A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
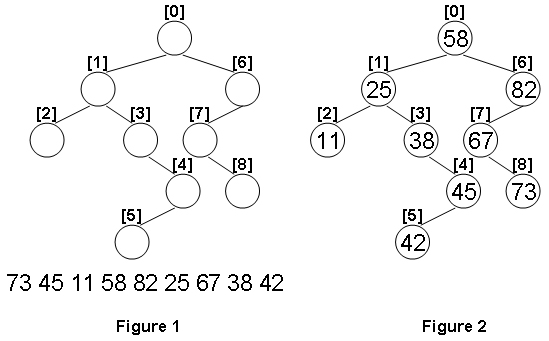
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤100) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format left_index right_index, provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then −1 will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
9
1 6
2 3
-1 -1
-1 4
5 -1
-1 -1
7 -1
-1 8
-1 -1
73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
Sample Output:
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <set> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <queue> 6 using namespace std; 7 const int maxn = 110; 8 int n; 9 struct node{ 10 int data; 11 int l=-1,r=-1; 12 }bst[maxn]; 13 int index=0; 14 int q[maxn]; 15 void inorder(int root){ 16 if(bst[root].l!=-1) inorder(bst[root].l); 17 bst[root].data = q[index++]; 18 if(bst[root].r!=-1) inorder(bst[root].r); 19 } 20 void level(int root){ 21 queue<int> que; 22 int cnt=0; 23 que.push(root); 24 while(!que.empty()){ 25 int now=que.front(); 26 que.pop(); 27 printf("%d",bst[now].data); 28 cnt++; 29 if(cnt!=n) printf(" "); 30 if(bst[now].l!=-1) que.push(bst[now].l); 31 if(bst[now].r!=-1) que.push(bst[now].r); 32 } 33 } 34 int main(){ 35 scanf("%d",&n); 36 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 37 int l,r; 38 scanf("%d %d",&l,&r); 39 bst[i].l=l; 40 bst[i].r=r; 41 } 42 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 43 scanf("%d",&q[i]); 44 } 45 sort(q,q+n); 46 inorder(0); 47 level(0); 48 }
注意点:其实很简单的题目,又一次倒在了递归上。知道要把给定数据sort,但没想sort完后就是这棵树的中序遍历结果,只要把正常中序遍历时的打印改成赋值就能得到那棵树了。没想到中序遍历,所以自己一直在想怎么把这个有序序列一个个填到树里去,一直也没搞明白,看这题通过率0.5多,我还不会做,凉了。
看到树的题目,一般都会要建树,遍历,而对bst,一般都是要对给定序列排序的,这样能得到他的中序遍历结果,有助于建树
