上一篇讨论了SSL/TLS安全连接,主要是一套在通信层面的数据加密解决方案。但我们更需要一套方案来验证客户端。要把不能通过验证的网络请求过滤掉。
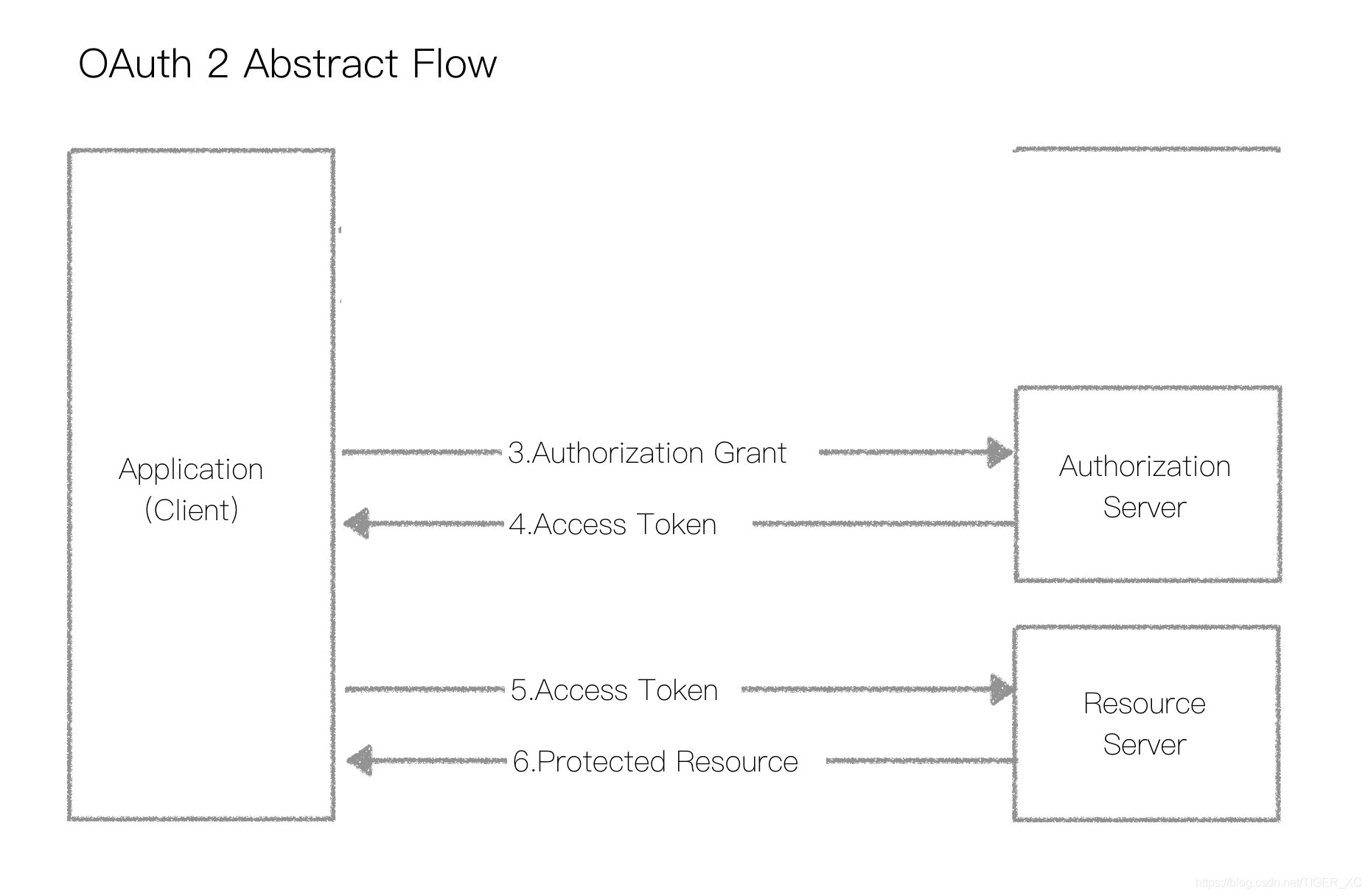
OAuth2是一套行业标准的网络资源使用授权协议,也就是为用户提供一种授权凭证,用户凭授权凭证来使用网络资源。申请凭证、然后使用凭证进行网络操作流程如下:
实际上OAuth2是一套3方授权模式,但我们只需要资源管理方授权,所以划去了1、2两个步骤。剩下的两个步骤,包括:申请令牌,使用令牌,这些在官方文件中有详细描述。用户身份和令牌的传递是通过Http Header实现的,具体情况可参考RFC2617,RFC6750
简单来说:用户向服务器提交身份信息申请令牌,下面是一个HttpRequest样例:
POST /token HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Authorization: Basic czZCaGRSa3F0MzpnWDFmQmF0M2JW
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
上面Basic后面一串代码就是 user+password的加密文,它的产生方法示范如下:
final case class BasicHttpCredentials(username: String, password: String) extends jm.headers.BasicHttpCredentials {
val cookie = {
val userPass = username + ':' + password
val bytes = userPass.getBytes(`UTF-8`.nioCharset)
Base64.rfc2045.encodeToChar(bytes, false)
}
def render[R <: Rendering](r: R): r.type = r ~~ "Basic " ~~ cookie
override def scheme: String = "Basic"
override def token: String = String.valueOf(cookie)
override def params: Map[String, String] = Map.empty
}
注:在OAuth2版本中如果使用https://,则容许明文用户和密码。
服务端在返回的HttpResponse中返回令牌access_token:
{"access_token":"2e510027-0eb9-4367-b310-68e1bab9dc3d", "token_type":"bearer", "expires_in":3600}
注意:这个expires_in是应用系统自定义内部使用的参数,也就是说应用系统必须自备令牌过期失效处理机制。
得到令牌后每个使用网络资源的Request都必须在Authorization类Header里附带这个令牌,如:
GET /resource HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Authorization: Bearer 2e510027-0eb9-4367-b310-68e1bab9dc3d
Bearer后就是服务端返回的令牌值。我们还是设计一个例子来示范整个授权使用过程。先看看下面一些基本操作代码:
object JsonMarshaller extends SprayJsonSupport with DefaultJsonProtocol {
