参考链接 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/90255760
树状图是一种数据结构,它是由n(n>=1)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
树中结点数 = 总分叉数 +1。(这里的分叉数就是所有结点的度之和)
二叉树
二叉树(binary tree)是指树中节点的度不大于2的有序树,它是一种最简单且最重要的树。二叉树的递归定义为:二叉树是一棵空树,或者是一棵由一个根节点和两棵互不相交的,分别称作根的左子树和右子树组成的非空树;左子树和右子树又同样都是二叉树
结点的度:一个结点拥有子树的数目称为结点的度
树的度:树中所有结点的度的最大值
结点的层次:从根结点开始,假设根结点为第1层,根结点的子节点为第2层,依此类推,如果某一个结点位于第L层,则其子节点位于第L+1层
树的深度:也称为树的高度,树中所有结点的层次最大值称为树的深度
森林:由m(m≥0)棵互不相交的树构成一片森林。如果把一棵非空的树的根结点删除,则该树就变成了一片森林,森林中的树由原来根结点的各棵子树构成
深度为h的二叉树中至多含有(2^h)-1个节点
若在任意一棵二叉树中,有n0个叶子节点,有n2个度为2的节点,则必有n0=n2+1
二叉树镜像:对于二叉树中任意节点 root,设其左 / 右子节点分别为 left, right ;则在二叉树的镜像中的对应 root 节点,其左 / 右子节点分别为 right, leftr
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; /** * 功能:把一个数组的值存入二叉树中,然后进行4种方式的遍历 */ public class BinaryTree { int[] array = {4,2,7,1,3,6,9}; static List<Node> nodeList = null; /** * 内部类:节点 * * */ static class Node { public Node leftChild; public Node rightChild; public int data; public Node(int newData) { leftChild = null; rightChild = null; data = newData; } } public void createBinTree() { nodeList = new LinkedList<Node>(); // 将一个数组的值依次转换为Node节点 for (int nodeIndex = 0; nodeIndex < array.length; nodeIndex++) { nodeList.add(new Node(array[nodeIndex])); //链表末尾添加元素 } // 对前lastParentIndex-1个父节点按照父节点与孩子节点的数字关系建立二叉树 for (int parentIndex = 0; parentIndex < array.length / 2 - 1; parentIndex++) { //array.length / 2 - 1 // 左孩子 nodeList.get(parentIndex).leftChild = nodeList .get(parentIndex * 2 + 1); // 右孩子 nodeList.get(parentIndex).rightChild = nodeList .get(parentIndex * 2 + 2); } // 最后一个父节点:因为最后一个父节点可能没有右孩子,所以单独拿出来处理 int lastParentIndex = array.length / 2 - 1; // 左孩子 nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).leftChild = nodeList .get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 1); // 右孩子,如果数组的长度为奇数才建立右孩子 if (array.length % 2 == 1) { nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).rightChild = nodeList .get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 2); } } /** * 先序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * * 遍历的节点 */ public static void preOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; System.out.print(node.data + " "); preOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); preOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); } /** * 中序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * * 遍历的节点 */ public static void inOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); System.out.print(node.data + " "); inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); } /** * 后序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * */ public static void postOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; postOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); postOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); System.out.print(node.data + " "); } /** * 镜像遍历 * */ public static Node mirrorTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Node leftChild = mirrorTraverse(node.leftChild); Node rightChild = mirrorTraverse(node.rightChild); node.leftChild = rightChild; node.rightChild = leftChild;//左右交换 return node; }
//判断二叉树是否为对称
public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binTree = new BinaryTree(); binTree.createBinTree(); // nodeList中第0个索引处的值即为根节点 Node root = nodeList.get(0); //Node , nodeList 是静态的 System.out.println("qianxu bainli :"); preOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("houxu bianli :"); postOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); Node root_mirror = mirrorTraverse(root); System.out.println("jing xiang qianxu bianli :"); preOrderTraverse(root_mirror); System.out.println(); } }
