【Velocity Obstacle】
Two circular objects A,B, at time t(0), with velocity V(A),V(B). A represent the robot, and B represent obstacle.
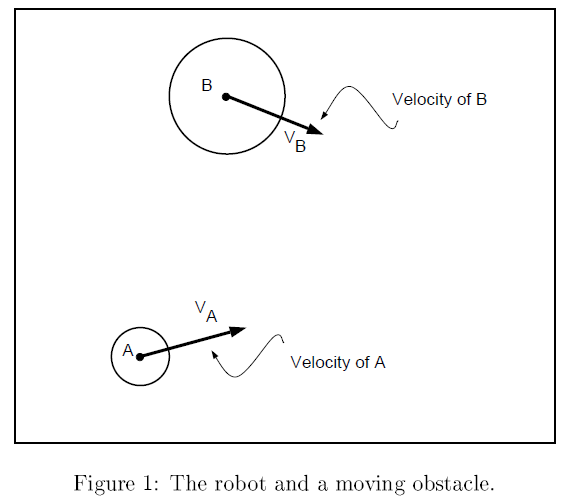
Collision Cone:
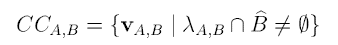
V(A,B) is the relative velocity of A&B. V(A,B) = V(A) - V(B). And λ(A,B) is the line of V(A,B).

By translating CC(A,B) by V(B),we get absolute Velocity Obstacle VO:


The VO partitions the absolute velocities of A into avoiding & colliding velocities. Selecting V(A) outside of VO would avoid collision with B:
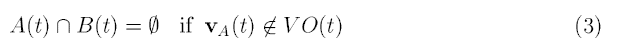
Velocities on the boundaries of VO would result in A grazing B.
To avoid multiple obstacles, we consider the union of the individual velocity obstacles:
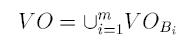
Since VO is based on a linear approximation of the obstacle's trajectory, using it to predict remote collisions may be inaccurate.
To account for imminent collisions:


【Avoidance Maneuver】
躲避策略。
Feasible Acceleration: 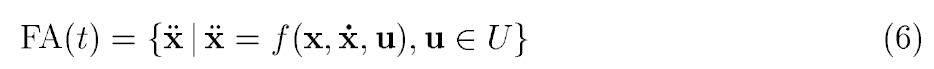
RV: Reachable Velocity:

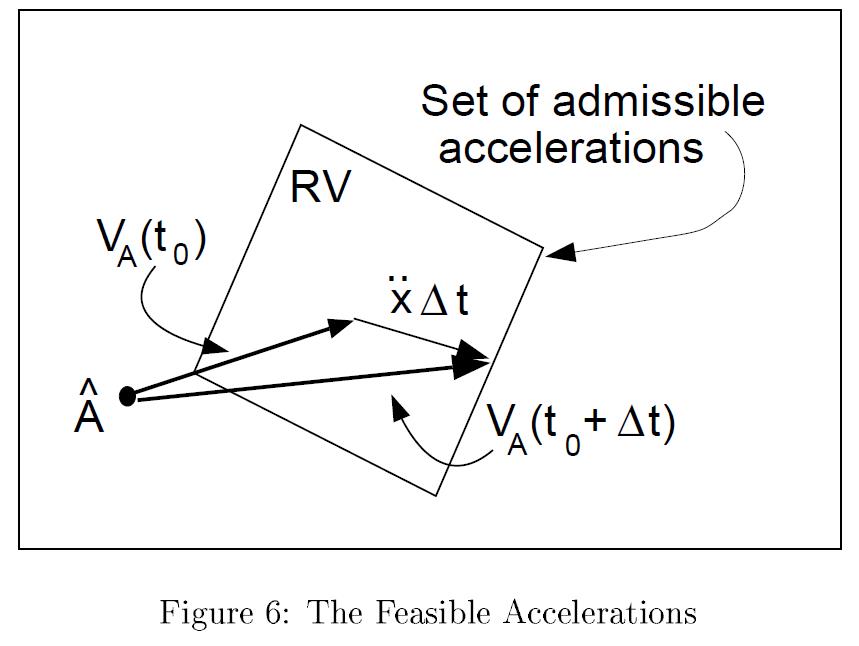
Reachable Avoidance Velocity (RAV):
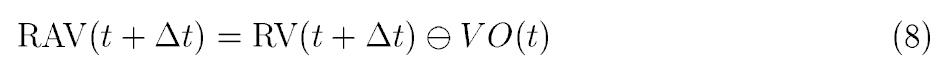

A maneuver avoiding obstacle B can be computed by selecting any velocity in RAV.
【Structure of the Avoidance Maneuvers】
躲避策略的结构。