodeCnt)<<endl; 137 cout<<"m_nNodeCnt = "<<m_nNodeCnt; 138 cout<<",m_nElementCnt = "<<m_nElementCnt; 139 cout<<",nodeCnt = "<<nodeCnt<<endl; 140 } 141 142 template<class T,class K> 143 TrieTree<T,K>::TrieTree() 144 { 145 m_pHead = new Node(); 146 m_nElementCnt = 0; 147 m_nNodeCnt = 1; 148 } 149 150 151 template<class T,class K> 152 TrieTree<T,K>::~TrieTree() 153 { 154 destory(m_pHead); 155 } 156 157 template<class T,class K> 158 bool TrieTree<T, K>::remove( K key ,bool free_memory) 159 { 160 int m = 0; 161 Node **p_find = NULL; 162 if(m_pHead == NULL) 163 { 164 return false; 165 } 166 p_find = &m_pHead; 167 while( key > 0 ) 168 { 169 m = key%10; 170 if((*p_find) != NULL) 171 { 172 p_find = &(*p_find)->child[m]; 173 } 174 else 175 { 176 break; 177 } 178 key /= 10; 179 } 180 if((*p_find) != NULL) 181 { 182 // 不释放节点空间 183 if( free_memory == false ) 184 { 185 if((*p_find)->data == NULL) 186 { 187 return false; 188 } 189 delete (*p_find)->data; 190 (*p_find)->data = NULL; 191 m_nElementCnt--; 192 return true; 193 } 194 // 释放节点空间 195 else 196 { 197 //并不是所有节点都能释放,没有子节点的节点才能释放 198 bool hasChild = false; 199 for(int i = 0;i < Dimension;i++) 200 { 201 if((*p_find)->child[i] != NULL) 202 { 203 hasChild = true; 204 } 205 } 206 // 释放节点,直接delete 207 if(hasChild == false) 208 { 209 delete (*p_find); 210 (*p_find) = NULL; 211 m_nElementCnt--; 212 m_nNodeCnt--; 213 } 214 // 不能释放节点,释放data,data = NULL 215 else 216 { 217 if((*p_find)->data == NULL) 218 { 219 return false; 220 } 221 T *pData = (*p_find)->data; 222 (*p_find)->data = NULL; 223 delete pData; 224 pData = NULL; 225 m_nElementCnt--; 226 return true; 227 } 228 } 229 } 230 else 231 { 232 return false; 233 } 234 } 235 236 template<class T,class K> 237 bool TrieTree<T, K>::insert( T *data,K key,bool overwrite) 238 { 239 int m = 0; 240 Node **p_find = NULL; 241 if(m_pHead == NULL) 242 { 243 return false; 244 } 245 p_find = &m_pHead; 246 while( key > 0 ) 247 { 248 m = key%10; 249 if((*p_find) == NULL) 250 { 251 (*p_find) = new Node(); 252 m_nNodeCnt++; 253 } 254 p_find = &(*p_find)->child[m]; 255 key /= 10; 256 } 257 if((*p_find) == NULL) 258 { 259 (*p_find) = new Node(); 260 (*p_find)->data = data; 261 m_nNodeCnt++; 262 m_nElementCnt++; 263 return true; 264 } 265 else 266 { 267 if((*p_find)->data == NULL) 268 { 269 (*p_find)->data = data; 270 m_nElementCnt++; 271 return true; 272 } 273 else 274 { 275 if(overwrite == false) 276 { 277 return false; 278 } 279 else 280 { 281 (*p_find)->data = data; 282 m_nElementCnt++; 283 return true; 284 } 285 } 286 } 287 } 288 289 #endif
测试代码:
void test1() { int cnt = 0; time_t s,e; int n = 10,m = 0; TrieTree<R,int> a; set<R*> b; for(m = 1;m < 7;m++) { cout<<"item count:"<<n<<endl; s = clock(); for(int i = 1;i < n;i++) { R *r = new R(i); a.insert(r,i); } //a.dump(); for(int i = 1;i < n/2;i++) { a.remove(i,true); } e = clock(); cout<<"TrieTree Use Time:"<<e-s<<endl; s = clock(); for(int i = 1;i < n;i++) { R *r = new R(i); b.insert(r); } b.clear(); e = clock(); cout<<"Set Use Time:"<<e-s<<endl; cout<<"-------------------"<<endl; n*=10; } } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }
测试结果:
以上仅是我个人的观点,代码也仅仅是练练手而已,不保证理论和实现完全正确,仅供参考。