qianxu bainli :
4 2 1 3 7 6 9
zhongxu bianli :
1 2 3 4 6 7 9
houxu bianli :
1 3 2 6 9 7 4
jing xiang qianxu bianli :
4 7 9 6 2 3 1
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
递归 在前序遍历中找到root,再root.left root.right
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int n;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map =new HashMap();
TreeNode buildtree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr){
if(prel>prer){
return null;
}
int pro = prel; //在preorder中找根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pro]);
int iro = map.get(preorder[pro]); //在inorder中找根节点
int num = iro -inl;//左子树中节点数目
root.left = buildtree(preorder,inorder,prel+1,prel+num,inl,iro-1);
root.right = buildtree(preorder,inorder,prel+num+1,prer,iro+1,inr);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
n = preorder.length;
if(n==0){
return null;
}
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
TreeNode root = buildtree(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
return root;
}
}
序列化和反序列化二叉树
序列化二叉树
序列化:将java对象转化为字节序列的过程。
反序列化:将字节序列转化为java对象的过程。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Codec { // Encodes a tree to a single string. public String serialize(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // null也放进队列 TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if (cur == null) { builder.append("#!"); continue; } builder.append(cur.val+"!");//这里不能直接用转义字符如 | 和. queue.offer(cur.left); queue.offer(cur.right); } return builder.toString(); } // Decodes your encoded data to tree. public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { if (data == null || data.length() == 0) { return null; } // String[] str = new String[data.length()]; String[] str = data.split("!"); // for (int i = 0; i < data.length(); i++) { // str[i] = String.valueOf(data.charAt(i));//单个字符依次处理,如果-1就会把-作为一个字符 // } int id = 0; TreeNode head = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[id++])); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(head); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if (!str[id].equals("#")) { cur.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[id++])); queue.offer(cur.left); } else { id++; } if (!str[id].equals("#")) { cur.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[id++])); queue.offer(cur.right); } else { id++; } } return head;
树的很多递归题,想清楚如何分解为子问题就好做了
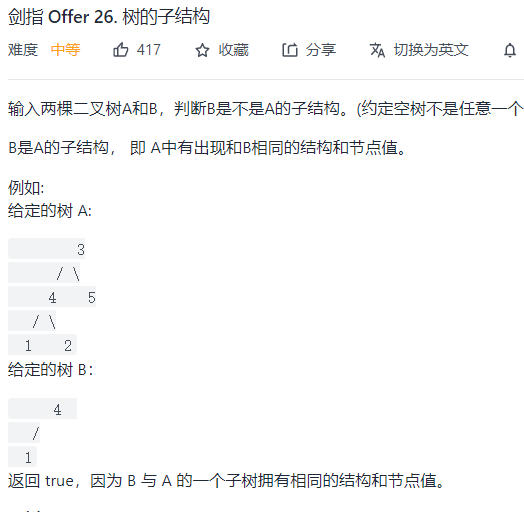
class Solution { public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) { if(A==null||B==null){ return false; } return dfs(A,B)||isSubStructure(A.left,B)||isSubStructure(A.right,B); } boolean dfs(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){ if(q==null) { return true;//匹配完成 } if(p==null){ return false;//匹配失败 }//两个if 的顺序不能换 return (p.val==q.val)&&(dfs(p.left,q.left)&&(dfs(p.right,q.right))); } }
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
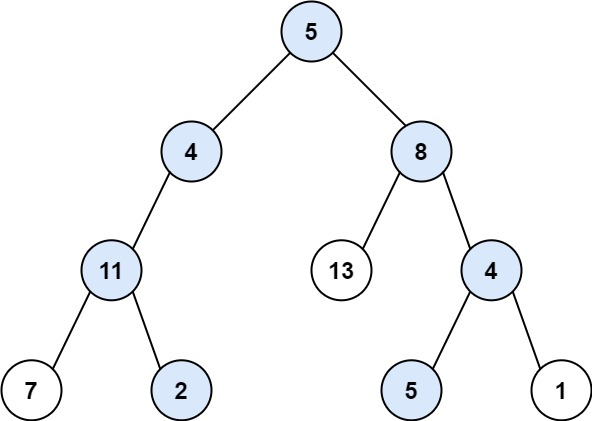
class Solution { // 必须LinkedList<..>不然无法用l.removeLast(); LinkedList<Integer> l = new LinkedList<>(); LinkedList<List<Integer>> ll =new LinkedList<List<Integer>>(); public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) { dfs(root,target); return ll; } void dfs(TreeNode root,int tar){ if(root==null){ return ; } l.add(root.val); tar-=root.val; System.out.println(root.val+" "+tar); if(tar==0&&root.left==null&&root.right==null){ ll.add(new LinkedList(l)); } dfs(root.left,tar); dfs(root.right,tar); l.removeLast(); } }
