1. 查
1.1 行元素查询操作
像SQL那样打印列表前20元素,show函数内可用int类型指定要打印的行数:
df.show() df.show(30)
以树的形式打印概要:
df.printSchema()
获取头几行到本地:
list = df.head(3) # Example: [Row(a=1, b=1), Row(a=2, b=2), ... ...] list = df.take(5) # Example: [Row(a=1, b=1), Row(a=2, b=2), ... ...]
查询总行数:
df.count()
取别名:
df.select(df.age.alias('age_value'),'name')
查询某列为null的行:
from pyspark.sql.functions import isnull
df = df.filter(isnull("col_a"))
输出list类型,list中每个元素是Row类:
list = df.collect()#注:此方法将所有数据全部导入到本地,返回一个Array对象
查询概况
df.describe().show()
以及查询类型,之前是type,现在是df.printSchema()
root |-- user_pin: string (nullable = true) |-- a: string (nullable = true) |-- b: string (nullable = true) |-- c: string (nullable = true) |-- d: string (nullable = true) |-- e: string (nullable = true) ...
去重set操作,跟py中的set一样,可以distinct()一下去重,同时也可以.count()计算剩余个数
data.select('columns').distinct().show()
随机抽样有两种方式,一种是在HIVE里面查数随机;另一种是在pyspark之中
#HIVE里面查数随机 sql = "select * from data order by rand() limit 2000" #pyspark之中 sample = result.sample(False,0.5,0) # randomly select 50% of lines
1.2 列元素操作
获取Row元素的所有列名:
r = Row(age=11, name='Alice') print(r.columns) # ['age', 'name']
选择一列或多列:select
df["age"] df.age df.select(“name”) df.select(df[‘name’], df[‘age’]+1) df.select(df.a, df.b, df.c) # 选择a、b、c三列 df.select(df["a"], df["b"], df["c"]) # 选择a、b、c三列
重载的select方法:
#同时显示id列 、id + 1列
jdbcDF.select(jdbcDF( "id" ), jdbcDF( "id") + 1 ).show( false)
#还可以用where按条件选择
jdbcDF.where("id = 1 or c1 = 'b'" ).show()
1.3 排序
orderBy和sort:按指定字段排序,默认为升序
train.orderBy(train.Purchase.desc()).show(5) Output: +-------+----------+------+-----+----------+-------------+--------------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+--------+ |User_ID|Product_ID|Gender| Age|Occupation|City_Category|Stay_In_Current_City_Years|Marital_Status|Product_Category_1|Product_Category_2|Product_Category_3|Purchase| +-------+----------+------+-----+----------+-------------+--------------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+--------+ |1003160| P00052842| M|26-35| 17| C| 3| 0| 10| 15| null| 23961| |1002272| P00052842| M|26-35| 0| C| 1| 0| 10| 15| null| 23961| |1001474| P00052842| M|26-35| 4| A| 2| 1| 10| 15| null| 23961| |1005848| P00119342| M|51-55| 20| A| 0| 1| 10| 13| null| 23960| |1005596| P00117642| M|36-45| 12| B| 1| 0| 10| 16| null| 23960| +-------+----------+------+-----+----------+-------------+--------------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+--------+ only showing top 5 rows
1.4 抽样
sample是抽样函数
t1 = train.sample(False, 0.2, 42) t2 = train.sample(False, 0.2, 43) t1.count(),t2.count() Output: (109812, 109745)
withReplacement = True or False代表是否有放回。fraction = x, where x = .5,代表抽取百分比
1.5 按条件筛选when / between
when(condition, value1).otherwise(value2)联合使用:
那么:当满足条件condition的指赋值为values1,不满足条件的则赋值为values2.
