关于进程 process
====================================================================================
What is a process? 什么是进程
Process life cycle 进程的生命周期
Process states 进程状态
什么是进程?
进程是已启动的可执行程序的运行实例,进程有以下组成部分:
• 已分配内存的地址空间;
• 安全属性,包括所有权凭据和特权;
• 程序代码的一个或多个执行线程;
• 进程状态。
程序: 二进制文件,静态 /bin/date, /usr/sbin/httpd,/usr/sbin/sshd, /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ngix
进程: 是程序运行的过程, 动态,有生命周期及运行状态。
进程的生命周期
父进程复制自己的地址空间(fork)创建一个新的(子)进程结构。每个新进程分配一个唯一的进程 ID (PID),满足跟踪安全性
之需。PID 和 父进程 ID (PPID)是子进程环境的元素,任何进程都可以创建子进程,所有进程都是第一个系统进程的后代:
Centos5/6: init
Centos7: systemd
子进程继承父进程的安全性身份、过去和当前的文件描述符、端口和资源特权、环境变量,以及程序代码。随后,子进程可能exec
自己的程序代码。通常,父进程在子进程运行期间处于睡眠(sleeping)状态。当子进程完成时发出(exit)信号请求,在退出时,
子进程已经关闭或丢弃了其资源环境,剩余的部分称之为僵停(僵尸Zombie)。父进程在子进程退出时收到信号而被唤醒,清理剩
余的结构,然后继续执行其自己的程序代码。
进程状态
在多任务处理操作系统中,每个CPU(或核心)在一个时间点上只能处理一个进程。在进程运行时,它对CPU 时间和资源分配的要求
会不断变化,从而为进程分配一个状态,它随着环境要求而改变。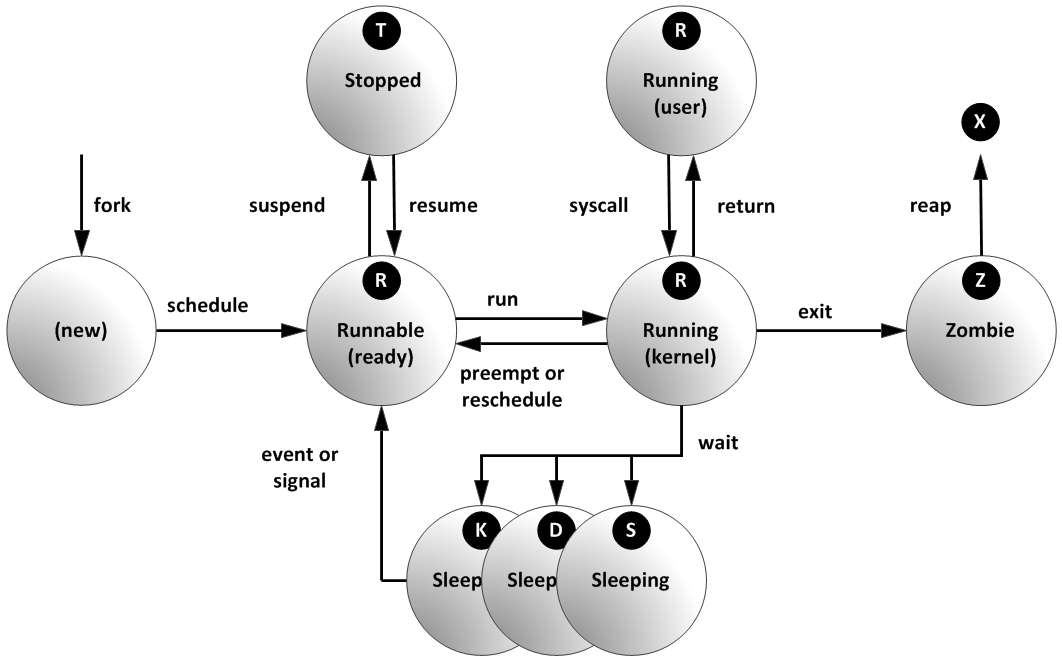
查看进程Process
了解如进程的:
• PID,PPID
• 当前的进程状态
• 内存的分配情况
• CPU和已花费的实际时间
• 用户UID,它决定进程的特权
静态查看进程 ps
注:ps -aux 不同于 ps aux
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |less
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.0 2164 648 ? Ss 08:47 0:00 init [5]
USER: 运行进程的用户
PID: 进程ID
%CPU: CPU占用率
%MEM: 内存占用率
VSZ: 占用虚拟内存
RSS: 占用实际内存 驻留内存
TTY: 进程运行的终端
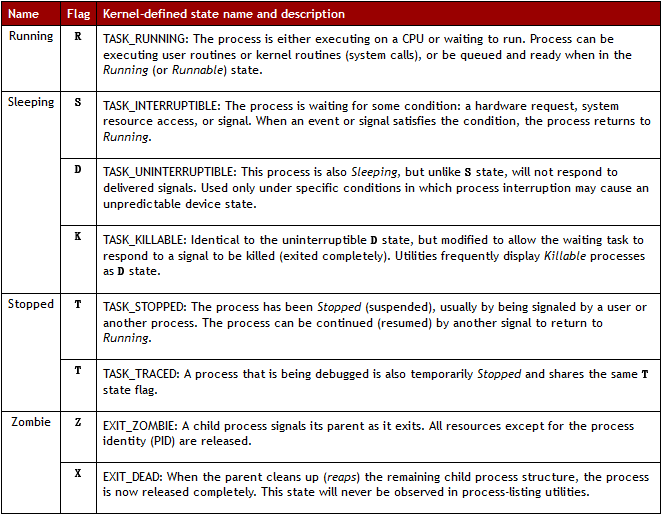
STAT: 进程状态 man ps (/STATE)
R 运行
S 可中断睡眠 Sleep
D 不可中断睡眠
T 停止的进程
Z 僵尸进程
X 死掉的进程
Ss s进程的领导者,父进程
S< <优先级较高的进程
SN N优先级较低的进程
R+ +表示是前台的进程组
Sl 以线程的方式运行
START: 进程的启动时间
TIME: 进程占用CPU的总时间
COMMAND: 进程文件,进程名
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux --sort %cpu |less
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux --sort -%cpu |less
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux --sort rss |less
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux --sort -rss |less
[alice@CentOS7 ~]$ sudo yum -y install httpd
[alice@CentOS7 ~]$ sudo systemctl start httpd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps auxf |grep httpd
root 9279 0.0 0.0 4264 672 pts/1 S+ 14:37 0:00 \_ grep httpd
root 8310 0.0 0.1 10092 2912 ? Ss 14:19 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8311 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8312 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8313 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8314 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8315 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8316 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8318 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8319 0.0 0.0 10092 2060 ? S 14:19 0:00 \_ /usr/sbin/httpd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 08:47 ? 00:00:00 init [5]
//自定义显示字段
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo user,pid,ppid,%mem,command