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树(二叉排序树),是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
- 任意节点的左,右子树也分别为二叉搜索树;
- 没有键值相等的节点。
参考链接:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1672910
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner; /** * 功能:把一个数组的值存入二叉搜索树中 */ public class BinarySearchTree { public int size; public Node root; public int k, ret; /** * 内部类:节点 */ static class Node { public Node leftChild; public Node rightChild; public int data; public Node(int newData) { leftChild = null; rightChild = null; data = newData; } } // insert 作为叶子节点插入 public boolean add(int data) { if (root == null) { root = new Node(data); size++; return true; } Node p = root; while (p != null) { if (p.data < data) { if (p.rightChild == null) { p.rightChild = new Node(data); size++; return true; } p = p.rightChild; } else if (p.data > data) { if (p.leftChild == null) { p.leftChild = new Node(data); size++; return true; } p = p.leftChild; } else { System.out.println(p.data + " " + data); System.out.println("输入数据与节点的数据相同,插入失败"); return false; } } return true; } // find public Node find(int data) { Node p = root; while (p != null) { if (p.data == data) { return p; } else if (p.data < data) { p = p.rightChild; } else { p = p.leftChild; } } return null; } // delete public void delete(int data) { Node p = root; Node par = null;// p 的父节点 while (p != null && p.data != data) { par = p; if (p.data < data) { p = p.rightChild; } else { p = p.leftChild; } } if (p == null) { return; } // 要删除节点有左右子节点 if (p.leftChild != null && p.rightChild != null) { Node minp = p.rightChild; Node minpar = p;// minp的父节点 while (minp.leftChild != null) { minpar = minp; minp = p.leftChild; } p.data = minp.data; par = minpar; p = minp; } Node ch = null;// 保存要删除节点的子节点 // 要删除节点只有一个子节点(左或右) if (p.leftChild != null) { ch = p.leftChild; } else if (p.rightChild != null) { ch = p.rightChild; } // 要删除节点没有子节点 else { ch = null; } // 删除根节点且只有一个节点 if (par == null) { root = ch; } if (par.leftChild == p) { par.leftChild = ch; } else if (par.rightChild == p) { par.rightChild = ch; } size--; } // delete min public void deletemin() { Node p = root; Node par = null; while (p.leftChild != null) { par = p; p = p.leftChild; } System.out.println("min :" + p.data); Node ch = null; if (par == null) { root = ch; } par.leftChild = ch; size--; } // delete max public void deletemax() { Node p = root; Node par = null; while (p.rightChild != null) { par = p; p = p.rightChild; } System.out.println("max :" + p.data); Node ch = null; if (par == null) { root = ch; } par.rightChild = ch; size--; } /** * 中序遍历 * * 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已 * * * 遍历的节点 */ public static void inOrderTraverse(Node node) { if (node == null) return; inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild); System.out.print(node.data + " "); inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild); } // 第K大的元素 public int kthLargest(Node root, int k) { this.k = k; dfs(root); return ret; } public void dfs(Node root) { if (root == null) { return; } dfs(root.rightChild); if (--k == 0) { ret = root.data; return; } dfs(root.leftChild); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = { 33, 16, 50, 13, 18, 34, 58, 51, 