本文主的主要内容是一些随机算法,主要有四种,下面来详细的介绍:
1 生成随机数
一般c语言中提供了随机数生成函数,
其一是伪随机数--rand:用于返回一个0-32767之间的伪随机数;
其二是随机种子函数--srand:用来初始化随机数发生器的随机种子
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main() { int i,j; srand((int)time(0)); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { printf("%d ",rand()); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
当然也可以生成一定范围内的随机数
比如生成0——100之间的随机数
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main() { int i,j; srand((int)time(0)); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { printf("%d ",rand()*100/32767); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
也可以生成100——200之间的随机数
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main() { int i,j; srand((int)time(0)); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { printf("%d ",rand()/1000+100); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
2 生成[0,1]之间均匀分布的随机数算法
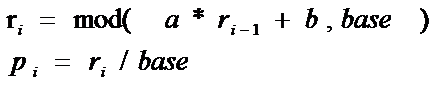
在这里采用一种方式生成随机数
其中i=1,2,3.。。。
而pi就是地推倒的第i个随机数
根据经验,一般选取基数base=256.0,一般为2的整数倍;另外的两个常数选取a=17.0 和b=139.0
需要注意
(1)这里的取模运算是针对浮点型数据的,而c语言中的取模运算不能用于浮点数数据的操作,这样就需要用户自己编写取模的程序;
(2)ri是随着递推而每次更新的。因此,如果将这个算法编写出函数,需要考虑参数是传值还是传地址;
递推更新,所以在这里要传地址,否则得不到结果!
#include <stdio.h> double rand0_1(double *r) { double base=256.0; double a=17.0; double b=139.0; double temp1=a*(*r)+b; //printf("%lf",temp1); double temp2=(int)(temp1/base); //得到余数 double temp3=temp1-temp2*base; //printf("%lf ",temp2); //printf("%lf ",temp3); *r=temp3; double p=*r/base; return p; } int main() { double r=5.0; printf("output 10 number between 0 and 1: "); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { printf("%10.5lf ",rand0_1(&r)); } return 0; }
3 产生任意范围内的随机数,比如产生[m,n]之间的随机数
这个很容易,只要将之前的[0,1]之间的随机数这样处理就行了
m+(m-n)*rand0_1(&r)就行了;
#include <stdio.h> double rand0_1(double *r) { double base=256.0; double a=17.0; double b=139.0; double temp1=a*(*r)+b; //printf("%lf",temp1); double temp2=(int)(temp1/base); //得到余数 double temp3=temp1-temp2*base; //printf("%lf ",temp2); //printf("%lf ",temp3); *r=temp3; double p=*r/base; return p; } int main() { double m=1.0,n=5.0; double r=5.0; printf("output 10 number between 0 and 1: "); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { printf("%10.5lf ",m+(n-m)*rand0_1(&r)); } return 0; }
4 正态分布的随机数生成算法
符合正太分布的随机数在研究中也很重要,下面给出一种生成正态分布数的方法
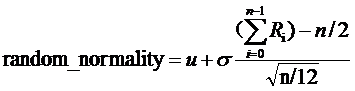
其中Ri表示[0,1]之间均匀分布的随机数;
u为均值,![]()
 为方差,当n趋向于无穷大的时候,得到随机的随机分布为正态分布;
上面设计的代码都已经运行通过!
为方差,当n趋向于无穷大的时候,得到随机的随机分布为正态分布;
上面设计的代码都已经运行通过!
 为方差,当n趋向于无穷大的时候,得到随机的随机分布为正态分布;
为方差,当n趋向于无穷大的时候,得到随机的随机分布为正态分布;
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> double rand0_1(double *r) { double base=256.0; double a=17.0; double b=139.0; double temp1=a*(*r)+b; //printf("%lf",temp1); double temp2=(int)(temp1/base); //得到余数 double temp3=temp1-temp2*base; //printf("%lf ",temp2); //printf("%lf ",temp3); *r=temp3; double p=*r/base; return p; } double random_normality(double u,double t,double *r ,double n) { double total=0.0; double result; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { total+=rand0_1(r); } result=u+t*(total-n/2)/sqrt(n/12); return result; } int main() { double r=5.0; double u=2.0; double t=3.5; double n=12; printf("output 10 number between 0 and 1: "); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { printf("%10.5lf ",random_normality(u,t,&r,n)); } return 0; }
补充知识点:leveldb中使用了一个简单的方式来实现随机化数;算法的核心是seed_ = (seed_ * A) % M,
下面把源代码贴出来,不难,可以和上面的参考下
private: uint32_t seed_; public: explicit Random(uint32_t s) : seed_(s & 0x7fffffffu) { // Avoid bad seeds. if (seed_ == 0 || seed_ == 2147483647L) { seed_ = 1; } } uint32_t Next() { static const uint32_t M = 2147483647L; // 2^31-1 static const uint64_t A = 16807; // bits 14, 8, 7, 5, 2, 1, 0 // We are computing // seed_ = (seed_ * A) % M, where M = 2^31-1 // // seed_ must not be zero or M, or else all subsequent computed values // will be zero or M respectively. For all other values, seed_ will end // up cycling through every number in [1,M-1] uint64_t product = seed_ * A; // Compute (product % M) using the fact that ((x << 31) % M) == x. seed_ = static_cast<uint32_t>((product >> 31) + (product & M)); // The first reduction may overflow by 1 bit, so we may need to // repeat. mod == M is not possible; using > allows the faster // sign-bit-based test. if (seed_ > M) { seed_ -= M; } return seed_; } // Returns a uniformly distributed value in the range [0..n-1] // REQUIRES: n > 0 uint32_t Uniform(int n) { return Next() % n; } // Randomly returns true ~"1/n" of the time, and false otherwise. // REQUIRES: n > 0 bool OneIn(int n) { return (Next() % n) == 0; } // Skewed: pick "base" uniformly from range [0,max_log] and then // return "base" random bits. The effect is to pick a number in the // range [0,2^max_log-1] with exponential bias towards smaller numbers. uint32_t Skewed(int max_log) { return Uniform(1 << Uniform(max_log + 1)); } };
这里面也直接取模得到一定范围内的随机数,简单明了。