《SIFT原理与源码分析》系列文章索引:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianyalu/p/5467813.html
由前一步《DoG尺度空间构造》,我们得到了DoG高斯差分金字塔:
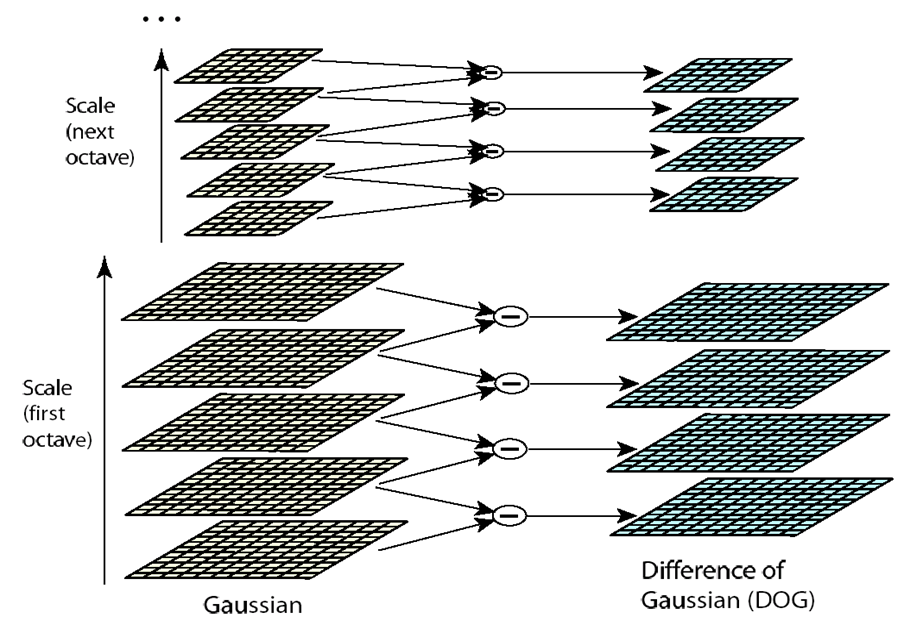
如上图的金字塔,高斯尺度空间金字塔中每组有五层不同尺度图像,相邻两层相减得到四层DoG结果。关键点搜索就在这四层DoG图像上寻找局部极值点。
DoG局部极值点
寻找DoG极值点时,每一个像素点和它所有的相邻点比较,当其大于(或小于)它的图像域和尺度域的所有相邻点时,即为极值点。如下图所示,比较的范围是个3×3的立方体:中间的检测点和它同尺度的8个相邻点,以及和上下相邻尺度对应的9×2个点——共26个点比较,以确保在尺度空间和二维图像空间都检测到极值点。

在一组中,搜索从每组的第二层开始,以第二层为当前层,第一层和第三层分别作为立方体的的上下层;搜索完成后再以第三层为当前层做同样的搜索。所以每层的点搜索两次。通常我们将组Octaves索引以-1开始,则在比较时牺牲了-1组的第0层和第N组的最高层
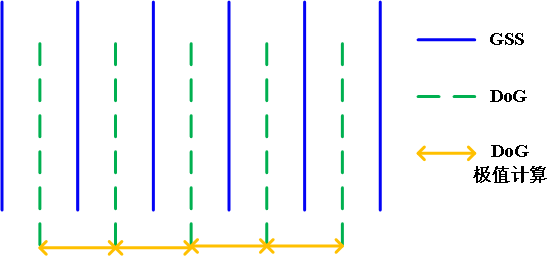
高斯金字塔,DoG图像及极值计算的相互关系如上图所示。
关键点精确定位
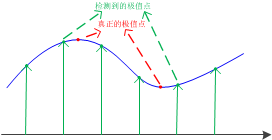
以上极值点的搜索是在离散空间进行搜索的,由下图可以看到,在离散空间找到的极值点不一定是真正意义上的极值点。可以通过对尺度空间DoG函数进行曲线拟合寻找极值点来减小这种误差。
利用DoG函数在尺度空间的Taylor展开式:
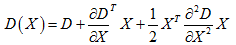
则极值点为:
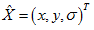
程序中还除去了极值小于0.04的点。如下所示:
// Detects features at extrema in DoG scale space. Bad features are discarded // based on contrast and ratio of principal curvatures. // 在DoG尺度空间寻特征点(极值点) void SIFT::findScaleSpaceExtrema( const vector<Mat>& gauss_pyr, const vector<Mat>& dog_pyr, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints ) const { int nOctaves = (int)gauss_pyr.size()/(nOctaveLayers + 3); // The contrast threshold used to filter out weak features in semi-uniform // (low-contrast) regions. The larger the threshold, the less features are produced by the detector. // 过滤掉弱特征的阈值 contrastThreshold默认为0.04 int threshold = cvFloor(0.5 * contrastThreshold / nOctaveLayers * 255 * SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE); const int n = SIFT_ORI_HIST_BINS; //36 float hist[n]; KeyPoint kpt; keypoints.clear(); for( int o = 0; o < nOctaves; o++ ) for( int i = 1; i <= nOctaveLayers; i++ ) { int idx = o*(nOctaveLayers+2)+i; const Mat& img = dog_pyr[idx]; const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[idx-1]; const Mat& next = dog_pyr[idx+1]; int step = (int)img.step1(); int rows = img.rows, cols = img.cols; for( int r = SIFT_IMG_BORDER; r < rows-SIFT_IMG_BORDER; r++) { const short* currptr = img.ptr<short>(r); const short* prevptr = prev.ptr<short>(r); const short* nextptr = next.ptr<short>(r); for( int c = SIFT_IMG_BORDER; c < cols-SIFT_IMG_BORDER; c++) { int val = currptr[c]; // find local extrema with pixel accuracy // 寻找局部极值点,DoG中每个点与其所在的立方体周围的26个点比较 // if (val比所有都大 或者 