66, 55, 15, 17, 25, 19, 27 }; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); BinarySearchTree binseTree = new BinarySearchTree(); for (int x : a) { binseTree.add(x); } // nodeList中第0个索引处的值即为根节点 Node root = binseTree.root; // Node , nodeList 是静态的 System.out.println("zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println(root.data + " 二叉搜索树中节点数目 " + binseTree.size); binseTree.deletemin(); System.out.println("zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); binseTree.deletemax(); System.out.println("zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); Node ff = binseTree.find(25); System.out.println("25的子节点 :" + ff.leftChild.data + " " + ff.rightChild.data); int y = input.nextInt(); int x = binseTree.kthLargest(root, y); System.out.println("第" + y + "大的数为: " + x); binseTree.delete(50); System.out.println("删除50后zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println(root.data + " 二叉搜索树中节点数目 " + binseTree.size); binseTree.delete(18); System.out.println("删除18后zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println(root.data + " 二叉搜索树中节点数目 " + binseTree.size); binseTree.delete(55); System.out.println("删除55后zhongxu bianli :"); inOrderTraverse(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println(root.data + " 二叉搜索树中节点数目 " + binseTree.size); } }
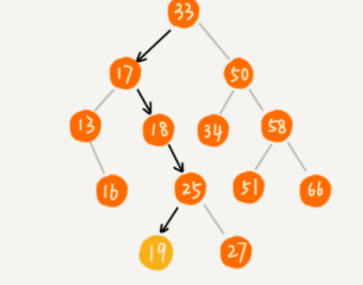
zhongxu bianli :
13 15 16 17 18 19 25 27 33 34 50 51 55 58 66
33 二叉搜索树中节点数目 15
min :13
zhongxu bianli :
16 17 18 19 25 27 33 34 50 51 55 58 66
max :66
zhongxu bianli :
16 17 18 19 25 27 33 34 50 51 55 58
25的子节点 :19 27
4
第4大的数为: 50
删除50后zhongxu bianli :
16 17 18 19 25 27 33 34 34 51 55 58
33 二叉搜索树中节点数目 12
删除18后zhongxu bianli :
16 17 17 19 25 27 33 34 34 51 55 58
33 二叉搜索树中节点数目 11
删除55后zhongxu bianli :
16 17 17 19 25 27 33 34 34 51 58
33 二叉搜索树中节点数目 10
二叉搜索树转换为排序的循环双向链表
class Solution { Node head,pre;//成员变量 public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) { if(root==null){ return null; } dfs(root); head.left = pre; pre.right =head; return head; } void dfs(Node cur){ if(cur==null){ return ; } dfs(cur.left); if(pre==null) { head=cur; } if(pre!=null){ pre.right =cur; cur.left = pre; } pre = cur; dfs(cur.right); } }
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 true,否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
参考以下这颗二叉搜索树:
5
/ \
2 6
/ \
1 3
示例 1:
输入: [1,6,3,2,5]
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: [1,3,2,6,5]
输出: true
方法1 递归
class Solution { public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) { int n =postorder.length; return dfs(postorder,0,n-1); } public boolean dfs(int []postorder,int l,int r){
// r 根 左子树都比root小,右子树都比root大 if(l>=r) return true;//一个节点或者Null int p =l; while(postorder[p]<postorder[r]) p++; int m =p; while(postorder[p]>postorder[r]) p++; return p==r&&dfs(postorder,l,m-1)&&dfs(postorder,m,r-1); } }
根右左
n n-1 1
a:10 15 18 20 12 13 11 7 8 5 1
a[i] >a[i+1] i+1是i的右节点
a[i]<a[i+1] i一定是某个root的左节点,root是所有大于a[i]且距离a[i]最近的节点.任意的a[x] 1<=x<=i-1 一定小于root .原因:a[x] 属于root的左子树或者a[x]属于root的父节点或更高节点的左子树
方法2 后序遍历 倒序
class Solution { public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) { Stack<Integer>sta =new Stack(); int n =postorder.length; int root =Integer.MAX_VALUE; for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ if(postorder[i]>root) return false;//不能大于root while(!sta.isEmpty()&&sta.peek()>postorder[i]) root = sta.pop();//大于postorder[i]且离postorder[i]最近 sta.push(postorder[i]); } return true; } }