otherwise表示,不满足条件的情况下,应该赋值为啥。
demo1:
>>> from pyspark.sql import functions as F >>> df.select(df.name, F.when(df.age > 4, 1).when(df.age < 3, -1).otherwise(0)).show() +-----+------------------------------------------------------------+ | name|CASE WHEN (age > 4) THEN 1 WHEN (age < 3) THEN -1 ELSE 0 END| +-----+------------------------------------------------------------+ |Alice| -1| | Bob| 1| +-----+------------------------------------------------------------+
demo 2:多个when串联
df = df.withColumn('mod_val_test1',F.when(df['rand'] <= 0.35,1).when(df['rand'] <= 0.7, 2).otherwise(3))
between(lowerBound, upperBound)
筛选出某个范围内的值,返回的是TRUE or FALSE
>>> df.select(df.name, df.age.between(2, 4)).show() +-----+---------------------------+ | name|((age >= 2) AND (age <= 4))| +-----+---------------------------+ |Alice| true| | Bob| false| +-----+---------------------------+
选择dataframe中间的特定行数
而我使用的dataframe前两种方法都没法解决。特点如下:
特定列中的内容为字符串,并非数值,不能直接比较大小。
所选取数据为中间行,如第10~20行,不能用函数直接选取。
最终的解决方法如下:
首先添加行索引,然后选择特定区间内的行索引,从而选取特定中间行。
第一步,添加行索引。
from pyspark.sql.functions import monotonically_increasing_id dfWithIndex = df.withColumn(“id”,monotonically_increasing_id())
第二步,筛选特定行。
dfWithIndex.select(dfWithIndex.name, dfWithIndex.id.between(50, 100)).show()
2.增、改
2.1 新建数据
有这么两种常规的新建数据方式:createDataFrame、.toDF()
sqlContext.createDataFrame(pd.dataframe())#是把pandas的dataframe转化为spark.dataframe格式,所以可以作为两者的格式转化
from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConf
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
from pyspark import sql
conf = SparkConf().setAppName("myFirstApp").setMaster("local")
sc = SparkContext(conf=conf)
sqlContext = sql.SQLContext(sc)
a = sc.parallelize([[1, "a"], [2, "b"], [3, "c"], [4, "d"], [5, "e"]]).toDF(['ind', "state"])
a.show()
from pyspark.sql import Row
row = Row("spe_id", "InOther")
x = ['x1','x2']
y = ['y1','y2']
new_df = sc.parallelize([row(x[i], y[i]) for i in range(2)]).toDF()
row代表的是该数据集的列名。
2.2 新增数据列 withColumn
withColumn是通过添加或替换与现有列有相同的名字的列,返回一个新的DataFrame
result3.withColumn('label', 0)
或者案例
>>> train.withColumn('Purchase_new', train.Purchase /2.0).select('Purchase','Purchase_new').show(5)
Output:
+--------+------------+
|Purchase|Purchase_new|
+--------+------------+
| 8370| 4185.0|
| 15200| 7600.0|
| 1422| 711.0|
| 1057| 528.5|
| 7969| 3984.5|
+--------+------------+
only showing top 5 rows
**报错:**AssertionError: col should be Column,一定要指定某现有列
有两种方式可以实现:
一种方式通过functions
from pyspark.sql import functions
result3 = result3.withColumn('label', functions.lit(0))
但是!! 如何新增一个特别List??(参考:王强的知乎回复)
python中的list不能直接添加到dataframe中,需要先将list转为新的dataframe,然后新的dataframe和老的dataframe进行join操作, 下面的例子会先新建一个dataframe,然后将list转为dataframe,然后将两者join起来。
from pyspark.sql.functions import lit
df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(
[(1, "a", 23.0), (3, "B", -23.0)], ("x1", "x2", "x3"))
from pyspark.sql.functions import monotonically_increasing_id
df = df.withColumn("id", monotonically_increasing_id())
df.show()
+---+---+-----+---+
| x1| x2| x3| id|
+---+---+-----+---+
| 1| a| 23.0| 0|
| 3| B|-23.0| 1|
+---+---+-----+---+
from pyspark.sql import Row
l = ['jerry', 'tom']
row = Row("pid", "name")
new_df = sc.parallelize([row(i, l[i]) for i in range(0,len(l))]).toDF()
new_df.show()
+---+-----+
|pid| name|
+---+-----+
| 0|jerry|
| 1| tom|
+---+-----+
join_df = df.join(new_df, df.id==new_df.pid)
join_df.show()
+---+---+-----+---+---+-----+
| x1| x2| x3| id|pid| name|
+---+---+-----+---+---+-----+
| 1| a| 23.0| 0| 0|jerry|
| 3| B|-23.0| 1| 1| tom|
+---+---+-----+---+---+-----+
#####**坑啊!!!**其中,monotonically_increasing_id()生成的ID保证是单调递增和唯一的,但不是连续的。
所以,有可能,单调到1-140000,到了第144848个,就变成一长串:8845648744563,所以千万要注意!!
