使用Python操作Elasticsearch数据索引的教程
Elasticsearch是一个分布式、Restful的搜索及分析服务器,Apache Solr一样,它也是基于Lucence的索引服务器,但我认为Elasticsearch对比Solr的优点在于:
- 轻量级:安装启动方便,下载文件之后一条命令就可以启动;
- Schema free:可以向服务器提交任意结构的JSON对象,Solr中使用schema.xml指定了索引结构;
- 多索引文件支持:使用不同的index参数就能创建另一个索引文件,Solr中需要另行配置;
- 分布式:Solr Cloud的配置比较复杂。
环境搭建
启动Elasticsearch,访问端口在9200,通过浏览器可以查看到返回的JSON数据,Elasticsearch提交和返回的数据格式都是JSON.
|
1
|
>> bin/elasticsearch -f |
安装官方提供的Python API,在OS X上安装后出现一些Python运行错误,是因为setuptools版本太旧引起的,删除重装后恢复正常。
|
1
|
>> pip install elasticsearch |
索引操作
对于单条索引,可以调用create或index方法。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
from datetime import datetimefrom elasticsearch import Elasticsearches = Elasticsearch() #create a localhost server connection, or Elasticsearch("ip")es.create(index="test-index", doc_type="test-type", id=1, body={"any":"data", "timestamp": datetime.now()}) |
Elasticsearch批量索引的命令是bulk,目前Python API的文档示例较少,花了不少时间阅读源代码才弄清楚批量索引的提交格式。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
from datetime import datetimefrom elasticsearch import Elasticsearchfrom elasticsearch import helperses = Elasticsearch("10.18.13.3")j = 0count = int(df[0].count())actions = []while (j < count): action = { "_index": "tickets-index", "_type": "tickets", "_id": j + 1, "_source": { "crawaldate":df[0][j], "flight":df[1][j], "price":float(df[2][j]), "discount":float(df[3][j]), "date":df[4][j], "takeoff":df[5][j], "land":df[6][j], "source":df[7][j], "timestamp": datetime.now()} } actions.append(action) j += 1 if (len(actions) == 500000): helpers.bulk(es, actions) del actions[0:len(actions)]if (len(actions) > 0): helpers.bulk(es, actions) del actions[0:len(actions)] |
在这里发现Python API序列化JSON时对数据类型支撑比较有限,原始数据使用的NumPy.Int32必须转换为int才能索引。此外,现在的bulk操作默认是每次提交500条数据,我修改为5000甚至50000进行测试,会有索引不成功的情况。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
#helpers.py source codedef streaming_bulk(client, actions, chunk_size=500, raise_on_error=False, expand_action_callback=expand_action, **kwargs): actions = map(expand_action_callback, actions) # if raise on error is set, we need to collect errors per chunk before raising them errors = [] while True: chunk = islice(actions, chunk_size) bulk_actions = [] for action, data in chunk: bulk_actions.append(action) if data is not None: bulk_actions.append(data) if not bulk_actions: returndef bulk(client, actions, stats_only=False, **kwargs): success, failed = 0, 0 # list of errors to be collected is not stats_only errors = [] for ok, item in streaming_bulk(client, actions, **kwargs): # go through request-reponse pairs and detect failures if not ok: if not stats_only: errors.append(item) failed += 1 else: success += 1 return success, failed if stats_only else errors |
对于索引的批量删除和更新操作,对应的文档格式如下,更新文档中的doc节点是必须的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
{ '_op_type': 'delete', '_index': 'index-name', '_type': 'document', '_id': 42,}{ '_op_type': 'update', '_index': 'index-name', '_type': 'document', '_id': 42, 'doc': {'question': 'The life, universe and everything.'}} |
常见错误
- SerializationError:JSON数据序列化出错,通常是因为不支持某个节点值的数据类型
- RequestError:提交数据格式不正确
- ConflictError:索引ID冲突
- TransportError:连接无法建立
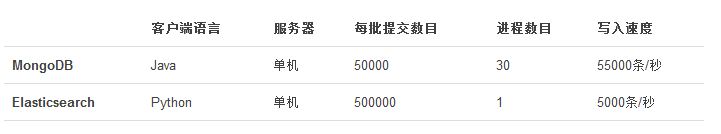
性能
上面是使用MongoDB和Elasticsearch存储相同数据的对比,虽然服务器和操作方式都不完全相同,但可以看出数据库对批量写入还是比索引服务器更具备优势。
Elasticsearch的索引文件是自动分块,达到千万级数据对写入速度也没有影响。但在达到磁盘空间上限时,Elasticsearch出现了文件合并错误,并且大量丢失数据(共丢了100多万条),停止客户端写入后,服务器也无法自动恢复,必须手动停止。在生产环境中这点比较致命,尤其是使用非Java客户端,似乎无法在客户端获取到服务端的Java异常,这使得程序员必须很小心地处理服务端的返回信息。