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo user,pid,ppid,%mem,command |grep httpd
root 8310 1 0.1 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8311 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8312 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8313 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8314 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8315 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8316 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8318 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 8319 8310 0.0 /usr/sbin/httpd
root 9236 6798 0.0 grep httpd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo user,pid,ppid,%mem,%cpu,command --sort -%cpu |less
//查看指定进程的PID
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ cat /run/sshd.pid
830
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep sshd
root 10180 0.0 0.0 7224 1024 ? Ss 16:00 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# pgrep -l sshd
10180 sshd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# pgrep sshd
10180
[root@CentOS7 ~]# pidof sshd
10180
//查看进程树
[root@CentOS7 ~]# pstree
动态查看进程 top
[root@CentOS7 ~]# top
[root@CentOS7 ~]# top -d 1
[root@CentOS7 ~]# top -d 1 -p 10126 查看指定进程的动态信息
[root@CentOS7 ~]# top -d 1 -p 10126,1
[root@CentOS7 ~]# top -d 1 -u apache 查看指定用户的进程
[root@CentOS7 ~]# top -d 1 -b -n 2 > top.txt 将2次top信息写入到文件
第一部分:系统整体统计信息
top - 14:15:04 up 47 min, 2 users, load average: 0.25, 0.18, 0.12
Tasks: 235 total, 1 running, 234 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
Cpu(s): 8.9%us, 1.0%sy, 0.0%ni, 90.1%id, 0.0%wa, 0.0%hi, 0.0%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 7944064k total, 746164k used, 7197900k free, 35724k buffers
Swap: 1048568k total, 0k used, 1048568k free, 261492k cached
load average: 0.86, 0.56, 0.78 系统最近 1分钟,5分钟,15分钟平均负载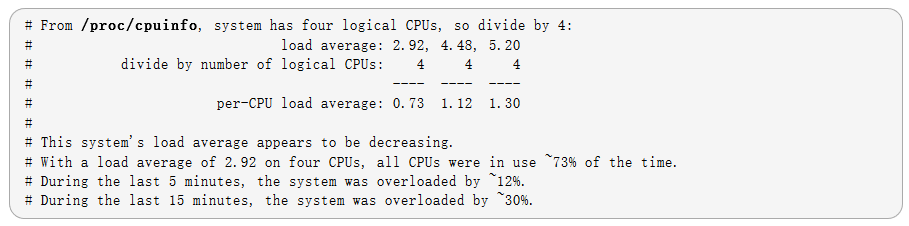
第二部分:进程信息
命令
h|?帮助
M 按内存的使用排序
P 按CPU使用排序
N 以PID的大小排序
R 对排序进行反转
f 自定义显示字段
1 显示所有CPU的负载
< 向前
> 向后
z 彩色
W 保存top环境设置
使用信号控制进程
kill,killall,pkill,top
给进程发送信号
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill -l //列出所有支持的信号
编号 信号名
1) SIGHUP 重新加载配置
2) SIGINT 键盘中断^C
3) SIGQUIT 键盘退出
9) SIGKILL 强制终止
15) SIGTERM 终止(正常结束),缺省信号
18) SIGCONT 继续
19) SIGSTOP 停止
20)SIGTSTP 暂停^Z
1: 给vsftpd进程发送信号1,15
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep vsftpd
root 9160 0.0 0.0 52580 904 ? Ss 21:54 0:00 /usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill -1 9160 //发送重启信号
root 9160 0.0 0.0 52580 904 ? Ss 21:54 0:00 /usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill 9160 //发送停止信号
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep vsftpd
//1
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
root 478 0.0 0.1 124144 1572 ? Ss 09:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/crond -n