另一种方式通过另一个已有变量:
result3 = result3.withColumn('label', df.result*0 )
修改原有df[“xx”]列的所有值:
df = df.withColumn(“xx”, 1)
修改列的类型(类型投射):
df = df.withColumn("year2", df["year1"].cast("Int"))
修改列名:
jdbcDF.withColumnRenamed( "id" , "idx" )
2.3 过滤数据
过滤数据(filter和where方法相同):
df = df.filter(df['age']>21) df = df.where(df['age']>21)
多个条件
jdbcDF .filter(“id = 1 or c1 = ‘b’” ).show()
对null或nan数据进行过滤:
from pyspark.sql.functions import isnan, isnull
df = df.filter(isnull("a")) # 把a列里面数据为null的筛选出来(代表python的None类型)
df = df.filter(isnan("a")) # 把a列里面数据为nan的筛选出来(Not a Number,非数字数据)
3、合并 join / union
3.1 横向拼接rbind
result3 = result1.union(result2) jdbcDF.unionALL(jdbcDF.limit(1)) # unionALL
3.2 Join根据条件
单字段Join
合并2个表的join方法:
df_join = df_left.join(df_right, df_left.key == df_right.key, "inner")
其中,方法可以为:inner, outer, left_outer, right_outer, leftsemi.
其中注意,一般需要改为:left_outer
多字段join
joinDF1.join(joinDF2, Seq("id", "name"))
混合字段
joinDF1.join(joinDF2 , joinDF1("id" ) === joinDF2( "t1_id"))
跟pandas 里面的left_on,right_on
3.2 求并集、交集
来看一个例子,先构造两个dataframe:
sentenceDataFrame = spark.createDataFrame((
(1, "asf"),
(2, "2143"),
(3, "rfds")
)).toDF("label", "sentence")
sentenceDataFrame.show()
sentenceDataFrame1 = spark.createDataFrame((
(1, "asf"),
(2, "2143"),
(4, "f8934y")
)).toDF("label", "sentence")
# 差集
newDF = sentenceDataFrame1.select("sentence").subtract(sentenceDataFrame.select("sentence"))
newDF.show()
+--------+
|sentence|
+--------+
| f8934y|
+--------+
# 交集
newDF = sentenceDataFrame1.select("sentence").intersect(sentenceDataFrame.select("sentence"))
newDF.show()
+--------+
|sentence|
+--------+
| asf|
| 2143|
+--------+
# 并集
newDF = sentenceDataFrame1.select("sentence").union(sentenceDataFrame.select("sentence"))
newDF.show()
+--------+
|sentence|
+--------+
| asf|
| 2143|
| f8934y|
| asf|
| 2143|
| rfds|
+--------+
# 并集 + 去重
newDF = sentenceDataFrame1.select("sentence").union(sentenceDataFrame.select("sentence")).distinct()
newDF.show()
+--------+
|sentence|
+--------+
| rfds|
| asf|
| 2143|
| f8934y|
+--------+
3.3 分割:行转列
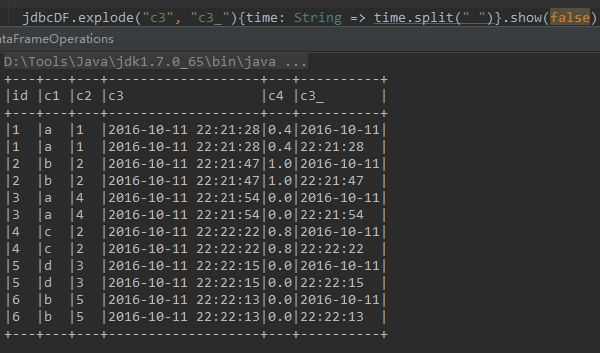
有时候需要根据某个字段内容进行分割,然后生成多行,这时可以使用explode方法
下面代码中,根据c3字段中的空格将字段内容进行分割,分割的内容存储在新的字段c3_中,如下所示
jdbcDF.explode( "c3" , "c3_" ){time: String => time.split( " " )}
4 统计
4.1 频数统计与筛选
jdbcDF.stat.freqItems(Seq ("c1") , 0.3).show()#根据c4字段,统计该字段值出现频率在30%以上的内容
4.2 分组统计
交叉分析:
train.crosstab('Age', 'Gender').show()
Output:
+----------+-----+------+
|Age_Gender| F| M|
+----------+-----+------+
| 0-17| 5083| 10019|
| 46-50|13199| 32502|
| 18-25|24628| 75032|
| 36-45|27170| 82843|
| 55+| 5083| 16421|
| 51-55| 9894| 28607|
| 26-35|50752|168835|
+----------+-----+------+
groupBy方法整合:
train.groupby('Age').agg({'Purchase': 'mean'}).show()
Output:
+-----+-----------------+
| Age| avg(Purchase)|
+-----+-----------------+
|51-55|9534.808030960236|
|46-50|9208.625697468327|
| 0-17|8933.464640444974|
|36-45|9331.350694917874|
|26-35|9252.690632869888|
| 55+|9336.280459449405|
|18-25|9169.663606261289|
+-----+-----------------+
另外一些demo:
df['x1'].groupby(df['x2']).count().reset_index(name='x1')