case class UserInfo(username: String, password: String)
case class AuthToken(access_token: String = java.util.UUID.randomUUID().toString,
token_type: String = "bearer",
expires_in: Int = 3600)
case class AuthUser(credentials: UserInfo,
token: AuthToken = new AuthToken(expires_in = 60 * 60 * 8),
loggedInAt: String = LocalDateTime.now().toString)
val validUsers = Seq(UserInfo("johnny", "p4ssw0rd"),UserInfo("tiger", "secret"))
val loggedInUsers = mutable.ArrayBuffer.empty[AuthUser]
def getValidUser(credentials: Credentials): Option[UserInfo] =
credentials match {
case p @ Credentials.Provided(_) =>
validUsers.find(user => user.username == p.identifier && p.verify(user.password))
case _ => None
}
def authenticateUser(credentials: Credentials): Option[AuthUser] =
credentials match {
case p @ Credentials.Provided(_) =>
loggedInUsers.find(user => p.verify(user.token.access_token))
case _ => None
}
implicit val fmtCredentials = jsonFormat2(UserInfo.apply)
implicit val fmtToken = jsonFormat3(AuthToken.apply)
implicit val fmtUser = jsonFormat3(AuthUser.apply)
}
validUers: Seq[UserInfo] 模拟是个在服务端数据库里的用户登记表,loggedInUsers是一个已经通过验证的用户请单。函数 getValidUser(credentials: Credentials) 用传人参数Credentials来获取用户信息Option[UserInfo]。Credentials是这样定义的:
object Credentials {
case object Missing extends Credentials
abstract case class Provided(identifier: String) extends Credentials {
/**
* First applies the passed in `hasher` function to the received secret part of the Credentials
* and then safely compares the passed in `secret` with the hashed received secret.
* This method can be used if the secret is not stored in plain text.