val比所有都小) if( std::abs(val) > threshold && ((val > 0 && val >= currptr[c-1] && val >= currptr[c+1] && val >= currptr[c-step-1] && val >= currptr[c-step] && val >= currptr[c-step+1] && val >= currptr[c+step-1] && val >= currptr[c+step] && val >= currptr[c+step+1] && val >= nextptr[c] && val >= nextptr[c-1] && val >= nextptr[c+1] && val >= nextptr[c-step-1] && val >= nextptr[c-step] && val >= nextptr[c-step+1] && val >= nextptr[c+step-1] && val >= nextptr[c+step] && val >= nextptr[c+step+1] && val >= prevptr[c] && val >= prevptr[c-1] && val >= prevptr[c+1] && val >= prevptr[c-step-1] && val >= prevptr[c-step] && val >= prevptr[c-step+1] && val >= prevptr[c+step-1] && val >= prevptr[c+step] && val >= prevptr[c+step+1]) || (val < 0 && val <= currptr[c-1] && val <= currptr[c+1] && val <= currptr[c-step-1] && val <= currptr[c-step] && val <= currptr[c-step+1] && val <= currptr[c+step-1] && val <= currptr[c+step] && val <= currptr[c+step+1] && val <= nextptr[c] && val <= nextptr[c-1] && val <= nextptr[c+1] && val <= nextptr[c-step-1] && val <= nextptr[c-step] && val <= nextptr[c-step+1] && val <= nextptr[c+step-1] && val <= nextptr[c+step] && val <= nextptr[c+step+1] && val <= prevptr[c] && val <= prevptr[c-1] && val <= prevptr[c+1] && val <= prevptr[c-step-1] && val <= prevptr[c-step] && val <= prevptr[c-step+1] && val <= prevptr[c+step-1] && val <= prevptr[c+step] && val <= prevptr[c+step+1]))) { int r1 = r, c1 = c, layer = i; // 关键点精确定位 if( !adjustLocalExtrema(dog_pyr, kpt, o, layer, r1, c1, nOctaveLayers, (float)contrastThreshold, (float)edgeThreshold, (float)sigma) ) continue; float scl_octv = kpt.size*0.5f/(1 << o); // 计算梯度直方图 float omax = calcOrientationHist( gauss_pyr[o*(nOctaveLayers+3) + layer], Point(c1, r1), cvRound(SIFT_ORI_RADIUS * scl_octv), SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTR * scl_octv, hist, n); float mag_thr = (float)(omax * SIFT_ORI_PEAK_RATIO); for( int j = 0; j < n; j++ ) { int l = j > 0 ? j - 1 : n - 1; int r2 = j < n-1 ? j + 1 : 0; if( hist[j] > hist[l] && hist[j] > hist[r2] && hist[j] >= mag_thr ) { float bin = j + 0.5f * (hist[l]-hist[r2]) / (hist[l] - 2*hist[j] + hist[r2]); bin = bin < 0 ? n + bin : bin >= n ? bin - n : bin; kpt.angle = (float)((360.f/n) * bin); keypoints.push_back(kpt); } } } } } } }
删除边缘效应
除了DoG响应较低的点,还有一些响应较强的点也不是稳定的特征点。DoG对图像中的边缘有较强的响应值,所以落在图像边缘的点也不是稳定的特征点。