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ sudo kill -1 478
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
root 478 0.0 0.1 124144 1572 ? Ss 09:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/crond -n
//15
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ sudo kill 478
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ sudo systemctl start crond
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
root 22319 0.0 0.1 124140 1548 ? Ss 14:54 0:00 /usr/sbin/crond -n
2:信号测试9,15
[root@CentOS7 ~]# touch file1 file2
[root@CentOS7 ~]# tty
/dev/pts/1
[root@CentOS7 ~]# vim file1
[root@CentOS7 ~]# tty
/dev/pts/2
[root@CentOS7 ~]# vim file2
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep vim
root 4362 0.0 0.2 11104 2888 pts/1 S+ 23:02 0:00 vim file1
root 4363 0.1 0.2 11068 2948 pts/2 S+ 23:02 0:00 vim file2
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill 4362
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill -9 4363
[root@CentOS7 ~]# killall vim //给所有vim进程发送信号
[root@CentOS7 ~]# killall httpd
3:信号测试18,19
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep sshd
root 5571 0.0 0.0 64064 1164 ? Ss 09:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill -STOP 5571
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep sshd
root 5571 0.0 0.0 64064 1164 ? Ts 09:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill -cont 5571
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep sshd
root 5571 0.0 0.0 64064 1164 ? Ss 09:35 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
root 22319 0.0 0.1 124140 1568 ? Ss 14:54 0:00 /usr/sbin/crond -n
yang 22427 0.0 0.0 112648 964 pts/2 R+ 15:07 0:00 grep --color=auto crond
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ sudo kill -19 22319
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
root 22319 0.0 0.1 124140 1568 ? Ts 14:54 0:00 /usr/sbin/crond -n
yang 22431 0.0 0.0 112648 964 pts/2 R+ 15:07 0:00 grep --color=auto crond
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ sudo kill -cont 22319
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ ps aux |grep crond
root 22319 0.0 0.1 124140 1568 ? Ss 14:54 0:00 /usr/sbin/crond -n
yang 22436 0.0 0.0 112648 960 pts/2 R+ 15:08 0:00 grep --color=auto crond
踢出一个从远程登录到本机的用户
[root@CentOS7 ~]# pkill --help
pkill: invalid option -- '-'
Usage: pkill [-SIGNAL] [-fvx] [-n|-o] [-P PPIDLIST] [-g PGRPLIST] [-s SIDLIST]
[-u EUIDLIST] [-U UIDLIST] [-G GIDLIST] [-t TERMLIST] [PATTERN]
[root@CentOS7 ~]# pkill -u alice
[root@CentOS7 ~]# w
15:46:44 up 2:19, 4 users, load average: 0.17, 0.12, 0.08
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root tty1 :0 21:32 ? 4:22 4:22 /usr/bin/Xorg :
root pts/0 :0.0 15:46 0.00s 0.00s 0.00s w