* Use of this method instead of manual String equality testing is recommended in order to guard against timing attacks.
*
* See also [[EnhancedString#secure_==]], for more information.
*/
def verify(secret: String, hasher: String ⇒ String): Boolean
/**
* Safely compares the passed in `secret` with the received secret part of the Credentials.
* Use of this method instead of manual String equality testing is recommended in order to guard against timing attacks.
*
* See also [[EnhancedString#secure_==]], for more information.
*/
def verify(secret: String): Boolean = verify(secret, x ⇒ x)
}
def apply(cred: Option[HttpCredentials]): Credentials = {
cred match {
case Some(BasicHttpCredentials(username, receivedSecret)) ⇒
new Credentials.Provided(username) {
def verify(secret: String, hasher: String ⇒ String): Boolean = secret secure_== hasher(receivedSecret)
}
case Some(OAuth2BearerToken(token)) ⇒
new Credentials.Provided(token) {
def verify(secret: String, hasher: String ⇒ String): Boolean = secret secure_== hasher(token)
}
case Some(GenericHttpCredentials(scheme, token, params)) ⇒
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("cannot verify generic HTTP credentials")
case None ⇒ Credentials.Missing
}
}
}
在apply函数里定义了verify函数功能。这个时候Credentials的实际类型是BasicHttpCredentials。另一个函数authenticateUser(credentials: Credentials)是用Crentials来验证令牌的,那么它的类型应该是OAuth2BearerToken了,具体验证令牌的过程是从loggedInUser清单里对比找出拥有相同令牌的用户。这就意味着每次一个用户通过验证获取令牌后服务端必须把用户信息和令牌值保存起来方便以后对比。我们再来看看route的定义:
val route =
pathEndOrSingleSlash {
get {
complete("Welcome!")
}
} ~
path("auth") {
authenticateBasic(realm = "auth", getValidUser) { user =>
post {
val loggedInUser = AuthUser(user)
loggedInUsers.append(loggedInUser)
complete(loggedInUser.token)
}
}
} ~
path("api") {
authenticateOAuth2(realm = "api", authenticateUser) { validToken =>
complete(s"It worked! user = $validToken")
}
}
现在这段代码就比较容易理解了:authenticateBasic(realm = "auth", getValidUser) {user => ...} 用上了自定义的geValidUser来产生user对象。而authenticateOAuth2(realm = "api", authenticateUser) { validToken =>...}则用了自定义的authenticateUser函数来验证令牌。
下面我们写一段客户端代码来测试上面这个webserver的功能:
import akka.actor._
import akka.stream._
import akka.http.scaladsl.Http
import akka.http.scaladsl.model.headers._
import scala.concurrent._
import akka.http.scaladsl.model._
import org.json4s._
import org.json4s.jackson.JsonMethods._
import scala.concurrent.duration._
object Oauth2Client {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
implicit val system = ActorSystem()
implicit val materializer = ActorMaterializer()
// needed for the future flatMap/onComplete in the end
implicit val executionContext = system.dispatcher
val helloRequest = HttpRequest(uri = "http://192.168.11.189:50081/")
val authorization = headers.Authorization(BasicHttpCredentials("johnny", "p4ssw0rd"))
val authRequest = HttpRequest(
HttpMethods.POST,
uri = "http://192.168.11.189:50081/auth",
headers = List(authorization)
)
val futToken: Future[HttpResponse] = Http().singleRequest(authRequest)
val respToken = for {
resp <- futToken
jstr <- resp.entity.dataBytes.runFold("") {(s,b) => s + b.utf8String}
} yield jstr
val jstr = Await.result[String](respToken,2 seconds)
println(jstr)
val token = (parse(jstr).asInstanceOf[JObject] "access_token").values
println(token)
val authentication = headers.Authorization(OAuth2BearerToken(token.toString))
val apiRequest = HttpRequest(
HttpMethods.POST,
uri = "http://192.168.11.189:50081/api",
).addHeader(authentication)