分组汇总:
train.groupby('Age').count().show()
Output:
+-----+------+
| Age| count|
+-----+------+
|51-55| 38501|
|46-50| 45701|
| 0-17| 15102|
|36-45|110013|
|26-35|219587|
| 55+| 21504|
|18-25| 99660|
+-----+------+
应用多个函数:
from pyspark.sql import functions df.groupBy(“A”).agg(functions.avg(“B”), functions.min(“B”), functions.max(“B”)).show()
整合后GroupedData类型可用的方法(均返回DataFrame类型): avg(*cols) —— 计算每组中一列或多列的平均值 count() —— 计算每组中一共有多少行,返回DataFrame有2列,一列为分组的组名,另一列为行总数 max(*cols) —— 计算每组中一列或多列的最大值 mean(*cols) —— 计算每组中一列或多列的平均值 min(*cols) —— 计算每组中一列或多列的最小值 sum(*cols) —— 计算每组中一列或多列的总和
4.3 apply 函数
将df的每一列应用函数f:
df.foreach(f) 或者 df.rdd.foreach(f)
将df的每一块应用函数f:
df.foreachPartition(f) 或者 df.rdd.foreachPartition(f)
4.4 【Map和Reduce应用】返回类型seqRDDs
map函数应用
可以参考:Spark Python API函数学习:pyspark API(1)
train.select('User_ID').rdd.map(lambda x:(x,1)).take(5)
Output:
[(Row(User_ID=1000001), 1),
(Row(User_ID=1000001), 1),
(Row(User_ID=1000001), 1),
(Row(User_ID=1000001), 1),
(Row(User_ID=1000002), 1)]
其中map在spark2.0就移除了,所以只能由rdd.调用。
data.select('col').rdd.map(lambda l: 1 if l in ['a','b'] else 0 ).collect()
print(x.collect())
print(y.collect())
[1, 2, 3]
[(1, 1), (2, 4), (3, 9)]
还有一种方式mapPartitions:
def _map_to_pandas(rdds):
""" Needs to be here due to pickling issues """
return [pd.DataFrame(list(rdds))]
data.rdd.mapPartitions(_map_to_pandas).collect()
返回的是list。
udf 函数应用:
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf
from pyspark.sql.types import StringType
import datetime
# 定义一个 udf 函数
def today(day):
if day==None:
return datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(int(time.time())).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
else:
return day
# 返回类型为字符串类型
udfday = udf(today, StringType())
# 使用
df.withColumn('day', udfday(df.day))
有点类似apply,定义一个 udf 方法, 用来返回今天的日期(yyyy-MM-dd)。
5、删除
df.drop('age').collect()
df.drop(df.age).collect()
dropna函数:
df = df.na.drop() # 扔掉任何列包含na的行 df = df.dropna(subset=['col_name1', 'col_name2']) # 扔掉col1或col2中任一一列包含na的行
ex:
train.dropna().count() Output: 166821
填充NA,包括fillna
train.fillna(-1).show(2) Output: +-------+----------+------+----+----------+-------------+--------------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+--------+ |User_ID|Product_ID|Gender| Age|Occupation|City_Category|Stay_In_Current_City_Years|Marital_Status|Product_Category_1|Product_Category_2|Product_Category_3|Purchase| +-------+----------+------+----+----------+-------------+--------------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+--------+ |1000001| P00069042| F|0-17| 10| A| 2| 0| 3| -1| -1| 8370| |1000001| P00248942| F|0-17| 10| A| 2| 0| 1| 6| 14| 15200| +-------+----------+------+----+----------+-------------+--------------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+--------+ only showing top 2 rows
6、去重
6.1 distinct:返回一个不包含重复记录的DataFrame
返回当前DataFrame中不重复的Row记录。该方法和接下来的dropDuplicates()方法不传入指定字段时的结果相同。
示例:
jdbcDF.distinct()
6.2 dropDuplicates:根据指定字段去重
根据指定字段去重。类似于select distinct a, b操作
示例:
train.select('Age','Gender').dropDuplicates().show()
Output:
+-----+------+
| Age|Gender|
+-----+------+
|51-55| F|
|51-55| M|
|26-35| F|
|26-35| M|
|36-45| F|
|36-45| M|
|46-50| F|
|46-50| M|
| 55+| F|
| 55+| M|
|18-25| F|
| 0-17| F|
|18-25| M|
| 0-17| M|
+-----+------+
7、 格式转换
pandas-spark.dataframe互转
Pandas和Spark的DataFrame两者互相转换:
pandas_df = spark_df.toPandas() spark_df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(pandas_df)
转化为pandas,但是该数据要读入内存,如果数据量大的话,很难跑得动
两者的异同:
- Pyspark DataFrame是在分布式节点上运行一些数据操作,而pandas是不可能的;
- Pyspark DataFrame的数据反映比较缓慢,没有Pandas那么及时反映;
- Pyspark DataFrame的数据框是不可变的,不能任意添加列,只能通过合并进行;
- pandas比Pyspark DataFrame有更多方便的操作以及很强大
转化为RDD
与Spark RDD的相互转换:
rdd_df = df.rdd df = rdd_df.toDF()
8、SQL操作
DataFrame注册成SQL的表:
df.createOrReplaceTempView("TBL1")
进行SQL查询(返回DataFrame):
conf = SparkConf()
ss = SparkSession.builder.appName("APP_NAME").config(conf=conf).getOrCreate()
df = ss.sql(“SELECT name, age FROM TBL1 WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19″)
9、读写csv
在Python中,我们也可以使用SQLContext类中 load/save函数来读取和保存CSV文件:
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
sqlContext = SQLContext(sc)
df = sqlContext.load(source="com.databricks.spark.csv", header="true", path = "cars.csv")
df.select("year", "model").save("newcars.csv", "com.databricks.spark.csv",header="true")
其中,header代表是否显示表头。
其中主函数:
save(path=None, format=None, mode=None, partitionBy=None, **options)[source]
Parameters:
- path – the path in a Hadoop supported file system
- format – the format used to save
- mode –
- specifies the behavior of the save operation when data already exists.
- append: Append contents of this DataFrame to existing data.
- overwrite: Overwrite existing data.
- ignore: Silently ignore this operation if data already exists.
- error (default case): Throw an exception if data already exists.
- partitionBy – names of partitioning columns
- options – all other string options
延伸一:去除两个表重复的内容
场景是要,依据B表与A表共有的内容,需要去除这部分共有的。使用的逻辑是merge两张表,然后把匹配到的删除即可。
from pyspark.sql import functions
def LeftDeleteRight(test_left,test_right,left_col = 'user_pin',right_col = 'user_pin'):
print('right data process ...')
columns_right = test_right.columns
test_right = test_right.withColumn('user_pin_right', test_right[right_col])
test_right = test_right.withColumn('notDelete', functions.lit(0))
# 删除其余的
for col in columns_right:
test_right = test_right.drop(col)
# 合并
print('rbind left and right data ...')
test_left = test_left.join(test_right, test_left[left_col] == test_right['user_pin_right'], "left")
test_left = test_left.fillna(1)
test_left = test_left.where('notDelete =1')
# 去掉多余的字段
for col in ['user_pin_right','notDelete']:
test_left = test_left.drop(col)
return test_left
%time test_left = LeftDeleteRight(test_b,test_a,left_col = 'user_pin',right_col = 'user_pin')
延伸二:报错
Job aborted due to stage failure: Task 3 in stage 0.0 failed 4 times, most recent failure: Lost task 3.3 in
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/80500349
spark udfs函数:https://blog.csdn.net/u013817676/article/details/86748386
Spark常见问题汇总:https://my.oschina.net/tearsky/blog/629201