root pts/3 172.16.8.100 15:46 2.00s 0.01s 0.00s sleep 50000
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ w
15:17:25 up 5:42, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
yang pts/0 123.120.22.32 15:00 21.00s 0.00s 0.00s -bash
yang pts/1 123.120.22.32 15:00 5.00s 0.00s 0.00s w
yang pts/2 123.120.22.32 12:04 13.00s 0.12s 0.02s vim file1
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ pkill -t pts/2 //终止pts/2上所有进程
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ pkill -9 -t pts/2 //终止pts/2上所有进程 并结束该pts/2
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ w
15:20:59 up 5:45, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
yang pts/0 123.120.22.32 15:00 3:55 0.00s 0.00s -bash
yang pts/1 123.120.22.32 15:00 3.00s 0.01s 0.00s w
yang pts/2 123.120.22.32 15:20 3.00s 0.00s 0.00s -bash
[yang@iZm5eiwihahzq6ds23gbf6Z ~]$ sudo pkill -u yang
进程优先级nice
Linux 进程调度及多任务
相对优先级nice
查看进程的nice级别
启动具有不同nice级别的进程
更改现有进程的nice级别
Linux 进程调度及多任务
每个CPU(或CPU核心)在一个时间点上只能处理一个进程,通过时间片技术,Linux实际能够运行的进程(和线程数)可以超
出实际可用的CPU及核心数量。Linux内核进程调度程序将多个进程在CPU核心上快速切换,从而给用户多个进程在同时运行的印象。
相对优先级 nice
由于不是每个进程都与其他进程同样重要,可告知进程调度程序为不同的进程使用不同的调度策略。常规系统上运行的大多
数进程所使用的调度策略为 SCHED_OTHER (也称为SCHED_NORMAL),但还有其它一些调度策略用于不同的目的。
SCHED_OTHER 调度策略运行的进程的相对优先级称为进程的 nice 值,可以有40种不同级别的nice值。

nice 值越高: 表示优先级越低,例如+19,该进程容易将CPU 使用量让给其他进程。
nice 值越低: 表示优先级越高,例如-20,该进程更不倾向于让出CPU。
查看进程的nice级别
1. 使用top查看nice级别
NI: 实际nice级别
PR: 将nice级别显示为映射到更大优先级队列,-20映射到0,+19映射到39
3. 使用ps查看nice级别
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo pid,command,nice --sort=-nice
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo pid,command,nice,cls --sort=-nice
TS 表示该进程使用的调度策略为SCHED_OTHER
启动具有不同nice级别的进程
启动进程时,通常会继承父进程的 nice级别,默认为0。
[root@CentOS7 ~]# nice -n -5 sleep 6000 &
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo command,pid,nice |grep sleep
[root@CentOS7 ~]# nice -n -20 systemctl start httpd
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps axo pid,command,nice,cls |grep httpd
11116 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11119 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11120 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11121 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11122 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11123 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11124 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11125 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
11126 /usr/sbin/httpd -20 TS
更改现有进程的nice级别
1. 使用top更改nice级别
r 调整进程的优先级(Nice Level) (-20高) ---0--- (19低)
2. 使用shell更改nice级别
[root@CentOS7 ~]# sleep 7000 &
[3] 10089
[root@CentOS7 ~]# renice -20 10089
10089: old priority 0, new priority -20
控制 jobs
控制是一个命令行功能,允许一个shell 实例来运行和管理多个命令。
如果没有控制,父进程fork()一个子进程后,将sleeping,直到子进程退出。