val futAuth: Future[HttpResponse] = Http().singleRequest(apiRequest)
println(Await.result(futAuth,2 seconds))
scala.io.StdIn.readLine()
system.terminate()
}
}
测试显示结果如下:
{"access_token":"6280dcd7-71fe-4203-8163-8ac7dbd5450b","expires_in":28800,"token_type":"bearer"}
6280dcd7-71fe-4203-8163-8ac7dbd5450b
HttpResponse(200 OK,List(Server: akka-http/10.1.8, Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2019 09:32:32 GMT),HttpEntity.Strict(text/plain; charset=UTF-8,It worked! user = AuthUser(UserInfo(johnny,p4ssw0rd),AuthToken(6280dcd7-71fe-4203-8163-8ac7dbd5450b,bearer,28800),2019-07-03T17:32:32.627)),HttpProtocol(HTTP/1.1))
下面是服务端源代码:
build.sbt
name := "oauth2"
version := "0.1"
scalaVersion := "2.12.8"
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
"com.typesafe.akka" %% "akka-http" % "10.1.8",
"com.typesafe.akka" %% "akka-stream" % "2.5.23",
"com.pauldijou" %% "jwt-core" % "3.0.1",
"de.heikoseeberger" %% "akka-http-json4s" % "1.22.0",
"org.json4s" %% "json4s-native" % "3.6.1",
"com.typesafe.akka" %% "akka-http-spray-json" % "10.1.8",
"com.typesafe.scala-logging" %% "scala-logging" % "3.9.0",
"org.slf4j" % "slf4j-simple" % "1.7.25",
"org.json4s" %% "json4s-jackson" % "3.6.7"
)
OAuth2Server.scala
import akka.actor._ import akka.stream._ import akka.http.scaladsl.Http import akka.http.scaladsl.server.Directives._ import akka.http.scaladsl.server.directives.Credentials import java.time.LocalDateTime import scala.collection.mutable import akka.http.scaladsl.marshallers.sprayjson._ import spray.json._ object JsonMarshaller extends SprayJsonSupport with DefaultJsonProtocol { case class UserInfo(username: String, password: String) case class AuthToken(access_token: String = java.util.UUID.randomUUID().toString, token_type: String = "bearer", expires_in: Int = 3600) case class AuthUser(credentials: UserInfo, token: AuthToken = new AuthToken(expires_in = 60 * 60 * 8), loggedInAt: String = LocalDateTime.now().toString) val validUsers = Seq(UserInfo("johnny", "p4ssw0rd"),UserInfo("tiger", "secret")) val loggedInUsers = mutable.ArrayBuffer.empty[AuthUser] def getValidUser(credentials: Credentials): Option[UserInfo] = credentials match { case p @ Credentials.Provided(_) => validUsers.find(user => user.username == p.identifier && p.verify(user.password)) case _ => None } def authenticateUser(credentials: Credentials): Option[AuthUser] = credentials match { case p @ Credentials.Provided(_) => loggedInUsers.find(user => p.verify(user.token.access_token)) case _ => None } implicit val fmtCredentials = jsonFormat2(UserInfo.apply) implicit val fmtToken = jsonFormat3(AuthToken.apply) implicit val fmtUser = jsonFormat3(AuthUser.apply) } object Oauth2ServerDemo extends App { implicit val httpSys = ActorSystem("httpSystem") implicit val httpMat = ActorMaterializer() implicit val httpEC = httpSys.dispatcher import JsonMarshaller._ val route = pathEndOrSingleSlash { get { complete("Welcome!") } } ~ path("auth") { authenticateBasic(realm = "auth", getValidUser) { user => post { val loggedInUser = AuthUser(user) loggedInUsers.append(loggedInUser) complete(loggedInUser.token) } } } ~ path("api") { authenticateOAuth2(realm = "api", authenticateUser) { validToken => complete(s"It worked! user = $validToken") } } val (port, host) = (50081,"192.168.11.189") val bindingFuture = Http().bindAndHandle(route,host,port) println(s"Server running at $host $port. Press any key to exit ...") scala.io.StdIn.readLine() bindingFuture.flatMap(_.unbind()) .onComplete(_ => httpSys.terminate()) }