【Byte Order, Size, and Alignment】
By default, C types are represented in the machine’s native format and byte order, and properly aligned by skipping pad bytes if necessary (according to the rules used by the C compiler).
Alternatively, the first character of the format string can be used to indicate the byte order, size and alignment of the packed data, according to the following table:
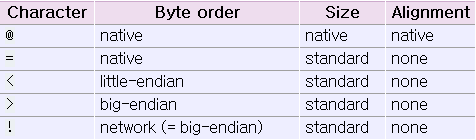
If the first character is not one of these, '@' is assumed.
Native size and alignment are determined using the C compiler’s sizeof expression. This is always combined with native byte order.
The form '!' is available for those poor souls who claim they can’t remember whether network byte order is big-endian or little-endian.
Notes:
- Padding is only automatically added between successive structure members. No padding is added at the beginning or the end of the encoded struct.
- No padding is added when using non-native size and alignment, e.g. with ‘<’, ‘>’, ‘=’, and ‘!’.