使用控制,可以选择性暂停,恢复,以及异步运行命令,让 shell 可以在子进程运行期间返回接受其他命令。
foreground, background, and controlling terminal
foreground: 前台进程是在终端中运行的命令,该终端为进程的控制终端。前台进程接收键盘产生的输入和信号,并允许从终端读取或写入到终端。
background: 后台进程没有控制终端,它不需要终端的交互。
示例1:
[root@CentOS7 ~]# sleep 3000 & //运行程序(时),让其在后台执行
[root@CentOS7 ~]# sleep 4000 //^Z,将前台的程序挂起(暂停)到后台
[2]+ Stopped sleep 4000
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ps aux |grep sleep
root 8895 0.0 0.0 100900 556 pts/0 S 12:13 0:00 sleep 3000
root 8896 0.0 0.0 100900 556 pts/0 T 12:13 0:00 sleep 4000
[root@CentOS7 ~]# jobs //查看后台
[1]- Running sleep 3000 &
[2]+ Stopped sleep 4000
[root@CentOS7 ~]# bg %2 //让2在后台运行
[root@CentOS7 ~]# fg %1 //将1调回到前台
[root@CentOS7 ~]# kill %1 //kill 1,终止PID为1的进程
[root@CentOS7 ~]# (while :; do date; sleep 2; done) & //进程在后台运行,但输出依然在当前终端
[root@CentOS7 ~]# (while :; do date; sleep 2; done) &>/dev/null &
示例2:如何管理远程主机
[root@CentOS7 ~]# ssh 172.16.50.240
[root@www ~]# yum -y install screen
[root@www ~]# screen -S install_apache
==断网后,重新连接==
[root@www ~]# screen -list
There are screens on:
28958.install_nginx (Detached)
29013.install_apache (Detached)
2 Sockets in /var/run/screen/S-root.
[root@www ~]# screen -r 29013
proc 文件系统
虚拟文件系统: 内核、进程运行的状态信息
[root@CentOS7 ~]# du -sh /proc
0 /proc
/proc/cpuinfo
[root@CentOS7 ~]# grep 'processor' /proc/cpuinfo //逻辑cpu的个数
processor : 0
processor : 1
[root@CentOS7 ~]# grep 'physical id' /proc/cpuinfo //物理cpu的个数
physical id : 0
physical id : 0
==flags
lm(64位)
vmx 支持虚拟化 Intel
svm 支持虚拟化 AMD
[root@CentOS7 ~]# egrep 'lm|vmx|svm' /proc/cpuinfo
flags : fpu vme de clflush dts acpi lm constant_tsc pni monitor ds_cpl vmx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr lahf_lm
flags : fpu vme de clflush dts acpi lm constant_tsc pni monitor ds_cpl vmx est tm2 ssse3 cx16 xtpr lahf_lm
[root@CentOS7 ~]# lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
CPU(s): 4
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 2
Socket(s): 1
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 3072K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-3
/proc/meminfo
[root@CentOS7 ~]# less /proc/meminfo
[root@CentOS7 ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 7950 704 6540 100 705 6908
Swap: 2047 0 2047
/proc/cmdline //内核启动参数
[root@CentOS7 ~]# cat /proc/cmdline
BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 root=UUID=9b17ab4e-cd93-4f84-bd1e-7241a0baac9b ro rhgb quiet LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
uptime
[root@CentOS7 ~]# uptime
17:20:58 up 8:33, 3 users, load average: 0.43, 0.36, 0.36
[root@CentOS7 ~]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
1
[root@CentOS7 ~]# echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
[root@CentOS7 ~]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
0