看到这个题目相信很多小伙伴都是懵懵的,平时我们的做法大都是下面的操作
@Component public class People{ @Autowired private Man man; }
这里如果Man是单例的,这种写法是没有问题的,但如果Man是原型的,这样是否会存在问题。
错误实例演示
这里有一个原型(生命周期为prototype)的类
package com.example.myDemo.component; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Scope(value = "prototype") public class Man { public void eat() { System.out.println("I like beef"); } }
有一个单例(生命周期为singleton)的类
package com.example.myDemo.component; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Lookup; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Woman { //使用依赖注入的方式,注入原型的Man
@Autowired private Man man; public void eat() { System.out.println("man:"+man); System.out.println("I like fruits"); } }
下面看测试方法,
package com.example.myDemo; import com.example.myDemo.component.MyFactoryBean; import com.example.myDemo.component.Woman; import com.example.myDemo.po.Student; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class}) public class MyDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac=SpringApplication.run(MyDemoApplication.class, args); Woman woman=(Woman)ac.getBean("woman"); for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ woman.eat(); } } }
看下测试结果,
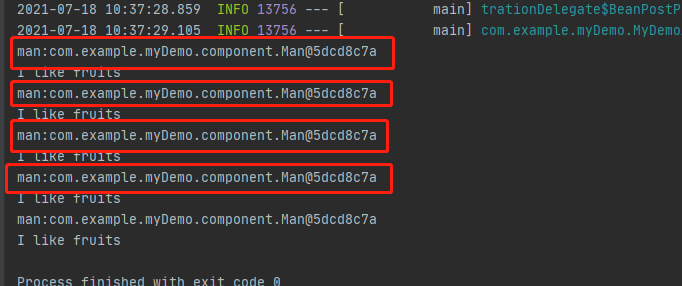
上面的结果显示Woman中的man是单例的,因为5次循环打印打出的结果是同一个对象,发生了什么,
Woman是单例的,Man是原型的,我们使用常规的@Autowired注解注入的却是同一个实例,这里想下为什么Man是一个对象,Woman是单例的,意味着在整个spring容器中只有一个实例,在属性注入的时候肯定也只会注入一次,所以其中Man属性也只能是一个实例,出现上图的结果也就不稀奇了。
现在有这样一个需求要向单例bean中注入原型bean,要怎么实现这样的需求
实现ApplicationContextAware接口
都知道ApplicationContextAware接口是spring提供的一个扩展点,实现该接口的类可以获得ApplicationContext
Woamn类改成下面的样子
package com.example.myDemo.component; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Lookup; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Woman implements ApplicationContextAware { private Man man; private ApplicationContext ac; public void eat() { this.man = (Man) ac.getBean("man"); System.out.println("man:" + man); System.out.println("I like fruits"); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.ac = applicationContext; } }
Woman实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,注入了ApplicaitonContext对象,然后再eat()方法中通过AppicationContext获得Man的实例,看测试结果,
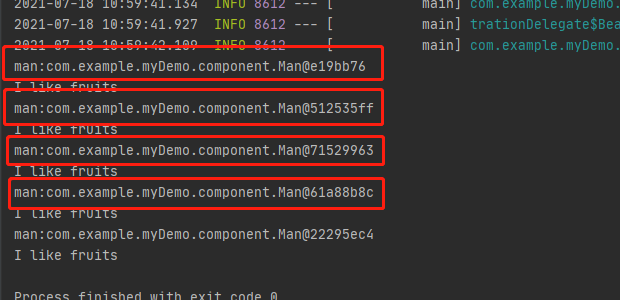
可以看到man属性是多例的也就是符合原型模式的定义。
思考下为什么采用这种方式可以达到注入原型bean的目的
在eat()方法中使用ApplicationContext的getBean方法获取Man,eat()方法每执行一次均会调用一次getBean方法,getbean方法在执行的时候的时候会判断Man的生命周期,如果是原型(prototype)的,那么每调用一次就会重新实例化一个Man,所以会出现上述的结果。
该方法有一个很大的缺点那就是和spring耦合度太高,不符合降低系统的耦合度的要求。
lookup method
spring也考虑了向一个单例bean中注入原型bean的情况,提供了@Lookup注解,在XML配置方式下是<lookup-method>标签,这里仅使用注解的方式演示,
Woman类修改如下,
package com.example.myDemo.component; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Lookup; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Woman { private Man man; public void eat() { this.man = createMan(); System.out.println("man:" + man); System.out.println("I like fruits"); } @Lookup public Man createMan(){ return null; } }
看下测试结果,
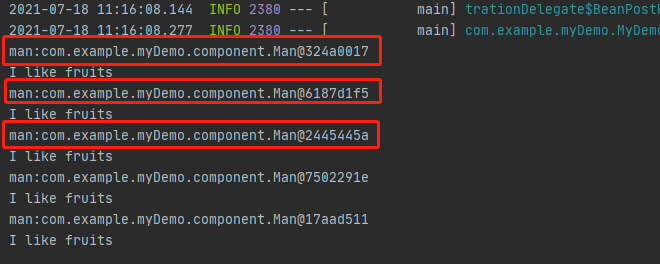
上图显示man是一个多例的,也就是向单例bean中注入了原型bean,其作用的是@Lookup注解。
通过@Lookup注解便完成了注入原型bean的目的,留个思考问题spring是如何做到的?
lookup method签名
被@Lookup注解或<lookup-method>配置的方法有如下要求,
public|protected [abstract] return-type methodName(no-argments)
- 方法可以是public也可以是protected;
- 方法可以是抽象的也可以是非抽象的;
- 方法的返回值是要注入的类型,这里是prototype类型的类;
- 方法没有入参;
- 方法体可以是空的。具体返回值可以是null或任何类型,对结果没有影响;
总结
分享了向单例bean中注入原型bean的方式,使用lookup的方式会更简洁些。
这还可能是道面试题哦,各位小伙伴注意喽。lookup的原理下次分享,敬请关注
推荐阅读
《一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之三:bean是如何实例化的》