一个平坦的DoG响应峰值在横跨边缘的地方有较大的主曲率,而在垂直边缘的地方有较小的主曲率。主曲率可以通过2×2的Hessian矩阵H求出:
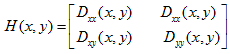
D值可以通过求临近点差分得到。H的特征值与D的主曲率成正比,具体可参见Harris角点检测算法。
为了避免求具体的值,我们可以通过H将特征值的比例表示出来。令 为最大特征值,
为最大特征值, 为最小特征值,那么:
为最小特征值,那么:
 为最大特征值,
为最大特征值, 为最小特征值,那么:
为最小特征值,那么: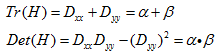
Tr(H)表示矩阵H的迹,Det(H)表示H的行列式。
令 表示最大特征值与最小特征值的比值,则有:
表示最大特征值与最小特征值的比值,则有:
 表示最大特征值与最小特征值的比值,则有:
表示最大特征值与最小特征值的比值,则有: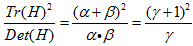
上式与两个特征值的比例有关。随着主曲率比值的增加,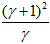 也会增加。我们只需要去掉比率大于一定值的特征点。Lowe论文中去掉r=10的点。
也会增加。我们只需要去掉比率大于一定值的特征点。Lowe论文中去掉r=10的点。
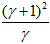 也会增加。我们只需要去掉比率大于一定值的特征点。Lowe论文中去掉r=10的点。
也会增加。我们只需要去掉比率大于一定值的特征点。Lowe论文中去掉r=10的点。// Interpolates a scale-space extremum's location and scale to subpixel // accuracy to form an image feature. Rejects features with low contrast. // Based on Section 4 of Lowe's paper. // 特征点精确定位 static bool adjustLocalExtrema( const vector<Mat>& dog_pyr, KeyPoint& kpt, int octv, int& layer, int& r, int& c, int nOctaveLayers, float contrastThreshold, float edgeThreshold, float sigma ) { const float img_scale = 1.f/(255*SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE); const float deriv_scale = img_scale*0.5f; const float second_deriv_scale = img_scale; const float cross_deriv_scale = img_scale*0.25f; float xi=0, xr=0, xc=0, contr; int i = 0; //三维子像元插值 for( ; i < SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS; i++ ) { int idx = octv*(nOctaveLayers+2) + layer; const Mat& img = dog_pyr[idx]; const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[idx-1]; const Mat& next = dog_pyr[idx+1]; Vec3f dD((img.at<short>(r, c+1) - img.at<short>(r, c-1))*deriv_scale, (img.at<short>(r+1, c) - img.at<short>(r-1, c))*deriv_scale, (next.at<short>(r, c) - prev.at<short>(r, c))*deriv_scale); float v2 = (float)img.at<short>(r, c)*2; float dxx = (img.at<short>(r, c+1) + img.at<short>(r, c-1) - v2)*second_deriv_scale; float dyy = (img.at<short>(r+1, c) + img.at<short>(r-1, c) - v2)*second_deriv_scale; float dss = (next.at<short>(r, c) + prev.at<short>(r, c) - v2)*second_deriv_scale; float dxy = (img.at<short>(r+1, c+1) - img.at<short>(r+1, c-1) - img.at<short>(r-1, c+1) + img.at<short>(r-1, c-1))*cross_deriv_scale; float dxs = (next.at<short>(r, c+1) - next.at<short>(r, c-1) - prev.at<short>(r, c+1) + prev.at<short>(r, c-1))*cross_deriv_scale; float