一.configparser模块
configparser用于处理特定格式的文件,其本质上是利用open来操作文件
1.获取所有节点
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('test.conf', encoding='utf-8') # 第一个参数为文件路径
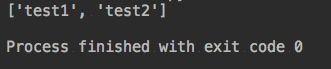
ret = config.sections()
print(ret)
2.获取指定节点下的所有键
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('test.conf', encoding='utf-8')
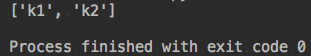
ret = config.options('test1')
print(ret)
3.获取指定节点下的所有的键值对
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('test.conf', encoding='utf-8')
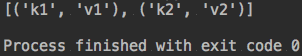
ret = config.items('test1')
print(ret)
4.获取指定节点下指定的key的值
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('test.conf', encoding='utf-8')
v = config.get('test1', 'k1')
# v = config.getint('test1', 'k1') # 默认获取的值为str类型,用getint获取的值会转为int
# v = config.getfloat('test2', 'k1')
# v = config.getboolean('test1', 'k1')
print(v)
5.删除,检查,添加节点
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('test.conf', encoding='utf-8')
# 检查
has_sec = config.has_section('section1')
print(has_sec)
# 添加节点
config.add_section("SEC_1")
config.write(open('test.conf', 'w'))
# 删除节点
config.remove_section("SEC_1")
config.write(open('test.conf', 'w'))
6、检查、删除、设置指定组内的键值对
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('test.conf', encoding='utf-8')
# 检查
has_opt = config.has_option('test1', 'k1')
print(has_opt)
# 删除
config.remove_option('test1', 'k1')
config.write(open('test.conf', 'w'))
# 设置
config.set('test1', 'k10', "123")
config.write(open('test.conf', 'w'))
二、系统命令
可以执行shell命令的相关模块和函数有:
- os.system
- os.spawn*
- os.popen* --废弃
- popen2.* --废弃
- commands.* --废弃,3.x中被移除

import commands result = commands.getoutput('cmd') result = commands.getstatus('cmd') result = commands.getstatusoutput('cmd')
以上执行shell命令的相关的模块和函数的功能均在 subprocess 模块中实现,并提供了更丰富的功能。
call
执行命令,返回状态码
ret = subprocess.call(["ls", "-l"], shell=False) ret = subprocess.call("ls -l", shell=True)
check_call
执行命令,如果执行状态码是 0 ,则返回0,否则抛异常
subprocess.check_call(["ls", "-l"]) subprocess.check_call("exit 1", shell=True)
check_output
执行命令,如果状态码是 0 ,则返回执行结果,否则抛异常
subprocess.check_output(["echo", "Hello World!"]) subprocess.check_output("exit 1", shell=True)
subprocess.Popen(...)
用于执行复杂的系统命令
参数:
- args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
- bufsize:指定缓冲。0 无缓冲,1 行缓冲,其他 缓冲区大小,负值 系统缓冲
- stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
- preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
- close_sfs:在windows平台下,如果close_fds被设置为True,则新创建的子进程将不会继承父进程的输入、输出、错误管道。
所以不能将close_fds设置为True同时重定向子进程的标准输入、输出与错误(stdin, stdout, stderr)。 - shell:同上
- cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
- env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
- universal_newlines:不同系统的换行符不同,True -> 同意使用
- startupinfo与createionflags只在windows下有效
将被传递给底层的CreateProcess()函数,用于设置子进程的一些属性,如:主窗口的外观,进程的优先级等等

import subprocess ret1 = subprocess.Popen(["mkdir","t1"]) ret2 = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t2", shell=True)
终端输入的命令分为两种:
- 输入即可得到输出,如:ifconfig
- 输入进行某环境,依赖再输入,如:python

import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t3", shell=True, cwd='/home/dev',)

import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, universal_newlines=True) obj.stdin.write("print(1) ") obj.stdin.write("print(2)") obj.stdin.close() cmd_out = obj.stdout.read() obj.stdout.close() cmd_error = obj.stderr.read() obj.stderr.close() print(cmd_out) print(cmd_error)

import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, universal_newlines=True) obj.stdin.write("print(1) ") obj.stdin.write("print(2)") out_error_list = obj.communicate() print(out_error_list)

import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, universal_newlines=True) out_error_list = obj.communicate('print("hello")') print(out_error_list)
三、shutil模块
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中
import shutil shutil.copyfileobj(open('old.xml','r'), open('new.xml', 'w'))
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
拷贝文件
shutil.copyfile('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copymode(src, dst)
仅拷贝权限。内容、组、用户均不变
shutil.copymode('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copystat(src, dst)
仅拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flags
shutil.copystat('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copy(src, dst)
拷贝文件和权限
import shutil shutil.copy('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.copy2(src, dst)
拷贝文件和状态信息
import shutil shutil.copy2('f1.log', 'f2.log')
shutil.ignore_patterns(*patterns)
shutil.copytree(src, dst, symlinks=False, ignore=None)
递归的去拷贝文件夹
import shutil shutil.copytree('folder1', 'folder2', ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('*.pyc', 'tmp*'))
import shutil shutil.copytree('f1', 'f2', symlinks=True, ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('*.pyc', 'tmp*'))
shutil.rmtree(path[, ignore_errors[, onerror]])
递归的去删除文件
import shutil shutil.rmtree('folder1')
shutil.move(src, dst)
递归的去移动文件,它类似mv命令,其实就是重命名。
import shutil shutil.move('folder1', 'folder3')
shutil.make_archive(base_name, format,...)
创建压缩包并返回文件路径,例如:zip、tar
创建压缩包并返回文件路径,例如:zip、tar
- base_name: 压缩包的文件名,也可以是压缩包的路径。只是文件名时,则保存至当前目录,否则保存至指定路径,
如:www =>保存至当前路径
如:/Users/wupeiqi/www =>保存至/Users/wupeiqi/ - format: 压缩包种类,“zip”, “tar”, “bztar”,“gztar”
- root_dir: 要压缩的文件夹路径(默认当前目录)
- owner: 用户,默认当前用户
- group: 组,默认当前组
- logger: 用于记录日志,通常是logging.Logger对象
#将 /Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test 下的文件打包放置当前程序目录 import shutil ret = shutil.make_archive("wwwwwwwwww", 'gztar', root_dir='/Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test') #将 /Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test 下的文件打包放置 /Users/wupeiqi/目录 import shutil ret = shutil.make_archive("/Users/wupeiqi/wwwwwwwwww", 'gztar', root_dir='/Users/wupeiqi/Downloads/test')
shutil 对压缩包的处理是调用 ZipFile 和 TarFile 两个模块来进行的,详细:

import zipfile # 压缩 z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'w') z.write('a.log') z.write('data.data') z.close() # 解压 z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'r') z.extractall() z.close()

import tarfile # 压缩 tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','w') tar.add('/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/bbs2.log', arcname='bbs2.log') tar.add('/Users/wupeiqi/PycharmProjects/cmdb.log', arcname='cmdb.log') tar.close() # 解压 tar = tarfile.open('your.tar','r') tar.extractall() # 可设置解压地址 tar.close()
