Andrew NG的Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml
在Linear Regression部分出现了一些新的名词,这些名词在后续课程中会频繁出现:
| Cost Function | Linear Regression | Gradient Descent | Normal Equation | Feature Scaling | Mean normalization |
| 损失函数 | 线性回归 | 梯度下降 | 正规方程 | 特征归一化 | 均值标准化 |
Model Representation
- m: number of training examples
- x(i): input (features) of ith training example
- xj(i): value of feature j in ith training example
- y(i): “output” variable / “target” variable of ith training example
- n: number of features
- θ: parameters
- Hypothesis: hθ(x) = θ0 + θ1x1 + θ2x2 + … +θnxn
Cost Function
IDEA: Choose θso that hθ(x) is close to y for our training examples (x, y).
A.Linear Regression with One Variable Cost Function
Cost Function: ![]()
Goal: ![]()
Contour Plot:
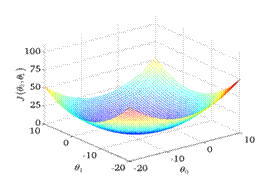
B.Linear Regression with Multiple Variable Cost Function
Cost Function: 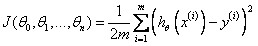
Goal: 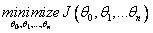
Gradient Descent
Outline

Gradient Descent Algorithm
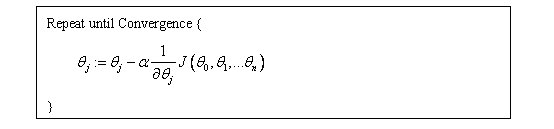
迭代过程收敛图可能如下:
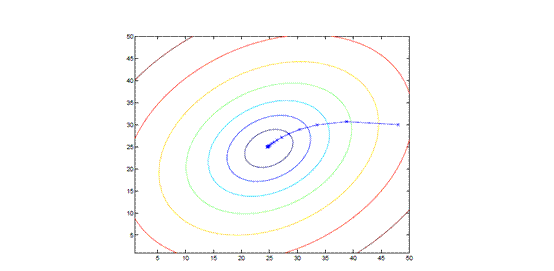
(此为等高线图,中间为最小值点,图中蓝色弧线为可能的收敛路径。)
Learning Rate α:
1) If α is too small, gradient descent can be slow to converge;
2) If α is too large, gradient descent may not decrease on every iteration or may not converge;
3) For sufficiently small α , J(θ) should decrease on every iteration;
Choose Learning Rate α: Debug, 0.001, 0.003, 0.006, 0.01, 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1.0;
“Batch” Gradient Descent: Each step of gradient descent uses all the training examples;
“Stochastic” gradient descent: Each step of gradient descent uses only one training examples.
Normal Equation
IDEA: Method to solve for θ analytically.
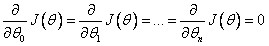 for every j, then
for every j, then 
Restriction: Normal Equation does not work when (XTX) is non-invertible.
PS: 当矩阵为满秩矩阵时,该矩阵可逆。列向量(feature)线性无关且行向量(样本)线性无关的个数大于列向量的个数(特征个数n).
Gradient Descent Algorithm VS. Normal Equation
Gradient Descent:
- Need to choose α;
- Needs many iterations;
- Works well even when n is large; (n > 1000 is appropriate)
Normal Equation:
- No need to choose α;
- Don’t need to iterate;
- Need to compute (XTX)-1 ;
- Slow if n is very large. (n < 1000 is OK)
Feature Scaling
IDEA: Make sure features are on a similar scale.
好处: 减少迭代次数,有利于快速收敛
Example: If we need to get every feature into approximately a -1 ≤ xi ≤ 1 range, feature values located in [-3, 3] or [-1/3, 1/3] fields are acceptable.
Mean normalization: 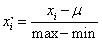
HOMEWORK
好了,既然看完了视频课程,就来做一下作业吧,下面是Linear Regression部分作业的核心代码:
1.computeCost.m/computeCostMulti.m
J=1/(2*m)*sum((theta'*X'-y').^2);
2.gradientDescent.m/gradientDescentMulti.m
h=X*theta-y; v=X'*h; v=v*alpha/m; theta1=theta; theta=theta-v;