dys = (next.at<short>(r+1, c) - next.at<short>(r-1, c) - prev.at<short>(r+1, c) + prev.at<short>(r-1, c))*cross_deriv_scale; Matx33f H(dxx, dxy, dxs, dxy, dyy, dys, dxs, dys, dss); Vec3f X = H.solve(dD, DECOMP_LU); xi = -X[2]; xr = -X[1]; xc = -X[0]; if( std::abs( xi ) < 0.5f && std::abs( xr ) < 0.5f && std::abs( xc ) < 0.5f ) break; //将找到的极值点对应成像素(整数) c += cvRound( xc ); r += cvRound( xr ); layer += cvRound( xi ); if( layer < 1 || layer > nOctaveLayers || c < SIFT_IMG_BORDER || c >= img.cols - SIFT_IMG_BORDER || r < SIFT_IMG_BORDER || r >= img.rows - SIFT_IMG_BORDER ) return false; } /* ensure convergence of interpolation */ // SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS:插值最大步数,避免插值不收敛,程序中默认为5 if( i >= SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS ) return false; { int idx = octv*(nOctaveLayers+2) + layer; const Mat& img = dog_pyr[idx]; const Mat& prev = dog_pyr[idx-1]; const Mat& next = dog_pyr[idx+1]; Matx31f dD((img.at<short>(r, c+1) - img.at<short>(r, c-1))*deriv_scale, (img.at<short>(r+1, c) - img.at<short>(r-1, c))*deriv_scale, (next.at<short>(r, c) - prev.at<short>(r, c))*deriv_scale); float t = dD.dot(Matx31f(xc, xr, xi)); contr = img.at<short>(r, c)*img_scale + t * 0.5f; if( std::abs( contr ) * nOctaveLayers < contrastThreshold ) return false; /* principal curvatures are computed using the trace and det of Hessian */ //利用Hessian矩阵的迹和行列式计算主曲率的比值 float v2 = img.at<short>(r, c)*2.f; float dxx = (img.at<short>(r, c+1) + img.at<short>(r, c-1) - v2)*second_deriv_scale; float dyy = (img.at<short>(r+1, c) + img.at<short>(r-1, c) - v2)*second_deriv_scale; float dxy = (img.at<short>(r+1, c+1) - img.at<short>(r+1, c-1) - img.at<short>(r-1, c+1) + img.at<short>(r-1, c-1)) * cross_deriv_scale; float tr = dxx + dyy; float det = dxx * dyy - dxy * dxy; //这里edgeThreshold可以在调用SIFT()时输入; //其实代码中定义了 static const float SIFT_CURV_THR = 10.f 可以直接使用 if( det <= 0 || tr*tr*edgeThreshold >= (edgeThreshold + 1)*(edgeThreshold + 1)*det ) return false; } kpt.pt.x = (c + xc) * (1 << octv); kpt.pt.y = (r + xr) * (1 << octv); kpt.octave = octv + (layer << 8) + (cvRound((xi + 0.5)*255) << 16); kpt.size = sigma*powf(2.f, (layer + xi) / nOctaveLayers)*(1 << octv)*2; return true; }
至此,SIFT第二步就完成了。参见《SIFT原理与源码分析》
本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8087239